Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the radiologic changes in the acetabulum after shelf acetabuloplasty in Legg-Calve-Perthes (LCP) disease.
Materials and Methods
From January 2003 to March 2006, 13 patients with unilateral LCP disease were treated by shelf acetabuloplasty. The mean follow-up period was 51 months. Pre-operative, post-operative, and annual follow-up radiographs were obtained to assess the changes in lateral subluxation ratio (LSR), acetabular head quotient (AHQ), acetabular depth index (ADI), acetabular height index (AHI), total depth index (TDI) and width of bone graft.
Results
The mean LSR decreased from 1.78±0.32 pre-operatively to 1.48±0.15 post-operatively, and remained 1.33±0.21 at last follow-up (p=0.011). The mean AHQ increased from 81.0±7.5% pre-operatively to 120.0±15.1% post-operatively, and remained 109.7±13.8% at final follow-up (p=0.001); the post-operative TDI that included the width of bone graft, decreased at follow-up. Furthermore, the mean ADI and AHI changed from 0.97±0.12, 1.13±0.07 pre-operatively to 1.04±0.02, 1.15±0.09 post-operatively; last follow-up results were 1.03±0.05 and 1.16±0.07, respectively. Between the 2 indices, post-operative ADI for 2 years was statistically significant (p<0.05). Also, the width of bone graft decreased from 24.4±3.6 mm post-operatively to 15.0±4.1 mm at final follow up (p<0.05).
Conclusion
The indices LSR and AHQ confirmed that the shelf acetabuloplasty could preserve the femoral head containment. The growth of the acetabulum after shelf acetabuloplasty was stimulated by increasing the depth of acetabulum in comparison with height for postoperative 2 years. Further follow-up is needed until skeletal maturity.
Figures and Tables
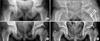 | Figure 1Radiographs of an 8-year-old boy who has unilateral Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. The patient underwent shelf acetabuloplasty and epiphysiodesis at age of 8 years. (A) Pre-operative radiograph, (B) post-operative radiograph, (C) follow-up radiograph at 2 years after metal removal, (D) follow-up radiograph at 4 years after operation. |
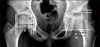 | Figure 2Schematic drawing of a hip affected by left Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. The measurement of the various radiological indices. In the affected hip, single quotation marks are added at each indice. LSR=A'/A, AHQ=(B'/C')/(B/C)×100, ADI=D'/D, AHI=H'/H, TDI=TD/D. A, medial joint space; B, the distance between the medial border of the femoral head and the lateral edge of the acetabulum; C, the distance between the medial border and the lateral rim of the femoral head; D, acetabular depth; H, acetabular height; TD, total acetabular depth; W, horizontal width of the graft; LSR, lateral subluxation ratio; AHQ, acetabular head quotient; TDI, total depth index. |
References
1. Love BR, Stevens PM, Williams PF. A long-term review of shelf arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980. 62:321–325.

2. Salter RB. Legg-Perthes disease: the scientific basis for the methods of treatment and their indications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980. (150):8–11.
3. Kruse RW, Guille JT, Bowen JR. Shelf arthroplasty in patients who have Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. A study of long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:1338–1347.

4. Yoo WJ, Choi IH, Cho TJ, Chung CY, Shin YW, Shin SJ. Shelf acetabuloplasty for children with Perthes' disease and reducible subluxation of the hip: prognostic factors related to hip remodelling. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009. 91:1383–1387.
5. Daly K, Bruce C, Catterall A. Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes' disease. A review of the end of growth. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999. 81:380–384.
7. Ghormley RK. Use of the anterior superior iliac spine and crest of the ilium in surgery of the hip joint. J Bone Joint Surg. 1931. 13:784–798.
8. Stulberg SD, Cooperman DR, Wallensten R. The natural history of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981. 63:1095–1108.

9. Heyman CH, Herndon CH. Legg-Perthes disease; a method for the measurement of the roentgenographic result. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1950. 32:767–778.
10. Van Der Geest IC, Kooijman MA, Spruit M, Anderson PG, De Smet PM. Shelf acetabuloplasty for Perthes' disease: 12-year follow-up. Acta Orthop Belg. 2001. 67:126–131.
11. van der Haven I, Kooijman MA, Havinga ME, van der Geest IC, Jacobs W, Anderson PG. Teardrop-femoral head distance after shelf acetabuloplasty for Perthes' disease. Acta Orthop Belg. 2003. 69:157–161.
12. Ponseti IV. Growth and development of the acetabulum in the normal child. Anatomical, histological, and roentgenographic studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978. 60:575–585.

13. Jacobs R, Moens P, Fabry G. Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in the early stage of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease with special emphasis on the remaining growth of the acetabulum: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2004. 13:21–28.

14. Domzalski ME, Glutting J, Bowen JR, Littleton AG. Lateral acetabular growth stimulation following a labral support procedure in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:1458–1466.
15. Gu Y, Da Paz Júnior AC. Can an enlarged acetabulum cover the femoral head well in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease? J Pediatr Orthop B. 1999. 8:173–176.

16. Cahuzac JP, de Gauzy JS, Vidal H, Gaubert J. The acetabular opening angle in Perthes' disease. Radiographic study of 62 unilateral cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992. 63:278–281.
17. Schneidmueller D, Carstens C, Thomsen M. Surgical treatment of overgrowth of the greater trochanter in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006. 26:486–490.

18. Van Tongel A, Fabry G. Epiphysiodesis of the greater trochanter in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: the importance of timing. Acta Orthop Belg. 2006. 72:309–313.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download