Abstract
Purpose
We wanted to report on the functional results and the presence of axial malalignment after performing minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal femur fractures with metaphyseal comminution.
Materials and Methods
Between March 2007 and June 2009, fifteen patients with distal femur fractures and metaphyseal comminution were treated with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, and they were followed for a mean of 17.0 months (range: 12-40 months). The fractures according to the AO/OTA classification were two cases of 33A and thirteen cases of 33C, and seven cases were open fracture. We analyzed the axial malalignment and functional results according to bone union and Sanders' score.
Results
All the fractures were united without a bone graft after a mean of 20.4 weeks (range: 16-26 weeks) after the definitive plate fixation. One case had superficial infection and a stiff knee. The average ROM of the knee was 123.6°. The average Sanders' score was 33.0, and the results were five cases of excellent results, eight cases of good results and two cases of fair results. There was axial malalignment such as varus malunion in 3 cases and valgus malunion in 2 cases and the average shortening of the limb length was 7.9 mm (range: 0.3-21.9 mm).
Figures and Tables
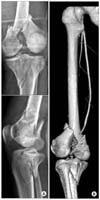 | Figure 1(A) The radiographs show intra-articular fracture of distal femur and fracture of proximal tibia. (B) A femoral angiogram demonstrates a complete block at the level of distal femur. |
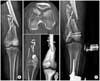 | Figure 3(A) The radiograph shows intra-articular fracture of the distal femur with metaphyseal comminution. (B) The CT scans show the fracture of posterior condyle. (C) The preliminary stabilization is achieved with spanning external fixator. |
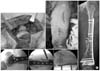 | Figure 4(A) The articular surface is exposed by parapatellar incision and repaired with 3.5 mm screws. (B) The plate is slid through submuscular space and fracture is reduced using the various instruments. (C) The photograph shows the preservation of soft tissue around fracture site. (D) The functional reduction is achieved by indirect reduction technique. |
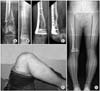 | Figure 5(A) The initial radiograph of a 36-year-old man shows distal femoral fracture with metaphyseal comminution. (B) The fracture site is not opened with a minimally invasive technique and fixed with LCP-DF® (synthesis, Switzerland). (C) Follow-up radiographs after 18 months show complete union of fracture. (D) The weight bearing line is shifted laterally from 29.2% to 38.5%. (E) However, the patient had an excellent knee function. |
References
1. Lee SH, Lee JY, Ha SH, Sohn HM, Lee KC. Treatment of distal femoral shaft and supracondylar fracture with a retrograde intramedullary nailing. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004. 17:103–109.
2. Kim SJ, Oh CW, Jeon IH, Kim HS, Park BC, Kyung HS, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal femoral fractures. J Korean Soc Fract. 2003. 16:474–481.

3. Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Miclau T, Tscherne H. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using the DCS in proximal and distal femoral fractures. Injury. 1997. 28:Suppl 1. A20–A30.

4. Kregor PJ. Distal femur fractures with complex articular involvement: management by articular exposure and submuscular fixation. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002. 33:153–175.
5. Kolb W, Guhlmann H, Windisch C, Marx F, Kolb K, Koller H. Fixation of distal femoral fractures with the Less Invasive Stabilization System: a minimally invasive treatment with locked fixed-angle screws. J Trauma. 2008. 65:1425–1434.

7. Oh JK, Oh CW, Park SH, Roh KJ, Jeong CW. Conformity of the LCP-DF (locking compression plate-distal femur) in Korean Adult Femur: a cadaver study. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:399–404.

8. Sanders R, Swiontkowski M, Rosen H, Helfet D. Double-plating of comminuted, unstable fractures of the distal part of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:341–346.

9. Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ. Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987. 69:745–749.

10. Matar WY, Boscariol R, Dervin GF. Open wedge high tibial osteotomy: a roentgenographic comparison of a horizontal and an oblique osteotomy on patellar height and sagittal tibial slope. Am J Sports Med. 2009. 37:735–742.
11. Smith TO, Hedges C, MacNair R, Schankat K, Wimhurst JA. The clinical and radiological outcomes of the LISS plate for distal femoral fractures: a systematic review. Injury. 2009. 40:1049–1063.

12. Schütz M, Müller M, Regazzoni P, et al. Use of the less invasive stabilization system (LISS) in patients with distal femoral (AO33) fractures: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005. 125:102–108.

14. Muller ME, Allgower M, Schneider R, Willenegger J. Femoral shaft and distal femur. Manual of internal fixation. 1990. 12th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;535–552.
15. Jazrawi LM, Kummer FJ, Simon JA, et al. New technique for treatment of unstable distal femur fractures by locked double-plating: case report and biomechanical evaluation. J Trauma. 2000. 48:87–92.

16. Nork SE, Segina DN, Aflatoon K, et al. he association between supracondylar-intercondylar distal femoral fractures and coronal plane fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:564–569.
17. Schandelmaier P, Partenheimer A, Koenemann B, Grün OA, Krettek C. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury. 2001. 32:Suppl 3. SC55–SC63.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download