Abstract
Purpose
To determine the factors influencing clinical results of revision surgery for spinal stenosis developed at the adjacent segment after spinal fusion.
Materials and Methods
Nineteen patients underwent revision surgery by adjacent segment disease after decompression and posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw instrumentation for spinal stenosis. The control group was matched in terms of age, sex, and number of fused segment, posterior interbody fusion.
Results
Oswestry disability index (ODI) was changed from 32.1 before surgery to 28.0 at the final follow up in the revision group. Compared to the improvement from 27.6 to 15.2 in the control group, there was a significant difference between both groups (p=0.002). Revision group had 1 nonunion and 2 proximal screw loosening. There was no late complication in the control group. In the revision group, 12 of 19 patients had disc degeneration before surgery at the upper lumbar segments which was not included in the fusion. They had an average 2.0 ODI improvement after revision surgery. On the other hand, 7 patients who had no degeneration at the unfused segment showed 7.4 ODI improvement.
Conclusion
The clinical result of revision surgery for spinal stenosis at the adjacent segment after spinal fusion was less satisfactory than the primary surgery. The contributing factors were late complications and preoperative disc degeneration at the segments which was not included in the fusion.
Figures and Tables
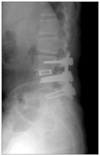
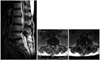
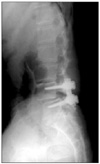 | Figure 1A 58-years-old woman underwent posterior fusion for spinal stenosis 5 years ago. Lateral radiograph shows disc space narrowing at L3-4 and L2-3. |
References
1. Lehmann TR, Spratt KF, Tozzi JE, et al. Long-term follow-up of lower lumbar fusion patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987. 12:97–104.

2. Nagata H, Schendel MJ, Transfeldt EE, Lewis JL. The effects of immobilization of long segments of the spine on the adjacent and distal facet force and lumbosacral motion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993. 18:2471–2479.

3. Aota Y, Kumano K, Hirabayashi S. Postfusion instability at the adjacent segments after rigid pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. J Spinal Disord. 1995. 8:464–473.

4. Guigui P, Lambert P, Lassale B, Deburge A. Long-term outcome at adjacent levels of lumbar arthrodesis. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1997. 83:685–696.
5. Cho JL, Park YS, Han JH, Lee CH, Rho WI. The changes of adjacent segments after spinal fusion: follow up more than three years after spinal fusion. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998. 5:239–246.
6. Etebar S, Cahill DW. Risk factors for adjacent-segment failure following lumbar fixation with rigid instrumentation for degenerative instability. J Neurosurg. 1999. 90:2 Suppl. 163–169.

7. Ha KY, Sung TP. Change of the adjacent mobile segment after cat spine fixation. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1997. 32:1808–1816.
8. Whitecloud TS 3rd, Davis JM, Olive PM. Operative treatment of the degenerated segment adjacent to a lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994. 19:531–536.

9. Phillips FM, Reuben J, Wetzel FT. Intervertebral disc degeneration adjacent to a lumbar fusion. An experimental rabbit model. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002. 84:289–294.
10. Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bullis D, Betz RR, Baldus C, Schoenecker PL. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord. 1992. 5:433–442.

11. Dupuis PR, Young-Hing K, Cassidy JD, Kirkaldy-Willis WH. Radiologic diagnosis of degenerative lumbar spinal instability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985. 10:262–276.

12. Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:1873–1878.

13. Ha KY, Kim KW, Park SJ, Lee YH. Changes of the adjacent unfused mobile segment after instrumental lumbar fusion: more than 5-years follow-up. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998. 5:205–214.
14. Penta M, Sandhu A, Fraser RD. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of disc degeneration 10 years after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995. 20:743–747.

15. Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, Hoff JT, McGillicuddy JE. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004. 29:1938–1944.

16. Lee CK. Lumbar spinal instability (olisthesis) after extensive posterior spinal decompression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983. 8:429–433.

17. Ahn DK, Lee S, Jeong KW, Park JS, Cha SK, Park HS. Adjacent segment failure after lumbar spine fusion-controlled study for risk factors. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2005. 40:203–208.
18. Djurasovic MO, Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Dimar JR 2nd, Puno RM, Johnson JR. Sagittal alignment as a risk factor for adjacent level degeneration: a case-control study. Orthopedics. 2008. 31:546.

19. Chen WJ, Lai PL, Niu CC, Chen LH, Fu TS, Wong CB. Surgical treatment of adjacent instability after lumbar spine fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:E519–E524.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download