Abstract
Purpose
We tried to reveal radiographic clues for the possibility of damages to the important structures, including the peroneal nerve and the anterior tibial artery, caused by a proximal interlocking screw with a medial to lateral oblique direction (ObML-PIS).
Materials and Methods
The length of the proximal tibiofiular joint (PTFJ) was measured from the tip of the fibular head to the end of PTFJ on the simple oblique radiographs of 22 cases of tibial intramedullary (IM) nailing. The center (O) of the IM nailing, from the tibial anterior cortex at the level of insertion of an ObML-PIS, was measured on the simple lateral radiographs. The angle POA (P: a point 10 mm anterior from the anterior fibular border, A: a point on the tangent line from the O point to the posteromedial cortex of the fibula) was measured on the MR axial view of 60 cases, and within this angle an ObML-PIS could injure the important anatomical structures. Transverse and 45-degree oblique diameters of the proximal tibia on the MR axial view were also measured.
Results
The PTFJ length was 18.5±3.3 mm and the O point was located at 15.3±3.4 mm posterior from the tibial anterior cortex. The angle POA was 21.4±6.2-67.8±6.7 degrees with medial to lateral oblique directions. The transverse diameter of the proximal tibia was 58.0±5.8 mm and the 45-degree oblique diameter was 50.7±6.2 mm.
Figures and Tables
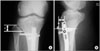 | Figure 1Radiographic measurements. Proximal tibiofibular joint length from a tip of the fibular head (d) is measured on a oblique radiograph (A) and a distance (ℓ) between IM nail center and anterior tibial cortex is measured at the level of the mediolateral interlocking screw on a lateral view (B). |
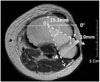 | Figure 2The center of intramedullary nail (O) is pointed at the MR axial view. The point P is located at 10 mm anterior from the anterior cortex of fibular head and the point A, at the tangent line on the medial cortex of the fibular head. If the interlocking screw is inserted within the angle POA, there could be much higher risk of injuries of the peroneal nerve or anterior tibial artery. |
References
1. Hems TE, Jones BG. Peroneal nerve damage associated with the proximal locking screws of the AIM tibial nail. Injury. 2005. 36:651–654.

2. Drosos GI, Stavropoulos NI, Kazakos KI. Peroneal nerve damage by oblique proximal locking screw in tibial fracture nailing: a new emerging complication? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007. 127:449–451.

3. Han KJ, Won YY, Kim TY, Khang SY. Pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery after closed intramedullary nailing of a tibial shaft fracture: a case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002. 37:574–576.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download