Abstract
Purpose
We evaluated the integrity after repairing the arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon using the suture-bridge technique in patients with full thickness rotator cuff tendon tears.
Materials and Methods
Forty two (males: 14, females: 28) consecutive shoulders that were treated with this index procedure and that had magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) taken at a mean of 9 months postoperatively were enrolled to estimate the postoperative intregrity of the repair. The mean age was 57 years (range: 44-75 years) and the mean follow-up period was 14 months (range: 12-16 months). The follow up MRI was evaluated using the Sugaya classification for postoperative cuff integrity. The clinical outcomes were evaluated by using the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) score, the Korean Shoulder Scoring System (KSS) and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). Significance was set at p values < 0.05
Results
In the 42 cases with follow up MRI, the cuff integrity was graded as type I in 10 cases, type II in 28, type III in 2, type IV in 1 and type V in 1 case. Out of the 39 cases having a medium to large tear, the type I and II cuff integrity was 92.3% and two patients had type III cuff integrity postoperatively, while the rate of retear was 33.3% (1 of 3) in the cases with massive tear. The overall rate of retear was 4.8%. For the intact postoperative repair rate, the precent of cases with fatty degeneration of grade 3 or less seen on preoperative MRI was 92.7%. For 41 patients, except for 1 case of type V retear, the UCLA score and the KSS score were significantly improved (p < 0.05) from 17.2 to 31.4 and from 58.2 to 90.8 on average, respectively, which showed satisfactory clinical outcomes regardless of the type of repair integrity.
Figures and Tables
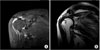 | Figure 1A 64-year-old female had painful limitation of motion of right shoulder preoperatively. (A) Preoperative massive tear of rotator cuff tendons: Black arrow head denotes full-thickness massive tear of rotator cuff tendons in preoperative MRA. (B) Repair integrity: White arrow head indicates Sugaya classification type I in follow-up MRA taken 7 months postoperatively. |
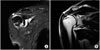 | Figure 2A 56-year-old male had right shoulder pain preoperatively. (A) Preoperative large tear of rotator cuff tendons: White arrow head denotes full-thickness large tear of rotator cuff tendons in preoperative MRA. (B) Repair integrity: White arrow head indicates Sugaya classification type II in follow-up MRA taken 8 months postoperatively. |
 | Figure 3A 55-year-old male was presented with retear of rotator cuff tendons. (A) Preoperative large retear of rotator cuff tendons: Black arrow head denotes full-thickness large retear of rotator cuff tendons in preoperative MRA. (B) Repair integrity: White arrow head indicates Sugaya classification type III in follow-up MRA taken 6 months postoperatively. |
Table 3
Functional Outcomes according to Repair Integrity of Rotator Cuff

The University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) score: Maximum scores are 10 points for pain and function; 5 points for motion, strength, and satisfaction; and 35 points total. The Korean Shoulder Scoring System (KSS) includes 5 domains totalling 100 points: function, 30 points; pain, 20; satisfaction, 10; range of motion, 20; and muscle power, consisting of strength, 10; and endurance, 10. *p<0.05.
References
1. Bales C, Anderson K. Arthroscopic double-row repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears using a suture bridge technique. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2007. 15:144–149.

2. Boileau P, Brassart N, Watkinson DJ, Carles M, Hatzidakis AM, Krishnan SG. Arthroscopic repair of full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus: does the tendon really heal? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1229–1240.

3. Burkhart SS, Danaceau SM, Pearce CE Jr. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: analysis of results by tear size and by repair technique-margin convergence versus direct tendon-to-bone repair. Arthroscopy. 2001. 17:905–912.
4. Franceschi F, Ruzzini L, Longo UG, et al. Equivalent clinical results of arthroscopic single-row and double-row suture anchor repair for rotator cuff tears: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2007. 35:1254–1260.
5. Kim DH, Elattrache NS, Tibone JE, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a single-row versus double-row suture anchor technique for rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2006. 34:407–414.

6. Park JY, Choi JH, Park HK, Yu JW, Seo JB. Single and double-row repair in rotator cuff tears. J Korean Shoulder Elbow Soc. 2006. 9:89–95.

7. Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86-A:219–224.

8. Park MC, Tibone JE, ElAttrache NS, Ahmad CS, Jun BJ, Lee TQ. Part II: Biomechanical assessment for a footprint-restoring transosseous-equivalent rotator cuff repair technique compared with a double-row repair technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007. 16:469–476.

9. DeOrio JK, Cofield RH. Results of a second attempt at surgical repair of a failed initial rotator-cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:563–567.

10. Sugaya H, Maeda K, Matsuki K, Moriishi J. Repair integrity and functional outcome after arthroscopic double-row rotator cuff repair. A prospective outcome study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. 89:953–960.
11. Goutallier D, Postel JM, Gleyze P, Leguilloux P, Van Driessche S. Influence of cuff muscle fatty degeneration on anatomic and functional outcomes after simple suture of full-thickness tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003. 12:550–554.

12. Tae SK, Rhee YG, Park TS, et al. The development and validation of an appraisal method for rotator cuff disorders: the Korean Shoulder Scoring System. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009. 18:689–696.

13. Grasso A, Milano G, Salvatore M, Falcone G, Deriu L, Fabbriciani C. Single-row versus double-row arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective randomized clinical study. Arthroscopy. 2009. 25:4–12.

14. Frank JB, ElAttrache NS, Dines JS, Blackburn A, Crues J, Tibone JE. Repair site integrity after arthroscopic transosseous-equivalent suture-bridge rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2008. 36:1496–1503.

15. Ellman H, Hanker G, Bayer M. Repair of the rotator cuff. End-result study of factors influencing reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68:1136–1144.

16. Apreleva M, Ozbaydar M, Fitzgibbons PG, Warner JJ. Rotator cuff tears: the effect of the reconstruction method on three-dimensional repair site area. Arthroscopy. 2002. 18:519–526.
17. Tuoheti Y, Itoi E, Yamamoto N, et al. Contact area, contact pressure, and pressure patterns of the tendon-bone interface after rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 2005. 33:1869–1874.

18. Cole BJ, ElAttrache NS, Anbari A. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repairs: an anatomic and biomechanical rationale for different suture-anchor repair configurations. Arthroscopy. 2007. 23:662–669.

19. Lafosse L, Brzoska R, Toussaint B, Gobezie R. The outcome and structural integrity of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with use of the double-row suture anchor technique. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. 90 Suppl 2 Pt 2:275–286.
20. Bishop J, Klepps S, Lo IK, Bird J, Gladstone JN, Flatow EL. Cuff integrity after arthroscopic versus open rotator cuff repair: a prospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006. 15:290–299.

21. Matthews TJ, Hand GC, Rees JL, Athanasou NA, Carr AJ. Pathology of the torn rotator cuff tendon. Reduction in potential for repair as tear size increases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006. 88:489–495.
22. Goutallier D, Postel JM, Bernageau J, Lavau L, Voisin MC. Fatty muscle degeneration in cuff ruptures. Pre- and postoperative evaluation by CT scan. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994. 304:78–83.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download