Abstract
A pilonidal cyst is known to be a recurrent infectious disease in the sacrococcygeal region and it usually affects adolescents and adults. It is often misdiagnosed as a simple abscess or a sebaceous cyst, so there are many patients with pilonidal cysts who have gone through several operations. Although many treatments for this malady have been reported, the principle treatment for pilonidal cysts is radical excision. We report here on two cases of pilonidal cyst and the patients were misdiagnosed as having a simple abscess. We planned to perform incision and drainage, but the lesions were finally diagnosed as pilonidal cysts and so we performed radical excision for the treatment. We also review the medical literature on abscesses that occur in the sacrococcygeal region in early adulthood.
Figures and Tables
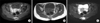
Figure 1
(A) T2WI sagittal view, an ovoid-shaped mass like lesion which is located in the subcutaneous fat layer, sacrum level is seen, which displays high signal intensity. (B) It displays iso-signal intensity at T1WI sagittal view. (C) It displays septal-like enhancement and central low signal intensity at Gd T1WI (However, it does not seem to invade the connected muscle and it is not seen the abnormal signal intensity at bone marrow, spinal canal and disc.).
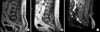
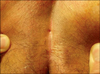
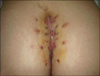
Figure 2
When the patient visited hospital, pilonidal sinus was detected at 5 cm upper from the anus during the inspection.
References
1. Hegele A, Strombach FJ, Schönbach F. Reconstructive surgical therapy of infected pilonidal sinus. Chirurg. 2003. 74:749–752.
2. Akinci OF, Coskun A, Uzunköy A. Simple and effective surgical treatment of pilonidal sinus: asymmetric excision and primary closure using suction drain and subcuiticular skin closure. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000. 43:701–707.
4. Chamberlain JW, Vawter GF. The congenital origin of pilonidal sinus. J Pediatr Surg. 1974. 9:441–444.

5. Karydakis GE. The etiology of pilonidal sinus. Hellenic Arm Forc Med Rev. 1975. 7:411–416.
6. Allen-Mersh TG. Pilonidal sinus: finding the right tract for treatment. Br J Surg. 1990. 77:123–132.
8. Karydakis GE. Hair insertion (pilonidal sinus). Hellenic Arm Forc Med Rev. 1968. 2:273–285.
9. Karydakis GE. Easy and successful treatment of pilonidal sinus after explanation of its causative process. AUST N Z J Surg. 1992. 62:385–389.

10. Bascom JU. Pilonidal sinus. Curr Pract Surg. 1994. 6:175–180.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download