Abstract
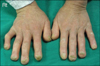
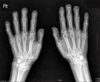
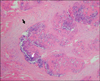
The Scleroderma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the connective tissue with involvement of the skin and other organs. It can be a manifestation of various disorders and occasionally acroosteolysis in the phalanges. Acroosteolysis is characterized by bone resorption or destruction in the phalanges, while the base is preserved. The pathogenesis of acroosteolysis in patients with scleroderma is a blood-flow disorder that is mainly associated with an abnormal accumulation of collagen in all tissues, microangiopathy and infections in the phalanges. The phalanges in patients with scleroderma are prone to continuous infections as a felon or skin ulcers due to atrophy of the subcutaneous tissue, dry and sclerotic skin, or a disorder of the immune system. We experienced a patient who had acroosteolysis with scleroderma of the phalanges, and this was associated with a felon. We report on this case along with a brief review of the literature.
Figures and Tables
References
2. Todd G, Saxe N. Idiopathic osteolysis. Arch Dermatol. 1994. 130:759–762.
3. Destouet JM, Murphy WA. Acquired acroosteolysis and acronecrosis. Arthritis Rhuem. 1983. 26:1150–1154.

5. Hong YS, Yang HI, Park SH, Lee SH, Cho CS, Kim HY. A case of Sjogren syndrome associated with acroosteolysis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 1996. 3:92–96.
6. Clark DC. Common acute hand infections. Am Fam Physician. 2003. 68:2167–2176.
7. D'Angelo WA, Fries JF, Masi AT, Shulman LE. Pathologic observations in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). A study of fifty-eight autopsy cases and fifty-eight matched controls. Am J Med. 1969. 46:428–440.
8. Kreig T, Meurer M. Systemic sclerosis. Clinical and pathophysiologic aspects. J Am Acad Dermato. 1988. 18:457–481.
9. Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rhematism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 1980. 23:581–590.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download