Abstract
Symmetrical peripheral gangrene (SPG) is characterized by distal ischemic damage in two or more extremities without a large vessel obstruction. This syndrome is associated with low cardiac output, sepsis, malignancy, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and the administration of vasoactive drugs. We report a case of SPG in a patient with pulmonary hemorrhage, sepsis and DIC who had been administered dopamine.
Figures and Tables
Figure 2
At three months after admission, the gangrenous lesions involving four limbs were demarcated.
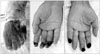
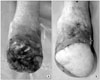
Figure 3
(A) After the demarcation of the gangrenous left foot, open amputation was performed at Lisfranc joint level. Vacuum-Assisted Closure dressing material was applied to open wound. (B) In one month after amputation, the patient underwent gracillis free flap to the open lower leg and there was no flap loss after all.
References
1. Hutchison J. Severe symmetrical gangrene of extremities. Br Med J. 1891. 2:8–9.
2. Johansen K, Hansen ST Jr. Symmetrical peripheral gangrene (purpura fulminans) complicating pneumococcal sepsis. Am J Surg. 1993. 165:642–645.

3. Hayes MA, Yau EH, Hinds CJ, Watson JD. Symmetrical peripheral gangrene: association with noradrenaline administration. Intensive Care Med. 1992. 18:433–436.

4. Molos MA, Hall JC. Symmetrical peripheral gangrene and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Arch Dermatol. 1985. 121:1057–1061.

5. Ghosh SK, Bandyopadhyay D, Ghosh A. Symmetrical peripheral gangrene: a prospective study of 14 consecutive cases in a tertiary-care hospital in eastern India. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010. 24:214–218.

6. Davis MD, Dy KM, Nelson S. Presentation and outcome of purpura fulminans associated with peripheral gangrene in 12 patients at Mayo Clinic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007. 57:944–956.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download