Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the relationship between cubitus varus deformities and rotatory abnormalities after bone union.
Materials and Methods
A total of 263 patients were diagnosed with Gartland type II supracondylar humerus fractures between May 1996 and May 2003 and underwent surgery. The Gartland method was used to classify the fractures. Of the 263 cases, 141 were type II, and 122 were type III. All patients underwent subcutaneous K-wire fixation after manual reduction except one that showed open radial nerve damage at the time of trauma. A mathematical method was used to evaluate rotation abnormalities in the axial plane.
Figures and Tables
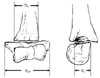 | Figure 1Calculation of rotational deformity in postoperative film. DR is rotated fragment's dimension. AP and lateral dimension are DAP & DL. |
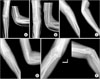 | Figure 2A 9-year-old male patient with cubitus varus deformity. (A) Preoperative radiographs. (B) Postoperative radiographs. (C) Fracture healed in cubitus varus deformity. (D) Radiographs after re-operation. (E) Radiographs at the last follow-up. |
References
1. Holmberg L. Fractures of the distal end of the humerus in children. Acta Chir Scand. 1945. 92:Suppl 103. 1–69.
2. Kim BH, Shin KS, Kim JH, Kim DJ. Clinical analysis of supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children. J Korean Soc Fract. 1992. 5:325–333.

3. Eid AM. Reduction of displaced supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children by manipulation in flexion. Acta Orthop Scand. 1978. 49:39–45.

4. D'Ambrosia RD. Supracondylar fractures of humerus--prevention of cubitus varus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972. 54:60–66.
5. Blount WP. Fractures in children. 1954. Baltimore: Wiliams & Wilkins;56–59.
6. Spear HC, Janes JM. Rupture of the brachial artery accompanying dislocation of the elbow or supracondylar fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1951. 33-A:889–894.

7. Spinner M, Schreiber SN. Anterior interosseous-nerve paralysis as a complication of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969. 51:1584–1590.

8. Henderson ER, Egol KA, van Bosse HJ, Schweitzer ME, Pettrone SK, Feldman DS. Calculation of rotational deformity in pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures. Skeletal Radiol. 2007. 36:229–235.

9. Buhl O, Hellberg S. Displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Acta Orthop Scand. 1982. 53:67–71.

10. Dodge HS. Displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children--treatment by Dunlop's traction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972. 54:1408–1418.

11. Sandegird E. Fracture of the lower end of the humerus in children: treatment and end results. Acta Chir Scand. 1943. 89:1–16.
12. Gruber MA, Hudson OC. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in childhood. End-result study of open reduction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964. 46:1245–1252.
13. Ariño VL, Lluch EE, Ramirez AM, Ferrer J, Rodriguez L, Baixauli F. Percutaneous fixation of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:914–916.
14. Swenson AL. The treatment of supracondylar fractures of the humerus by Kirschner-wire transfixion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1948. 30A:993–997.

15. Herzenberg JE, Koreska J, Carroll NC, Rang M. Biomechanical testing of pin fixation techniques for pediatric supracondylar elbow fractures. Orthop Trans. 1988. 12:678–679.
16. Zionts LE, McKellop HA, Hathaway R. Torsional strength of pin configurations used to fix supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994. 76:253–256.

17. Lee DY, Shim JI, Kim TS, et al. Treatment of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Korean Soc Fract. 1999. 12:179–186.

18. Fowles JV, Kassab MT. Displaced supracondylar fractures of the elbow in children. A report on the fixation of extension and flexion fractures by two lateral percutaneous pins. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974. 56B:490–500.
19. Kallio PE, Foster BK, Paterson DC. Difficult supracondylar elbow fractures in children: analysis of percutaneous pinning technique. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992. 12:11–15.
20. Alburger PD, Weidner PL, Betz RR. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992. 12:16–19.

21. Mehlman CT, Strub WM, Roy DR, Wall EJ, Crawford AH. The effect of surgical timing on the perioperative complications of treatment of supracondylar humeral fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83-A:323–327.

22. Labelle H, Bunnell WP, Duhaime M, Poitras B. Cubitus varus deformity following supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1982. 2:539–546.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download