Abstract
Purpose
To report the clinical and radiological outcomes of a mid-term follow-up of patients with femoroacetabular impingement treated using an arthroscopic method.
Materials and Methods
Of the patients who underwent an arthroscopic labrectomy (91 cases), femoroplasty (82 cases) or acetabuloplasty (9 cases) after a diagnosis of femoroacetabular impingement, 82 patients (91 cases) who had been followed up were examined. The preoperative and postoperative clinical outcomes were evaluated using the Modified Harris hip score, Hip Outcome Score, pain score and patient's satisfaction. The radiological assessment was performed by measuring the alpha angle, femoral offset, and center edge angle using simple radiographs and computed tomography.
Results
The patients consisted of 63 men and 19 women, whose mean age was 33.5 years (range, 15-70 years). The mean follow-up period was 42.2 months (range, 25-60 months). On the clinical results, the mean pain score improved from 0.72 points preoperatively to 2.02 points at the final follow-up. The Modified Harris hip score improved from 61.4 preoperatively to 83.4 at the final follow-up. The median patient satisfaction was 8.2 (range,0-10 points). On the radiological assessment, the alpha angle decreased from 60.9° to 40.4°, and the femoral offset recovered from 4.9 mm to 10.0 mm.
Conclusion
The arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement could be an excellent modality to prevent osteoarthritis of the hip. However, recovery of clinical results by arthroscopic treatment is not expected in elderly patients or those with developed osteoarthritis, a low preoperative Modified Harris hip score and concurrent degenerative disease.
Figures and Tables
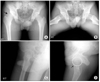 | Figure 1Plain radiographs representing a mixed type (mainly cam type) FAI with asphericity. Main complaints of this patient was limitation of abduction and internal rotation. (A, B, C) The oblique thin arrow in A shows right femoral head asphericity with formation of pistol grip deformity. (D) The small black arrow indicates the bump located at femoral head neck junction. |
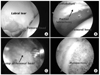 | Figure 2Arthroscopic surgery was performed. The arethroscopic view (A) shows labral tear with partial detachment. (B) Partial labrectomy and acetabular trimming was performed. (C) Femoral head neck junction bump was found. (D) Bumpectomy using arthroscopic burr was performed. |
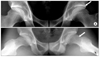 | Figure 3A 22-year-old male with mixed type FAI. (A, B) Simple radiographs showed marked femoral head neck bump and acetabular retroversion. |
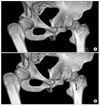 | Figure 4Comparison of preoperative and postoperative hip CT images. (A) preoperative CT, (B) postoperative CT. |
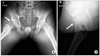 | Figure 5Postoperative radiographs. (A, B) Frog leg and groin lateral view demonstrate the right femoral bumpectomy site (arrows). |
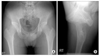 | Figure 64 year follow-up radiographs of the same patient. (A, B) Both anteroposterior view & groin lateral view demonstrate no evidence of progression of osteoarthritic changes or joint space narrowing, and well remodeling of the bumpectomy site was formed. |
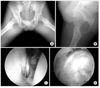 | Figure 7A 19-year-old man with mixed type FAI (mainly cam). (A, B) Simple radiographs show herniation pit on frog-leg view, and bump at femoral head-neck junction. (C, D) Arthroscopic partial labrectomy and femoroplasty was performed. |
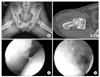 | Figure 8Patient's symptom was aggravated after a minor traffic accident occurred after 6 months, and despite of appropriate conservative treatment, symptom didn't relieve. (A) Simple radiographs with nonspecific findings. (B) MDCT shows remaining herniation pit, but femoral head remodeling was occurring. (C, D) Arthroscopic findings show capsulolabral adhesion and remnant labral tear, suggesting it to be a main factor of the patient's persisting pain. |
References
1. Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Notzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003. 417:112–120.
2. Ganz R, Bamert P, Hausner P, Isler B, Vrevc F. Cervicoacetabular impingement after femoral neck fracture. Unfallchirurg. 1991. 94:172–175.
3. Beaulé PE, Le Duff MJ, Zaragoza E. Quality of life following femoral head-neck osteochondroplasty for femoroacetabular impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. 89:773–779.

4. Beck M, Leunig M, Parvizi J, Boutier V, Wyss D, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement: part II. Midterm results of surgical treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 418:67–73.
5. Espinosa N, Rothenfluh DA, Beck M, Ganz R, Leunig M. Treatment of femoro-acetabular impingement: preliminary results of labral refixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:925–935.
6. Hwang DS, Yang JH, Nam DC. Arthroscopic treatment of osseous abnormalities as a cause of femoroacetabular impingement: preliminary clinical results. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007. 19:112–120.

7. Philippon MJ, Schenker ML. Arthroscopy for the treatment of femoroacetabular impingement in the athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2006. 25:299–308.

8. Sampson TG. Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: a proposed technique with clinical experience. Instr Course Lect. 2006. 55:337–346.
9. Siebenrok KA, Kalbermatten DF, Ganz R. Effect of pelvic tilt on acetabular retoversion: a study of pelves from cadavers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003. 407:241–248.
10. Tönnis D, Legal H, Graf R. Congenital dysplasia and dislocation of the hip in children and adults. 1987. New York: Springer;167.
11. Tannast M, Siebenrock KA, Anderson SE. Femoroacetabular impingement: radiographic diagnosis--what the radiologist should know. Am J Roentgenol. 2007. 188:1540–1552.

12. Vulpius O, Stöffel A. Orthopaadische Operationslehre. 1913. Stuttgart,Germany: F. Enke.
13. Lavigne M, Parvizi J, Beck M, Siebenrock KA, Ganz R, Leunig M. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement: part I. Techniques of joint preserving surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 418:61–66.
15. Byrd JW, Jones KS. Prospective analysis of hip arthroscopy with 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2000. 16:578–587.

16. Farjo LA, Glick JM, Sampson TG. Hip arthroscopy for acetabular tears. Arthroscopy. 1999. 15:132–137.
17. McCarthy JC, Busconi B. The role of hip arthroscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of hip disease. Can J surg. 1995. 38:Suppl. 13–17.

18. Santori N, Villar RN. Arthroscopic findings in the initial stages of hip osteoarthritis. Orthopedics. 1999. 22:405–409.

19. Seldes R, Tan V, Hunt J, et al. Anatomy, histologic features, and vascularity of the adult acetabular labrum. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. 382:232–240.

20. Beck M, Leunig M, Parvizi J, boutier V, Wyss D, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement: part II. Midterm results of surgical treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 418:67–73.
21. Tanzer M, Noiseux N. Osseous abnormalities and early osteoarthritis: the role of hip impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 429:170–177.
22. Guanche CA, Bare AA. Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement. Arthroscopy. 2006. 22:95–106.

23. Goker B, Doughan AM, Schnitzer TJ, Block JA. Quantification of progressive joint space narrowing in osteoarthritis of the hip: Longitudinal analysis of the contralateral hip after total hip arthroplasty. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. 43:938–944.

24. Conrozier T, Lequesne M, Favret H, et al. Measurement of the radiologic hip joint space width. An evaluation of various methods of measurement. Osteoarthrtis Cartilage. 2001. 9:281–286.
25. Streich NA, Gotterbarm T, Barié A, Schmitt H. Prognostic value of chondral defects on the outcome after arthroscopic treatment of acetabular labral tears. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009. 17:1257–1263.

26. Philippon MJ, Briggs KK, Yen YM, Kuppersmith DA. Outcomes following hip arthroscpy for femoroacetabular impingement with associated chondrolabral dysfunction: minimum two-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009. 91:16–23.
27. Stähelin L, Stähelin T, Josses BM, Herzog RF. Arthroscopic off set restoration in femoroacetabular cam impingement: accuracy and early clinical outcome. Arthroscopy. 2008. 24:51–57.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download