Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to assess the efficacy of posterior decompression and interbody fusion with posterior instrumentation in treating lumbar pyogenic spondylitis.
Materials and Methods
Twenty-one patients with lumbar pyogenic spondylitis who underwent posterior decompression and lumbar interbody fusion with posterior fixation were reviewed. Clinically infection control (CRP normalization time) and rehabilitation were investigated. And radiologically, timing of achievement of fusion and changes of sagittal alignment were investigated.
Results
Infection was controlled successfully without any recurrence and breakage of instrument. Stable interbody fusion was achieved in all cases within 6 months. Postoperative interval to achieve normal CRP was 28.7 (10-64) days. Ambulation was started on 5.8th (2-19) day. Sagittal angle was 12.3 degrees before operation, became more lordotic to 16.4 degrees, but decreased to 11 degrees at final follow-up. Final sagittal alignment was almost same with the preoperative status.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
(A) The author's grading of destruction in the vertebral body was made according to the extent of destruction. The MRI images show grade I (B) and II (C) destruction of the body.
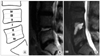
Figure 2
Mean sagittal angle of fixed segments at the last follow up showed difference of only 1.3 degrees compared to preoperative angle. Sagittal alignment of the infected segments showed similar pattern also.
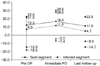
Figure 3
(A) Preoperative radiographs reveal pyogenic spondylitis in L2-3. (B) Preoperative MRI shows grade II destruction of the body and epidural abscess in T2 weight sagittal image, right psoas abscess and involvement of posterior column in an axial image.
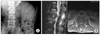
Figure 4
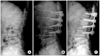
For patients with large dead space, we fixed another adjacent segment. We extended fixation to one level above and below. (A) Preoperative sagittal alignment of both fixed and infected segments was measured. (B) Sagittal alignment of both fixed and infected segments at the immediate postoperation was improved comparing to the preoperative angle. (C) Correction of the sagittal alignment was well maintained until the last follow up.
References
1. Kim YM, Won JH, Seo JB, Choi ES, Lee HS, Um SM. Pyogenic L4-5 spondylitis managed with percutaneous drainage followed by posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a case report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001. 8:513–519.
2. Hibbs RA. A further consideration of an operation for Pott's disease of the spine; with report of cases from the service of the New York orthopaedic hospital. Ann Surg. 1912. 55:682–688.
3. Hodgson AR, Stock FE. Anterior spinal fusion a preliminary communication on the radical treatment of Pott's disease and Pott's paraplegia. Br J Surg. 1956. 44:266–275.

4. Moon MS, Woo YK, Ok IY, et al. Posterior instrumentation for treatment of active dorsolumbar tuberculosis with kyphosis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1989. 24:660–665.

5. Cho DY, Kim EH, Koh ES, Cho KN. A comparative study of anterior interbody fusion with and without anterior instrumentation in multi-level tuberculosis of thoraco-lumbar spine. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1995. 30:298–306.

6. Chung YK, Kim SW, Han HM, Lee EJ, Choi SJ, Chang JD. The results of the surgical treatment using posterior spinal instrumentation for tuberculous spondylitis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999. 6:81–88.
7. Buyukbebeci O, Karakurum G, Guleç A, Erbgci A. Tubeculous osteomyelitis of the lumbosacral region: a spinal epidural abscess with presacral extension. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004. 124:346–348.
8. Chen WJ, Wu CC, Jung CH, Chen LH, Niu CC, Lai PL. Combined anterior and posterior surgeries in the treatment of spinal tuberculous spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. 398:50–59.

9. Kim DJ, Yun YH, Moon SH, Riew KD. Posterior instrumentation using compresive laminar hooks and anterior interbody arthrodesis for the treatment of tuberculosis of the lower lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004. 29:E275–E279.
10. Park JT, Ahn GY, Kim HG, Seong YH. The result of anterior fusion with anterior instrumentation in spinal tuberculosis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1996. 3:217–224.
11. Klöckner C, Valencia R. Sagittal alignment after anterior debridement and fusion with or without additional posterior instrumentation in the treatment of pyogenic and tuberculous spondylodiscitis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. 28:1036–1042.

12. Güven O, Kumano K, Yalcin S, Karahan M, Tsuji S. A single stage posterior approach and rigid fixation for preventing kyphosis in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994. 19:1039–1043.

13. Sundararaj GD, Behera S, Ravi V, Venkatesh K, Cherian VM, Lee V. Role of posterior stabilization in the management of tuberculosis of the dorsal and lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003. 85:100–106.
14. Park WW, Park YS, Cheon SJ, Jung JY. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion in the pyogenic discitis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001. 8:39–45.

15. Conterton JW, Irvin RT, Cheng KJ. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Ann Rev Microbial. 1981. 35:299–324.
16. Oga M, Arizono T, Takasita M, Sukioka Y. Eavaluation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis. Clinical and biologic study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993. 18:1890–1894.
17. Eysel P, Hopf C, Vogel I, Rompe JD. Primary stable anterior instrumentation or dorsoventral spondylodesis in spondylodisicitis? Results of a comparative study. Eur Spine J. 1997. 6:152–157.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download