Abstract
Purpose
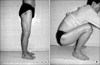
This study evaluated the prognostic factors of modified Thompson quadricepsplasty for a stiff knee.
Materials and Methods
From February 1987 to February 2007, 38 knees of 38 patients were managed with modified Thompson quadricepsplasty for a stiff knee. Thirty three males and 5 females were enrolled with a mean age of 36 years. The average follow-up duration was 92 months (range, 18 to 133 months). The most common cause of the stiff knee was a fracture around the knee in 33 cases. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to evaluate the prognostic factors.
Figures and Tables
References
2. Mira AJ, Markley K, Greer RB 3rd. A critical analysis of quadriceps function after femoral shaft fracture in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980. 62:61–67.

3. Hesketh KT. Experiences with the Thompson quadricepsplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1963. 45:491–495.

4. Thompson TC. Quadricepsplasty to improve knee function. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1944. 26:366–379.
5. Hahn SB, Lee WS, Han DY. A modified thompson quadricepsplasty for the stiff knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000. 82:992–995.

6. Cho WS, Jeong YG, Shin HK, Suh DO. Thompson quadricepsplasty in ankylosis of the knee joint. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2001. 36:355–360.

7. Judet R. Mobilization of the stiff knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959. 41:856–857.
8. Ebraheim NA, DeTroye RJ, Saddemi SR. Results of Judet quadricepsplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 1993. 7:327–330.

9. Wang Y, Greenwald RM, Dang G. New surgical technique for treatment of extraarticular knee ankylosis. Clin Orthop Relaf Res. 1997. 337:172–179.

10. Motmans R, Lammens J. Knee mobility in femoral lengthening using Ilizarov's method. Acta Orthop Belg. 2008. 74:184–189.
12. Dhillon MS, Panday AK, Aggarwal S, Nagi ON. Extra articular arthroscopic release in post-traumatic stiff knees: a prospective study of endoscopic quadriceps and patellar release. Acta Orthop Belg. 2005. 71:197–203.
13. Majewski M, Kentsch A. A new technique for arthroscopic management of painful stiff knee after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction due to femoral malposition. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2002. 10:335–339.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download