Abstract
Purpose
Intramedullary cartilage forming tumors in the meta-diaphysis of the long bones can represent an enchondroma or a low-grade chondrosarcoma, with the latter requiring adequate surgical treatment. However, these two lesions have overlapping clinical and histological features and so they pose a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. The purpose of this study was to analyze the clinical outcome and to determine the relevant clinical and radiographic parameters for deciding on the treatment for these tumors.
Materials and Methods
We conducted a retrospective review of 73 patients who were treated for enchondroma or low-grade chondrosarcoma that was located in the metaphysis or diaphysis of the bones. There were 20 men and 53 women with an average age of 49 years (range: 18-80). The locations were the proximal humerus (n=34), distal femur (24), proximal femur (6), proximal tibia (3), proximal fibula (2), humerus shaft (2) and femur shaft (2). 41 patients were treated surgically and 32 patients were simply observed based on the following parameters at presentation; the presence of pain, the tumor length and radiographic evidence of endosteal erosion.
Results
All of the 32 patients who were initially observed had no evidence of disease progression at the last follow-up (average: 3.2 years, range: 1.0-14.9). Forty (98%) of the surgically treated patients showed no recurrence at the the last follow-up (average: 4.3 years, range: 1.0-14.0).
Conclusion
The presence of pain, tumor length and radiographic evidence of endosteal erosion should be considered to determine the best course of treatment for intramedullary cartilage forming tumors in the meta-diaphysis of the long bones. With the appropriate selection of the patients, these tumors can be successfully treated nonoperatively.
Figures and Tables
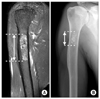 | Fig. 1Measurement of tumor length by MRI (A) and plain radiograph (B) of the same patient. The longest length of the tumor parallel to longitudinal axis of the bone was measured. The length measured by MRI was usually longer than the length measured by plain radiograph. |
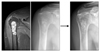 | Fig. 3A representative case treated by observation. A 45-year-old female presented with an incidentally found intramedullary cartilage tumor of the proximal humerus. The length of the tumor was 5.5 cm and endosteal erosion was absent. The lesion did not progress during 7 years of follow-up. |
References
1. Bauer HC, Brosjö O, Kreicbergs A, Lindholm J. Low risk of recurrence of enchondroma and low-grade chondrosarcoma in extremities. 80 patients followed for 2-25 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1995. 66:283–288.
2. Bjornsson J, McLeod RA, Unni KK, Ilstrup DM, Pritchard DJ. Primary chondrosarcoma of long bones and limb girdles. Cancer. 1998. 83:2105–2119.

3. Brien EW, Mirra JM, Kerr R. Benign and malignant cartilage tumors of bone and joint: their anatomic and theoretical basis with an emphasis on radiology, pathology and clinical biology. I. The intramedullary cartilage tumors. Skeletal Radiol. 1997. 26:325–353.
4. Eefting D, Schrage YM, Geirnaerdt MJ, et al. Assessment of interobserver variability and histologic parameters to improve reliability in classification and grading of central cartilaginous tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009. 33:50–57.

5. Flemming DJ, Murphey MD. Enchondroma and chondrosarcoma. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2000. 4:59–71.

6. Geirnaerdt MJ, Hermans J, Bloem JL, et al. Usefulness of radiography in differentiating enchondroma from central grade 1 chondrosarcoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997. 169:1097–1104.

7. Healey JH, Lane JM. Chondrosarcoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 119–129.
8. Leerapun T, Hugate RR, Inwards CY, Scully SP, Sim FH. Surgical management of conventional grade I chondrosarcoma of long bones. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007. 463:166–172.

9. Mirra JM, Gold R, Downs J, Eckardt JJ. A new histologic approach to the differentiation of enchondroma and chondrosarcoma of the bones. A clinicopathologic analysis of 51 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. 201:214–237.
10. Murphey MD, Flemming DJ, Boyea SR, Bojescul JA, Sweet DE, Temple HT. Enchondroma versus chondrosarcoma in the appendicular skeleton: differentiating features. Radiographics. 1998. 18:1213–1237.

11. Ozaki T, Lindner N, Hillmann A, Rodl R, Blasius S, Winkelmann W. Influence of intralesional surgery on treatment outcome of chondrosarcoma. Cancer. 1996. 77:1292–1297.

12. Rizzo M, Ghert MA, Harrelson JM, Scully SP. Chondrosarcoma of bone: analysis of 108 cases and evaluation for predictors of outcome. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. 224–233.
13. Schwab JH, Wenger D, Unni K, Sim FH. Does local recurrence impact survival in low-grade chondrosarcoma of the long bones? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007. 462:175–180.

14. Skeletal Lesions Interobserver Correlation among Expert Diagnosticians (SLICED) Study Group. Reliability of histopathologic and radiologic grading of cartilaginous neoplasms in long bones. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. 89:2113–2123.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download