Abstract
Purpose
Here we report the clinical results of arthroscopically assisted reduction and pin fixation supplemented with an external fixator for the treatment of comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal radius.
Materials and Methods
Thirty-seven patients with a minimum follow-up period of 1 year were enrolled. Radiographs obtained immediately after surgery and those obtained after osseous union were compared and analyzed. The objective and subjective function of the wrist were evaluated. The overall outcomes were assessed using a modified Green and O'Brien system.
Results
Eleven patients had an excellent outcome, 20 good, 4 fair and 2 poor. Loss of radial shortening, radial inclination, step-off, and a gap between the radiographs obtained immediately after surgery and at osseous union were not significant. The volar tilt angle of the final follow-up evaluation averaged 4.6°, which was significantly different compared to the contralateral side. The mean range of motion of the wrist ranged from 73% to 92%. The mean grip strength was 73% compared to the uninjured contralateral wrist. The mean DASH and PRWE outcome scores were 49.2 (range 35-67) and 31.0 (range 13-73), respectively.
Figures and Tables
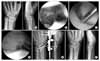 | Fig. 1(A) Preoperative radiographs of 50-year-old male patient who fell showing an AO type C3 distal radius fracture of his left wrist. (B) Arthroscopic examination revealed intraarticular impaction and gap formation. (C) The view through the midcarpal portal shows a grade II tear of the scapholunate interosseous ligament. (D) Arthroscopic image shows the restoration of the articular surface after reduction and pin fixation. (E) Arthroscopically assisted reduction and percutaneous pinning for the scapholunate interosseous ligament injury was performed. The ulnar styloid fracture was stabilized with a tension band wiring technique. (F) The postoperative 14-months radiographs show satisfactory healing. |
Table 1
Classification of Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Lesions Noted during Arthroscopy

From Palmer20).
References
1. Adolfsson L, Jörgsholm P. Arthroscopically-assisted reduction of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Br. 1998. 23:391–395.

2. Baratz ME, Des Jardins J, Anderson DD, Imbriglia JE. Displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: the effect of fracture displacement on contact stresses in a cadaver model. J Hand Surg Am. 1996. 21:183–188.
3. Bradway JK, Amadio PC, Cooney WP. Open reduction and internal fixation of displaced, comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71:839–847.

4. Chen AC, Chan YS, Yuan LJ, Ye WL, Lee MS, Chao EK. Arthroscopically assisted osteosynthesis of complex intraarticular fractures of the distal radius. J Trauma. 2002. 53:354–359.

5. Cheon SJ, Ku JG, Lee DH, Kim TH, Suh JT. Treatment of distal radius fractures using the percutaneous k-wire reduction-fixation and external fixator. J Korean Fracture Soc. 2006. 19:228–235.

6. Cooney WP, Berger RA. Treatment of complex fractures of the distal radius. Combined use of internal and external fixation and arthroscopic reduction. Hand Clin. 1993. 9:603–612.
7. Cooney WP, Bussey R, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Difficult wrist fractures. Perilunate fracture-dislocations of the wrist. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987. 214:136–147.
8. Doi K, Hattori Y, Otsuka K, Abe Y, Yamamoto H. Intra-articular fractures of the distal aspect of the radius: arthroscopically assisted reduction compared with open reduction and internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. 81:1093–1110.
9. Fernandez DL, Geissler WB. Treatment of displaced articular fractures of the radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1991. 16:375–384.

10. Geissler WB, Freeland AE, Savoie FH, McIntyre LW, Whipple TL. Intracarpal soft-tissue lesions associated with an intra-articular fracture of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996. 78:357–365.

11. Horesh Z, Volpin G, Hoerer D, Stein H. The surgical treatment of severe comminuted intraarticular fractures of the distal radius with the small AO external fixation device A prospective three-and-one-half-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. 147–153.
12. Hudak PL, Amadio PC, Bombardier C. The Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (UECG). Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: the DASH (disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand) [corrected]. Am J Ind Med. 1996. 29:602–608.
13. Kim BS, Lee KW, Kim HY, Choy WS, Lee SH. Triangular fibrocartilage complex and lunotriquetral ligament injury of distal radius fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2004. 39:391–396.

14. Knirk JL, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68:647–659.

15. Leung F, Tu YK, Chew WY, Chow SP. Comparison of external and percutaneous pin fixation with plate fixation for intra-articular distal radial fractures. A randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. 90:16–22.
16. Leung KS, Shen WY, Tsang HK, Chiu KH, Leung PC, Hung LK. An effective treatment of comminuted fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1990. 15:11–17.

17. Lindau T, Hagberg L, Adlercreutz C, Jonsson K, Aspenberg P. Distal radioulnar instability is an independent worsening factor in distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000. 376:229–235.

18. MacDermid JC. Development of a scale for patient rating of wrist pain and disability. J Hand Ther. 1996. 9:178–183.

19. Müler M, Nazarian S, Koch P, Schatzer J. The comprehensive classification of fractures of long bones. 1990. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;106–115.
20. Palmer AK. Triangular fibrocartilage complex lesions: a classification. J Hand Surg Am. 1989. 14:594–606.

21. Park JW. Operative treatment of distal radius fracture. J Korean Fracture Soc. 2006. 19:497–503.

22. Richards RS, Bennett JD, Roth JH, Milne K Jr. Arthroscopic diagnosis of intra-articular soft tissue injuries associated with distal radial fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1997. 22:772–776.

23. Ruch DS, Vallee J, Poehling GG, Smith BP, Kuzma GR. Arthroscopic reduction versus fluoroscopic reduction in the management of intra-articular distal radius fractures. Arthroscopy. 2004. 20:225–230.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download