Abstract
Purpose
We wanted to evaluate the usefulness of arthroscopic repair using the modified Mason-Allen Massive Cuff Stitch for medium sized full thickness rotator cuff tear. We verified the clinical results and evaluated the repair integrity after short term follow up.
Materials and Methods
Twenty-three cases of arthroscopically repaired full thickness tear of the rotator cuff of an estimated medium size were evaluated between December 2004 to May 2005. The average patient age was 54 years old (range: 43-69 years old), and the mean follow-up was 14 months (range: 12-17 months). We analyzed the results by paired t-test. The follow up MRIs were checked in 11 cases.
Results
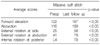
The VAS pain score was improved from a preoperative average of 7.0 to a postoperative average of 0.9, the ADL was improved from 11.1 to 26.0 and the UCLA score was improved from 13.6 to 32.5 (all p<0.05). 91.3% showed an excellent or good result at the final follow-up. The satisfied rate was 95.7% (22 cases). There was re-rupture of the repaired rotator cuff in one out of 11 cases (9.1%).
Figures and Tables
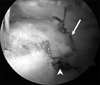 | Fig. 1The arthroscopic photographs showing the medium sized L shaped rotator cuff tear as viewed from the posterolateral portal. Side-to-side suture (arrow head) first repaired tendon to tendon lesion by margin convergence, and another horizontal mattress loop (arrow) was made at 10 mm medial to the edge of the cuff tendon. |
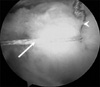 | Fig. 2The vertical single loop (arrow) from the anchors is made medial to the previous horizontal loop (arrow head). |
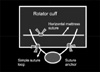
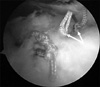 | Fig. 3Two sets of arthroscopic modified Mason-Allen stitch from one anchor is made, which is the Massive Cuff Stitch (MCS). The arthroscopic photographs showed the water-tight repaired rotator cuff. Two arrows indicate the arthroscopic modified Mason-Allen stitch, which looks the same as Fig. 2. Essentially broken into 2 separate loops, the horizontal mattress loop increases the strength of repair of a simple vertical loop. The modified Mason-Allen stitch is very difficult to do arthroscopically. Simple arthroscopic modification like separation of the loop and combined incorporation are the same as the modified Mason-Allen stitch. |
References
1. Bigliani LU, Morrison DS, April EW. Morphology of the acromion and its relationship to rotator cuff tears. Orthop Trans. 1986. 10:459–460.
2. Bungaro P, Rotini R, Traina F, et al. Comparative and experimental study on different tendinous grasping techniques in rotator cuff repair: a new reinforced stitch. Chir Organi Mov. 2005. 90:113–119.
4. Cummins CA, Murrell GA. Mode of failure of rotator cuff repair with suture anchors identified at revision surgery. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003. 12:128–133.
5. Ellman H. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression: analysis of one- to three-year results. Arthroscopy. 1987. 3:173–181.

6. Ellman H, Hanker G, Bayer M. Repair of the rotator cuff. End-result study of factors influencing reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68:1136–1144.

7. Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86:219–224.

8. Gartsman GM. Arthroscopic treatment of rotator cuff disease. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1995. 4:228–241.

9. Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Beck M, Schlegel U. Mechanical strength of repairs of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994. 76:371–380.

10. Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Perren SM, Nyffeler RW. Experimental rotator cuff repair. A preliminary study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. 81:1281–1290.

11. Groh GI, Simoni M, Rolla P, Rockwood CA. Loss of the deltoid after shoulder operations: an operative disaster. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1994. 3:243–253.

12. Hawkins RJ, Misamore GW, Hobeika PE. Surgery for full thickness rotator-cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985. 67:1349–1355.
13. Ko SH, Cho SD, Choe SW, et al. The evaluation for the usefulness of arthroscopic miniopen repair which related with large and massive sized full thickness rotator cuff tear and clinical results. J Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society. 2006. 9:83–88.

14. Ko SH, Cho SD, Gwak CY, Eo J, Yoo CH, Choe SW. Use of massive cuff stitch in arthroscopic repair of rotator cuff tears. J Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society. 2006. 9:181–188.

15. Ko SH, Cho SD, Lew SG, Park MS, Kwag CY, Woo JK. Comparison of arthroscopic versus mini open repair in medium and large sized full thickness rotator cuff tear - short term preliminary results -. J Korean Orthop Soc Sports Med. 2004. 3:73–80.
16. Ko SH, Cho SD, Park MS, et al. All arthroscopic repairs with biceps incorporation in large, massive sized full thickness rotator cuff tears. J Kor Musculoskeletal Transplantation Soc. 2005. 5:112–119.
17. Ko SH, Cho SD, Park MS, Woo JK. The use of bio suture anchor in the arthroscopic repair of medium sized full thickness rotator cuff tear in sports injury. J Kor Sports Med. 2005. 23:180–185.
18. Ko SH, Cho SD, Ryu SO, Gwak CY, Park MS. Arthroscopic repair of full thickness rotator cuff tear. J Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society. 2003. 6:161–166.
19. Ko SH, Rhee YG, Jeon HM, Lee CC. The usefulness of all arthroscopic repair with biceps incorporation in massive sized full thickness rotator cuff tears. J Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society. 2007. 10:106–111.
20. Lichtenberg S, Siebold R, Habermeyer P. Arthroscopic supraspinatus tendon repair using suture anchors and a modified Mason-Allen technique: an intra-articular approach. Arthroscopy. 2004. 20:1007–1011.

21. Ma CB, Comerford L, Wilson J, Puttlitz CM. Biomechanical evaluation of arthroscopic rotator cuff repairs: double-row compared with single-row fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:403–410.
22. Ma CB, MacGillivray JD, Clabeaux J, Lee S, Otis JC. Biomechanical evaluation of arthroscopic rotator cuff stitches. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86:1211–1216.

23. MacGillivray JD, Ma CB. An arthroscopic stitch for massive rotator cuff tears: the Mac stitch. Arthroscopy. 2004. 20:669–671.

24. Neer CS 2nd. Anterior acromioplasty for the chronic impingement syndrome in the shoulder: A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972. 54:41–50.
25. Pollock RG, Deliz ED, Mcllveen SJ, Flatow EL, Bigliani LU. Prosthetic replacement in rotator cuff-deficient shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1992. 1:173–186.

26. Richard RR, An K, Blgliani LU, et al. A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1994. 3:347–352.
27. Rockwood CA Jr. Shoulder function following decompression and irreparable cuff lesions. Orthop Trans. 1984. 8:92.
28. Schneeberger AG, von Roll A, Kalberer F, Jacob HA, Gerber C. Mechanical strength of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair techniques: an in vitro study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84:2152–2160.
29. Wiley AM. Superior humeral dislocation: a complication following decompression and debridement for rotator cuff tears. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. 263:135–141.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download