Abstract
Purpose
To describe the clinical features of herpes zoster that can be easily misdiagnosed as cervical or lumbar radiculopathy.
Materials and Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records and diagnostic studies of 7 patients with herpes zoster-related arm or leg pain.
Results
Except one immunocompromised patient with suspected postherpetic neuralgia or sequelae of herpetic myelitis, the other 6 patients with herpes zoster complained of very severe initial pain of sudden onset. Three patients did not show skin lesions on initial examination, and 2 of 5 patients with an MRI of the cervical or lumbar spine had findings consistent with their arm or leg pain and may have been confused with radiculopathy. Conservative treatment, including antiviral agents, improved the symptoms of all patients except the immunocompromised one. Selective nerve root blocks of the corresponding dermatomes were performed in 5 patients and extremity pain decreased over 50% in 4 of them.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
T2 axial (A) and sagittal (B) MRI images showing compression of right 6th cervical nerve by a hard disc (Case 1).
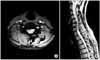
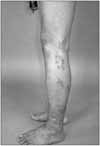
Fig. 2
Grouped erythematous vesicles in C5 and C6 dermatomes of right arm. The patient complained of pruritus in this area (Case 1).

References
3. Burkman KA, Gaines RW Jr, Kashani SR, Smith RD. Herpes zoster: a consideration in the differential diagnosis of radiculopathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1988. 69:132–134.
4. Christo PJ, Hobelmann G, Maine DN. Post-herpetic neuralgia in older adults: evidence-based approaches to clinical management. Drugs Aging. 2007. 24:1–19.
6. Dworkin RH, Johnson RW, Breuer J, et al. Recommendations for the management of herpes zoster. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. 44:Suppl 1. S1–S26.
8. Gardner-Thorpe C, Foster JB, Barwick DD. Unusual manifestations of herpes zoster. A clinical and electrophysiological study. J Neurol Sci. 1976. 28:427–447.
9. Hwang SM, Kang YC, Lee YB, Yoon KB, Ahn SK, Choi EH. The effects of epidural blockade on the acute pain in herpes zoster. Arch Dermatol. 1999. 135:1359–1364.

10. Jensen PK, Andersen EB, Boesen F, Dissing I, Vestergaard BF. The incidence of herniated disc and varicella zoster virus infection in lumboradicular syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. 1989. 80:142–144.

11. Kwon SB, Kim DW, Chung SL, Lee SJ. A clinical observation on acute pain and postherpetic neuralgia in patients with herpes zoster. Korean J Dermatol. 2000. 38:314–321.
12. Niv D, Maltsman-Tseikhin A. Postherpetic neuralgia: the never-ending challenge. Pain Pract. 2005. 5:327–340.

13. Roxas M. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia: diagnosis and therapeutic considerations. Altern Med Rev. 2006. 11:102–113.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download