Abstract
Purpose
The results of Sugioka's transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy are controversial. While many Japanese studies have reported favorable results, European and American studies have been disappointing. We present the results of Sugioka's rotational osteotomy for extensive osteonecrosis of the femoral head in young patients.
Methods and Materials
Between April. 1994 and May. 2004, Sugioka's osteotomy was performed for osteonecrosis involving a large part of the weight bearing area on 49 hips (46 patients). Of these 49 hips, 45 (43 patients) were available for follow-up. The patients were followed up for at least 2 years with an average of 52 months (range: 24-132 months). The major causes of osteonecrosis were chronic alcohol abuse in 33 hips. The mean age of the patients at the time of surgery was 31 years (range: 21-46), and the male to female ratio was 39:6. Six, 17 and 22 hips were classified as stage IIA, IIb and III using the Ficat and Alert classification, respectively.
Results
Thirty three of the 45 hips (74%) survived clinically and radiologically. Of these, the clinical results were excellent, good and fair in 15, 12 and 6 hips, respectively. Major complications were encountered in 12 hips [Progressive severe varus deformity in 7 hips (15%)], femur neck fracture in 3 hips (6%) and deep infection in 2 hips (4%). Among these 12 hips, seven hips (15%) required secondary THA. Five other hips (11%) were also subsequently converted to THA due to progressive collapse of the femoral head after the transtrochanteric osteotomy.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
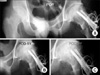
Radiographic findings of a 22-year-old man with alcohl induced ONFH collapse mild collapse of the left hip. (A) Preoperative atero-posterior radiograph of both hip joints, showing the collapse of the left femoral head (Ficat-Arlet stage IIb and Shimizu extent type C). (B) Preoperative radiograph (Sugioka's view) of both hip joints, showing the collapse of the left femoral head (Ficat-Arlet stage IIb and Shimizu extent type C). (C, D) Preoperative T2 weighted coronal MRI of both hips showing decreased signal intensity of the left femoral head (Ficat-Arlet stage IIb and Shimizu extent type C).
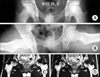
Fig. 2
Radiographic findings of a 22-year-old man with alcoholic ONFH with mild collapse of the left hip. (A) Immediate postoperative radiograph of both hip joints, anteroposterior view showing the transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy of left hip joint. (B) Postoperatively radiograph of both hip joints, anteroposterior view at one year after the osteotomy, showing preservation of the femoral head contour and joint space.
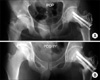
Fig. 3
Radiographic findings of a 22-year-old man with alcoholic ONFH with mild collapse of the left hip. (A) Postoperative radiograph of both hip joints. Anteroposterior view five years after the osteotomy showing preservation of the femoral head contour and joint space. (B) Postoperatively radiograph of both hip joints. Anteroposterior view ten year after the osteotomy showing preservation of the femoral head contour and joint space.
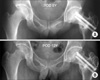
Fig. 4
Radiographic findings of a 27-year-old man with idiopathic ONFH with mild collapse of the left hip. (A) Preoperative radiograph of both hip joints. Anteroposterior view showing the collapse of left femoral head (Ficat-Arlet stage III and Shimizu extent type C). (B) Preoperative radiograph of both hip joints. Sugioka's view showing the collapse of left femoral head (Ficat-Arlet stage III and Shimizu extent type C). (C) Preoperative T2 weighted coronal MRI of both hip joints showing decreased signal intensity of the left femoral head (Ficat-Arlet stage III and Shimizu extent type C). (D) Preoperative T2 weighted axial MRI of both hip joints showing decreased signal intensity of left femoral head (Ficat-Arlet stage III and Shimizu extent type C).
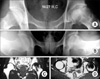
Fig. 5
Radiographic findings of a 27-year-old man with idiopathic ONFH with mild collapse of the left hip. (A) Immediate postoperatively radiograph of both hip joints. Anteroposterior view showing the transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy of the left hip joint. (B) Postoperative radiograph of both hip joints. Anteroposterior view five years after the osteotomy showing preservation of the femoral head contour and joint space. (C) Postoperatively radiograph of both hip joints. Anteroposterior view nine years after the osteotomy showing preservation of the femoral head contour and joint space.
References
1. Belal MA, Reichelt A. Clinical results of rotational osteotomy for treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1996. 115:80–84.

2. Dean MT, Cabanela ME. Transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy for avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993. 75:597–601.

3. Eyb R, Kotz R. The transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy of Sugioka. Early and late results in idiopathic aseptic femoral head necrosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1987. 106:161–167.
4. Hisatome T, Yasunaga Y, Takahashi K, Ochi M. Progressive collapse of transposed necrotic area after transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head induces osteoarthritic change. Mid-term results of transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004. 124:77–81.
5. Hungerford DS, Zizic TM. Alcoholism associated ischemic necrosis of the femoral head. Early diagnosis and treatment. Clin Orthop. 1978. 130:144–153.
6. Iano S, Ando M, Gotoh E, Matsuno T. Minimum 10-year results of Sugioka's osteotomy for femoral head osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 368:141–148.
7. Maistrelli G, Fusco U, Avai A, Bombelli R. Osteonecrosis of the hip treated by intertrochanteric osteotomy. A four- to 15-year follow up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:761–766.
8. Merle D'Aubigné R, Postel M, Mazabraud A, et al. Idiopathic necrosis of the femoral head in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965. 47:612–613.
9. Meyers MH. The treatment of osteonecrosis of the hip with fresh ostechondral allografts and with the muscle pedicle graft technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978. 130:202–209.
10. Mont MA, Hungerfold DS. Non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:459–474.

11. Ohzono K, Saito M, Takaoka K, et al. Natural history of nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991. 73:68–72.

12. Ondera S, Majima T, Abe Y, Ito H, Matsuno T, Minami A. Transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: relation between radiographic features and secondary collapse. J Orthop Sci. 2005. 10:367–373.
13. Rijnen WH, Gardeniers JW, Westrek BL, Buma P, Schreurs BW. Sugioka's osteotomy for femoral-head necrosis in young Caucasians. Int Orthop. 2005. 29:140–144.

14. Saito S, Ohzono K, Ono K. Joint-preserving operations for idiopathic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Resurts of core decompression, grafting and osteotolmy. J Bone joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:78–84.
15. Shimizu K, Moriya H, Akita T, Sakamoto M, Suguro T. Prediction of collapes with magnetic resonance imaging of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994. 76:215–223.
16. Smith SW, Fehring TK, Griffin WL, Beaver WB. Core decompression of the osteonecrotic femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77:674–680.

17. Sugano S, Takaoka K, Ohzono K, Matsui M, Saito M, Saito S. Rotational osteotomy for non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992. 74:734–739.

18. Sugioka Y. Transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy of the femoral head in the treatment of osteonecrosis affecting the hip: a new osteotomy operation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978. 130:191–201.
19. Sugioka Y. Transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy in the treatment of idiopathic and steroid-induced femoral head necrosis, Perthes' disease, slipped capital femoral epiphysis, and osteoarthritis of the hip. Indications and results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984. 184:12–23.
20. Sugioka Y, Hotokebuchi T, Tsutsui H. Transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy for idiopathic and steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head. Indications and long-term results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992. 277:111–120.
21. Sugioka Y, Katuski I, Hotokebuchi T. Transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy of the femoral head for the treatment of osteonecrosis. Follow-up statistics. Ciln Orthop Relat Res. 1982. 169:115–126.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download