Abstract
A fibrous tumor is a rare tumor that arises mainly in the visceral pleura but can occur in many locations throughout the body including the soft tissue, upper respiratory tract, peritoneum, retroperitoneum, periosteum, and intracranial portion. Recently, a solitary fibrous tumor was found in the central nervous system. However, the incidence of an intradural solitary fibrous tumor is quite low and there are no domestic reports of such cases. We report a case of intradural extramedullary solitary fibrous tumor of the thoracic spine. A favorable clinical result was obtained using surgical treatment. The immunohistological findings revealed the tumor to be reactive to vimentin and CD34 but negative to the S-100 protein, alpha smooth muscle actin and desmin.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Sagittal (upper row) and axial (lower row) T1 weighted magnetic resonance images show an irregular hypointense mass at the T7-8 level (left column). T2 weighted images show intermediate signal intensity area (right column).
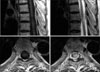
Fig. 3
Microscopic appearances of the fibrous tumor. Photomicrograph of the specimen show spindle cell proliferation and dense intracellular collagen deposition (A: HE stain, ×40 and B: HE stain, ×400). Immunohistochemical staining shows the tumor cells are focally positive for CD34 (C) and strongly positive for vimentin (D).

References
1. Alston SR, Francel PC, Jane JA. Solitary fibrous tumor of the spinal cord. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997. 21:477–483.

2. Carneiro SS, Scheithauer BW, Nascimento AG, Hirose T, Davis DH. Solitary fibrous tumor of the meninges: a lesion distinct from fibrous meningioma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study. Am J Clin Pathol. 1996. 106:217–224.
3. Hanau CA, Miettinen M. Solitary fibrous tumor: histological and immunohistochemical spectrum of benign and malignant variants presenting at different sites. Hum Pathol. 1995. 26:440–449.

4. Martin AJ, Fisher C, Igbaseimokumo U, Jarosz JM, Dean AF. Solitary fibrous tumours of the meninges: case series and literature review. J Neurooncol. 2001. 54:57–69.
5. Moran CA, Suster S, Koss MN. The spectrum of histologic growth patterns in benign and malignant fibrous tumors of the pleura. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1992. 9:169–180.
6. Ogawa T, Moriyama E, Beck H, Sonobe H. Solitary fibrous tumor of the thoracic spinal cord. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2005. 45:371–374.
7. Tihan T, Viglione M, Rosenblum MK, Olivi A, Burger PC. Solitary fibrous tumors in the central nervous system. A clinicopathologic review of 18 cases and comparison to meningeal hemangiopericytomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003. 127:432–439.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download