Abstract
Purpose
This study evaluated the radiological reference line of the posterior slope angle on the lateral view of a plain knee radiograph.
Materials and Methods
The lateral view of the plain knee and whole tibia radiographs were analyzed from thirty seven patients (fifty-two cases) who had undergone total knee arthroplasty. The posterior slope angle was measured on the lateral view of the tibia. On the lateral view of the knee, the posterior slope angle was measured with reference to the proximal tibial anatomical axis, the proximal tibial anterior cortical line, the proximal tibial posterior cortical line and the proximal fibular anatomical axis. These values were compared with the posterior slope angle measured on the whole tibia lateral view.
Results
The posterior slope angle, which was measured by the anterior cortical line as a reference line, was tilted slightly anteriorly to that measured by the whole tibial lateral anatomical axis (0.15 degree in average; anterior slope 3.95- posterior slope 5.57 degree). This difference was smallest among that of the measured angle by the other reference lines (p<0.001).
Figures and Tables
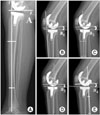
Fig. 1
(A) Measurement of the posterior slope angle (A) using lateral tibial anatomical axis. (B) Measurement of the posterior slope angle (a1) using the proximal tibial anterior cortical line. (C) Measurement of posterior slope angle (a2) using the proximal tibial anatomical axis. (D) Measurement of the posterior slope angle (a3) using the proximal tibial posterior cortical line. (E) Measurement of the posterior slope angle (a4) using the proximal fibular anatomical axis.
References
1. Brazier J, Migaud H, Gougeon F, Cotten A, Fontaine C, Duquennoy A. Evaluation of methods for radiographic measurement of the tibial slope. A study of 83 healthy knees. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1996. 82:195–200.
2. Choi CH, Kim JH, Chung HK, Choi YH. Measurement of posterior slope angle of the proximal tibia by MRI and X-ray. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2001. 36:569–573.

3. Chung JB, Han CD, Yang IW, Che JH. Radiographic analysis of the tibial axis on the antero-posterior and lateral view of knee. J Korean Knee Soc. 2005. 17:58–63.
4. Clarke HD, Scott WN, Insall JN, et al. Insall JN, Scott WN, editors. Anatomy. Surgery of the knee. 2001. 3rd ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone Inc;13–76.

5. Genin P, Weill G, Julliard R. The tibial slope. Proposal for a measurement method. J Radiol. 1993. 74:27–33.
6. Hofmann AA, Bachus KN, Wyatt RW. Effect of the tibial cut on subsidence following total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991. 269:63–69.

7. Jiang CC, Yip KM, Liu TK. Posterior slope angle of the medial tibial plateau. J Formos Med Assoc. 1994. 93:509–512.
8. Kuwano T, Urabe K, Miura H, et al. Importance of the lateral anatomic tibial slope as a guide to the tibial cut in total knee arthroplasty in Japanese patients. J Orthop Sci. 2005. 10:42–47.

9. Lotke PA, Ecker ML. Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977. 59:77–79.

10. Matsuda S, Mizu-uchi H, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Iwamoto Y. Tibial shaft axis does not always serve as a correct coronal landmark in total knee arthroplasty for varus knees. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18:56–62.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download