Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
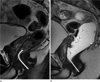 | Fig. 2A 40-year-old man with lower rectal cancer whose tumor distance from the anal verge was approximately 4 cm according to rigid sigmoidoscopy. The distance to the mass was measured from the anal verge to the distal tumor margin on MRI (lines). He underwent ultra-lower anterior resection surgery.
a. Sagittal T2 weighted image obtained before rectal gel distension shows that tumor distance from the anal verge measured approximately 4.4 cm.
b. Sagittal T2 weighted image obtained after rectal gel distension shows that tumor distance from the anal verge was approximately 6.2 cm, and the distance from anal verge (distal tumor margin) was exaggerated after gel filling.
|
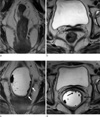 | Fig. 3A 66-year-old woman with lower rectal cancer (pT1).
a, b. Oblique coronal & axial T2 weighted images obtained before rectal gel distension show that the tumor was not well defined on MRI. T3 rectal cancer was diagnosed.
c, d. Oblique coronal & axial T2 weighted image obtained after rectal gel distension shows that the tumor was well defined on MRI. T1 rectal cancer (arrows) was diagnosed.
|
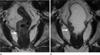 | Fig. 4A 70-year-old man with lower rectal cancer and sphincter invasion.
a. Oblique coronal T2 weighted image obtained before rectal gel distension shows that the tumor infiltrated the right external sphincter (arrow).
b. Oblique coronal T2 weighted image obtained after rectal gel distension shows more clearly that the tumor infiltrated the right external sphincter (arrow). However, there were no significantly different assessment scores between MRI with gel filling and MRI without gel filling.
|
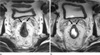 | Fig. 5A 45-year-old man with lower rectal cancer and CRM involvement.
a. Axial T2 weighted image obtained before rectal gel distension shows that the tumor invaded the anterior CRM (arrows).
b. Axial T2 weighted image obtained after rectal gel distension shows that the tumor invaded the anterior CRM (arrows). There were no significantly different assessment scores between MRI with gel filling and MRI without gel filling.
|
Table 1

Table 2
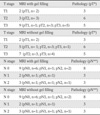
*pT - pathologic tumor staging
**pN - pathologic nodal staging
Note
1. T stages of MRI are as follows: T1, Tumor invades the submucosa; T2, Tumor invades the muscularis propria; T3, Tumor penetrates the muscularis propria and perirectal fat.
2. N stages of MRI are as follows; N0, no predicted lymph nodes positive for tumor; N1, <four predicted regional nodes positive for tumor; N2, >four predicted regional nodes positive for tumor. Prediction of regional nodes positive for tumor was size of LNs >8 mm in short axis.
3. Pathological stages are as follows: T1, limited to mucosa and submucosa; T2, extension into but not through muscularis propria; T3, invasion of perirectal fat; N0, no involved lymph nodes; N1, <four regional nodes positive for tumor; N2, >four regional nodes positive for tumor.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download