Abstract
Purpose
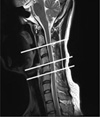
We report the results of the various parameters of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and CSF flow study of the cervical spinal cord using magnetic resonance (MR) imaging techniques.
Materials and Methods
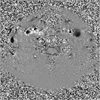
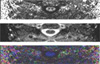
Intramedullary FA and MD were measured in the gray matter and posterior cord of the white matter and both lateral cords of the white matter at the C2-3, C4-5, C5-6 spinal levels. For the CSF flow study, velocity encoding was obtained at the C2-3, C4-5, C5-6 spinal levels.
Results
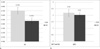
There was a significant difference of the FA and MD between the white matter and gray matter (p < 0.05). The FA of the gray matter was significantly different according to the cervical spinal cord levels (p < 0.05). Otherwise, the FA and MD parameters were not significantly different (p > 0.05). The mean peak systolic velocity and mean peak diastolic velocity were 5.18±2.00 cm/sec and -7.32±3.18 cm/sec, respectively from C2 to C6 spinal cords. There was no significant difference in these velocities among the cervical spinal cord (p > 0.05).
References
1. Ham KS, Shin MK, Choi HS. Neurophysiology. Hyunmoon;1997. p. 13–24.
2. Frank H, Netter MD. The CIBA Collection of medical illustrations: volume 1 Nervous system anatomy and physiology. Novartis;2000. p. 23–39.
3. Levitt MA, Flanders AE. Diagnostic capabilities of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in acute cervical spinal column injury. Am J Emerg Med. 1991; 9:131–135.
4. Renoux J, Facon D, Fillard P, Huynh I, Lasjaunias P, Ducreux D. MR diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking in inflammatory diseases of the spinal cord. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1947–1951.
5. Ducreux D, Fillard P, Facon D, et al. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging and fiber tracking in spinal cord lesions: current aln future indications. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2007; 17:137–147.
6. Thurnher MM, Law M. Diffusion-weighted imaging, diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography of the spinal cord. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009; 17:225–244.
7. Xiangshui M, Xiangjun C, Xiaoming Z, et al. 3T magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging and fibre tracking in cervical myelopathy. Clin Radiol. 2010; 65:465–473.
8. Facon D, Ozanne A, Fillard P, Lepeintre JF, Tournoux-Facon C, Ducreux D. MR diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking in spinal cord compression. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1587–1594.
9. Demir A, Ries M, Moonen CT, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient and apparent diffusion tensor maps in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Radiology. 2003; 229:37–43.
10. Mamata H, Jolesz FA, Maier SE. Apparent diffusion coefficient and fractional anisotropy in spinal cord: age and cervical spondylosis-related changes. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005; 22:38–43.
11. Korean Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. Magnetic resonance imaging. Ilchokak;2008. p. 173–179.
12. Bhadelia RA, Frederick E, Patz S, et al. Cough-associated headache in patients with Chiari I malformation: CSF flow analysis by means of cine phase-contrast MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:739–742.
13. Hofmann E, Warmuth-Metz M, Bendszus M, Solymosi L. Phase-contast MR imaging of the cervical CSF and spinal cord: volumetric motion analysis in patients with Chiari I malformation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:151–158.
14. Song KY, Ha YI, Kang DS, et al. Clinical applications of cine MR. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 1998; 27:808–814.
15. Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Hickman SJ, Parker GJ, et al. Investingating cervical spinal cord structure using axial diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage. 2002; 16:93–102.
16. Cerciqnani M, Horsfield M, Agosta F, Filippi M. Sensitivity-encoded diffusion tensor MR imaging of the cervical cord. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1254–1256.
17. Struck AF, Haughton VM. Idiopathic syringomyelia: phase contrast MR of cerebrospinal fluid flow dynamics at level of framen magnum. Radiology. 2009; 253:184–190.
18. Vargas MI, Delavelle J, Jlassi H, et al. Clinical applications of diffusion tensor tractography of the spinal cord. Neuroradiology. 2008; 50:25–29.
19. Lee JW, Kim JH, Park JB, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography in cervical compressive myelopathy: preliminary results. Skeletal Radiol. 2011; 40:1543–1551.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print









 XML Download
XML Download