Abstract
We report the radiological findings of regional enhancement of the liver adjacent to the right adrenal pheochromocytoma. CT and MRI showed focal strong enhancement of adjacent liver tissue in the arterial phase. However during the delayed phase, the lesion showed iso-attenuation with normal hepatic parenchyma and not delineated. The lesion did not show abnormal signal intensity on neither T1 nor T2 weighted images and indistinguishable from normal parenchyma. The enhancing hepatic lesion was spontaneously regressed on postoperative follow up CT which was taken several months after the adrenalectomy.
Figures and Tables
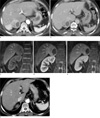
Fig. 1
Pheochromocytoma in a 67-year-old Female Patient with Palpitation, Chest Pain and Nausea.
a. Arterial (30S) phase CT shows a heterogeneously enhancing mass lesion in the right adrenal gland and a wedge-shaped enhancing lesion(arrows) in segment 7 of the liver.
b. In delayed (180S) image, hepatic lesion (arrows) shows iso-attenuation.
Five phase dynamic MR (c) precontrast, (d) 1 min, (e) 2 min, 3 min and 5 min(not shown) after contrast injection was performed. Lesion in segment 7 of the liver adjacent to the right adrenal mass presents strong enhancement (arrows) in 1 min delayed image and washes out afterwards.
f. In a follow-up CT after adrenalectomy, wedge shaped enhancing lesion in S7 of the liver is spontaneously regressed and there is no demonstrable lesion in arterial (45S) phase CT .
References
1. Kang JM, Lee WJ, Kim WB, et al. Systemic inflammatory syndrome and hepatic inflammatory cell infiltration caused by an interleukin-6 producing pheochromocytoma. Endocr J. 2005. 52:193–198.
2. Bravo EL, Gifford RW Jr. Pheochromocytoma. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1993. 22:329–341.
3. Fonseca V, Bouloux PM. Phaeochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993. 7:509–544.
4. Ikuta S, Yasui C, Kawanaka M, et al. Watery diarrhea, hypokalemia and achlorhydria syndrome due to an adrenal pheochromocytoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. 13:4649–4652.
5. Nijhoff MF, Dekkers OM, Vleming LJ, Smit JW, Romijn JA, Pereira AM. ACTH-producing pheochromocytoma: clinical considerations and concise review of the literature. Eur J Intern Med. 2009. 20:682–685.
6. Chung CH, Wang CH, Tzen CY, Liu CP. Intrahepatic cholestasis as a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with pheochromocytoma. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005. 28:175–179.
7. Morikawa T, Suzuki M, Unno M, Endo K, Katayose Y, Matsuno S. Malignant pheochromocytoma with hepatic metastasis diagnosed 10 years after a resection of the primary incidentaloma adrenal lesion: report of a case. Surg Today. 2001. 31:80–84.
8. Schlumberger M, Gicquel C, Lumbroso J, et al. Malignant pheochromocytoma: clinical, biological, histologic and therapeutic data in a series of 20 patients with distant metastases. J Endocrinol Invest. 1992. 15:631–642.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download