Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to describe arterial spin labeling MR image findings of status epilepticus.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective chart review within our institute revealed six patients who had been clinically diagnosed as status epilepticus and had also undergone MR imaging that included ASL in addition to routine sequences.
Results
Six patients with status epilepticus were studied by conventional MR and arterial spin labeling imaging. All patients showed increased regional CBF correlating with EEG pathology. Notably, in two patients, conventional MRI and DWI showed no abnormal findings whereas pCASL demonstrated regional increased CBF in both patients.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
a. The pre and post pulses provide background suppression necessary for better contrast. Saturation was performed with crusher gradients inferior to the labeling plane, allowing for the increase in sharpness of the bolus. The arterial spin labeling experiment then consists of acquiring a labeled and a non-labeled (control) image and subtracting them to obtain the flow image. A 3D fast spin echo (FSE) spiral sequence has been implemented to acquire the signal which has prepared by the labeling sequence. The slice loop is the inner most and is acquired in a centric fashion.
b. Quantification is performed as the equation, where 1.4 s for blood at 1.5 T is assumed. The partial saturation of the 'PD' reference image is corrected for a T1 of 1.2 s typical of gray matter (44). While a more fully relaxed signal would be desirable, the saturation of the receiver and the bright signal on the slightly T2-weighted FSE makes this undesirable. The partition coefficient, λ, was set to the whole brain average, 0.9, and the efficiency, ε, is set to 0.80 × 0.75. This quantification assumes the label remains in blood and thus T1 of the tissue, and the delay in the arrival time to the tissue, need not be quantified.
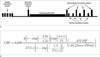
Fig. 2
An example of the ROI placement. ROIs were drawn in the both normal brain cortical areas and pathologic regions exhibiting the greatest CBF, and the values were recorded. CBF was calculated by dividing the measured values in ROIs by ten.
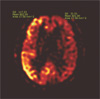
Fig. 3
60-year-old man presenting with generalized tonic-clonic seizure (patient 2).
a. A T2-weighted image shows tortuous vascular structure (shown as signal voids), which suggests the presence of an arteriovenous malformation in the left temporo-occipital lobe. Diffuse increased T2 signal intensity in the same area was noted. b. Left vertebral angiogram shows an arteriovenous malformation in the left temporo-occipital lobe. c. DWI results demonstrate high SI in the left frontoparietal lobe. d. decreased ADC values were also observed in the affected area. e. pCASL images demonstrate a marked increase in CBF in the left frontoparietal lobe.
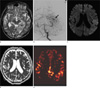
Fig. 4
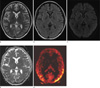
21-year-old woman presenting with depression and altered mentality (patient 3).
a, b. A T2-weighted image (a) and fluid attenuated inversion recovery image (b) show no focal abnormal signal intensity.
c. DWI fails to depict any signal change.
d. ADC also demonstrates normal values.
e. pCASL images show diffusely increased CBF in bilateral regions of the cortex, particularly in the biparietal and occipital lobes.
References
1. Jack C, Sharbrough F, Twomey C, et al. Temporal lobe seizures: lateralization with MR volume measurements of the hippocampal formation. Radiology. 1990. 175:423–429.
2. Jackson G, Berkovic S, Duncan J, Connelly A. Optimizing the diagnosis of hippocampal sclerosis using MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1993. 14:753–762.
3. Lansberg M, O'Brien M, Norbash A, Moseley M, Morrell M, Albers G. MRI abnormalities associated with partial status epilepticus. Neurology. 1999. 52:1021–1027.
4. Men S. Selective neuronal necrosis associated with status epilepticus: MR findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. 21:1837–1840.
5. Treiman DM, Meyers PD, Walton NY, et al. Veterans affairs status epilepticus cooperative study group. A comparison of four treatments for generalized convulsive status epilepticus. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339:792–798.
6. Shepherd SM. Management of status epilepticus. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1994. 12:941–961.
7. Meierkord H, Holtkamp M. Non-convulsive status epilepticus in adults: clinical forms and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2007. 6:329–339.
8. Devinsky O, Kelley K, Porter RJ, Theodore WH. Clinical and electroencephalographic features of simple partial seizures. Neurology. 1988. 38:1347–1352.
9. Williamson PD, Spencer DD, Spencer SS, Novelly RA, Mattson RH. Complex partial seizures of frontal lobe origin. Ann Neurol. 1985. 18:497–504.
10. Duncan R. Epilepsy, cerebral blood flow, and cerebral metabolic rate. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1992. 4:105–121.
11. Schwartz TH. Neurovascular coupling and epilepsy: hemodynamic markers for localizing and predicting seizure onset. Epilepsy Curr. 2007. 7:91–94.
12. Engelhorn T, Hufnagel A, Weise J, Baehr M, Doerfler A. Monitoring of acute generalized status epilepticus using multilocal diffusion MR imaging: early prediction of regional neuronal damage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. 28:321–327.
13. Hauf M, Slotboom J, Nirkko A, Von Bredow F, Ozdoba C, Wiest R. Cortical regional hyperperfusion in nonconvulsive status epilepticus measured by dynamic brain perfusion CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. 30:693–698.
14. Szabo K, Poepel A, Pohlmann-Eden B, et al. Diffusion-weighted and perfusion MRI demonstrates parenchymal changes in complex partial status epilepticus. Brain. 2005. 128:1369–1376.
15. Bauer J, Stefan H, Huk W, et al. CT, MRI and SPECT neuroimaging in status epilepticus with simple partial and complex partial seizures: case report. J Neurol. 1989. 236:296–299.
16. Katz A, Bose A, Lind SJ, Spencer SS. SPECT in patients with epilepsia partialis continua. Neurology. 1990. 40:1848–1850.
17. Tatum WO, Alavi A, Stecker MM. Technetium-99m-HMPAO SPECT in partial status epilepticus. J Nucl Med. 1994. 35:1087–1094.
18. Detre JA, Leigh JS, Williams DS, Koretsky AP. Perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1992. 23:37–45.
19. Dixon WT, Du LN, Faul DD, Gado M, Rossnick S. Projection angiograms of blood labeled by adiabatic fast passage. Magn Reson Med. 1986. 3:454–462.
20. Yang Y, Frank JA, Hou L, Ye FQ, McLaughlin AC, Duyn JH. Multislice imaging of quantitative cerebral perfusion with pulsed arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med. 1998. 39:825–832.
21. Pollock JM, Tan H, Kraft RA, Whitlow CT, Burdette JH, Maldjian JA. Arterial spin-labeled MR perfusion imaging: clinical applications. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009. 17:315–338.
22. Toledo M, Munuera J, Salas-Puig X, Santamarina E, Lacuey N, Rovira A. Localisation value of ictal arterial spin-labelled sequences in partial seizures. Epileptic Disord. 2011. 13:336–339.
23. Pollock JM, Deibler AR, West TG, Burdette JH, Kraft RA, Maldjian JA. Arterial spin-labeled magnetic resonance imaging in hyperperfused seizure focus: a case report. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2008. 32:291–292.
24. Dai W, Garcia D, De Bazelaire C, Alsop DC. Continuous flow-driven inversion for arterial spin labeling using pulsed radio frequency and gradient fields. Magn Reson Med. 2008. 60:1488–1497.
25. Garcia D, De Bazelaire C, Alsop D. Pseudo-continuous flow driven adiabatic inversion for arterial spin labeling. Proceedings of thirteenth scientific meeting and exhibition of the international society for magnetic resonance in medicine. 2005. May 7-13, 2005; Miami, Fla: ISMRM;37.
26. Kaplan PW. The clinical features, diagnosis, and prognosis of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Neurologist. 2005. 11:348–361.
27. Shneker BF, Fountain NB. Assessment of acute morbidity and mortality in nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Neurology. 2003. 61:1066–1073.
28. Cole AJ. Status epilepticus and periictal imaging. Epilepsia. 2004. 45:72–77.
29. Duffner F, Freudenstein D, Schiffbauer H, et al. Combining MEG and MRI with neuronavigation for treatment of an epileptiform spike focus in the precentral region: a technical case report. Surg Neurol. 2003. 59:40–45.
30. Sadowski EA, Bennett LK, Chan MR, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: risk factors and incidence estimation. Radiology. 2007. 243:148–157.
31. Wintermark M, Sesay M, Barbier E, et al. Comparative overview of brain perfusion imaging techniques. Stroke. 2005. 36:e83–e99.
32. Kang M, Choi JC, Kwon HJ, et al. Cerebral Perfusion MR findings before and after a carotid stent. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2009. 61:79–85.
33. Zaharchuk G, Bammer R, Straka M, et al. Arterial spin-label imaging in patients with normal bolus perfusion-weighted MR imaging findings: pilot identification of the borderzone sign. Radiology. 2009. 252:797–807.
34. Kim JA, Chung JI, Yoon PH, et al. Transient MR signal changes in patients with generalized tonicoclonic seizure or status epilepticus: periictal diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. 22:1149–1160.
35. Borgstrom L, Chapman A, Siesjo B. Glucose consumption in the cerebral cortex of rat during bicuculline induced status epilepticus. J Neurochem. 1976. 27:971–973.
36. Meldrum BS, Nilsson B. Cerebral blood flow and metabolic rate early and late in prolonged epileptic seizures induced in rats by bicuculline. Brain. 1976. 99:523–542.
37. Schomer DL. Focal status epilepticus and epilepsia partialis continua in adults and children. Epilepsia. 1993. 34:S29–S36.
38. Chapman A, Meldrum B, Siesio B. Cerebral metabolic changes during prolonged epileptic seizures in rats. J Neurochem. 1977. 28:1025–1035.
39. Engelhorn T, Doerfler A, Weise J, Baehr M, Forsting M, Hufnagel A. Cerebral perfusion alterations during the acute phase of experimental generalized status epilepticus: prediction of survival by using perfusion-weighted MR imaging and histopathology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 26:1563–1570.
40. O'Brien TJ. SPECT: methodology. Adv Neurol. 2000. 83:11–32.
41. Warach S, Levin J, Schomer D, Holman B, Edelman R. Hyperperfusion of ictal seizure focus demonstrated by MR perfusion imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994. 15:965–968.
42. Tatlidil R. Persistent postictal hyperperfusion demonstrated with PET. Epilepsy Res. 2000. 42:83–88.
43. Takeshita G, Toyama H, Nakane K, et al. Evaluation of regional cerebral blood flow changes on perifocal brain tissue SPECT before and after removal of arteriovenous malformations. Nucl Med Commun. 1994. 15:461–468.
44. Stanisz GJ, Odrobina EE, Pun J, et al. T1, T2 relaxation and magnetization transfer in tissue at 3T. Magn Reson Med. 2005. 54:507–512.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download