Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
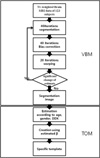 | Fig. 1Flowchart for the brain template creation.
In this study, we use two separated steps, VBM5 and TOM.
GM: Gray matter
WM: White matter
CSF: Cerebrospinal Fluid
VBM: Voxel-Based Morphometry
TOM: Template-O-Matic
|
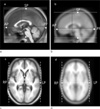 | Fig. 2Measured parameters shown on the images of the smoothed our brain template (a, c) and the MNI-152 template (b, d). The solid lines show the center position (0, 0, 0) in x, y z plane. The upper and lower dotted lines show the length of the SP-IP size and the middle dotted line is the length of the AP-PP line. The vertical lines show the length of the RP-LP line. |
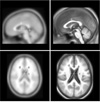 | Fig. 3Measured distances (mm) of the ventricle area for selecting landmark sites in the MNI-152 template (Upper left and bottom left) and the smoothed our brain template (Upper right and bottom right). |
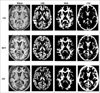 | Fig. 4Representative segmented images obtained in a cognitively normal (CN) control subject (upper row), in a patient with mild cognitive impairment (MCI, middle row), and in a patient with Alzheimer's disease (AD, bottom row).
Each subject is a 70 years-old woman.
GM: Gray matter
WM: White matter
CSF: Cerebrospinal Fluid
|
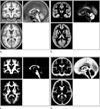 | Fig. 5The created standard brain templates of three-dimensional T1-weighted (a) and the corresponding tissue maps of gray matter(GM, b), white matter (WM, c), andcerebrospinal fluid (CSF, d). |
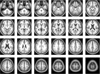 | Fig. 6The created standard brain template of three-dimensional T1-weighted images was shown as the axial plane slices. |
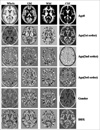 | Fig. 7Beta image volumes in a general linear model; The ages are the coefficients of the third order polynomial
Maps from the second row to the sixth row represent beta image volumes in a general linear model of the standard templates caused by the co-varietiesof age, gender, and DDX.
GM: Gray matter
WM: White matter
CSF: Cerebrospinal Fluid
DDX: Differential diagnosis
|
Table 1

Data are listed as the mean ± standard deviation.
CN: Cognitive Normal.
MCI: Mild Cognitive Impairment.
AD: Alzheimer's disease.
#Gender: statistically significant difference between MCI and AD (p = 0.007), but no significant differences between CN and MCI (p = 0.22) or between CN and AD (p = 0.13)
*Age: statistically significant difference between CN and AD (p = 0.0001) and between MCI and AD (p = 0.01), but no significant difference between CN and MCI (p = 0.08)
Table 2

#Template size (mm) and resolution (mm): X × Y × Z.
*Age, gender and DDX effects were considered in our template (Yes), but not in the MNI (No).
& normalized gray matter or white matter percentage: nGM or nWM equals to the number of GM voxels multipled by 100% devided by the total IC voxels more than 50% of GM or WM, respectively.
DDX: differential diagnosis, GM: gray matter, WM: white matter, IC: Intracranial, AP: anterior point, PC: posterior point, RP-LP: right point-left point, SP-IP: superior point-inferior point




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download