Abstract
Levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor alpha (sIL-2Rα) are known to increase in the sera of patients with certain malignancies, including malignant lymphoma. This study aimed to assess the clinical significance of the sIL-2Rα level in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). We used ELISA to measure the sIL-2Rα levels in 48 newly diagnosed and untreated patients with NHL and evaluated the correlation between the sIL-2Rα levels and clinical characteristics and the International Prognostic Index (IPI). We monitored serum sIL-2Rα in 7 patients to compare the changes in their clinical progress with these levels. High levels of serum sIL-2Rα (≥2,000 U/mL) correlated well with parameters defining the high risk group according to the IPI, i.e., high tumor burden at diagnosis (stage III+IV) and lactate dehydrogenase ≥472 U/L. The levels were also associated with B symptoms, bone marrow involvement, and poor response to therapy. The sIL-2Rα level decreased during complete remission and was elevated during disease progression or relapse. A high level of sIL-2Rα was significantly associated with a low survival rate. These results suggest that serum sIL-2Rα might be useful as a biomarker for evaluating the prognosis of patients with NHL at the time of diagnosis and during therapy. A well-controlled, large-scale study is needed to clarify the clinical significance of sIL-2Rα in specific groups of NHL.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Armitage JO., Weisenburger DD. New approach to classifying non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol. 1998. 16:2780–95.

2.Setoyama Y., Imai J., Ishikawa T., Sakaida H., Takaori-Kondo A., Kawamata S, et al. Usefulness of the measurement of serum soluble IL-2 receptor alpha chain levels in clinical monitoring of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Rinsho Byori. 1994. 42:834–42.
3.A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:987–94.
4.Bien E., Balcerska A. Serum soluble interleukin 2 receptor alpha in human cancer of adults and children: a review. Biomarkers. 2008. 13:1–26.
5.Gandhi MK., Lambley E., Burrows J., Dua U., Elliott S., Shaw PJ, et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA is a biomarker for EBV-positive Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clinical Cancer Research. 2006. 12:460–4.

6.Rubin LA., Galli F., Greene WC., Nelson DL., Jay G. The molecular basis for the generation of the human soluble interleukin 2 receptor. Cytokine. 1990. 2:330–6.

7.Waldmann TA. Anti-Tac (daclizumab, Zenapax) in the treatment of leukemia, autoimmune diseases, and in the prevention of allograft rejection: a 25-year personal odyssey. J Clin Immunol. 2007. 27:1–18.

8.Kitagawa JI., Hara T., Tsurumi H., Goto N., Kanemura N., Yoshikawa T, et al. Serum-soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) is an extremely strong prognostic factor for patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified (PTCL-U). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009. 135:53–59.

9.Oki Y., Kato H., Matsuo K., Kuwatsuka Y., Taji H., Yamamoto K, et al. Prognostic value of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor level in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma, treated with CHOP- or RCHOP-based therapy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008. 49:1345–51.

10.Wakao D., Murohashi I., Tominaga K., Yoshida K., Kishimoto K., Yagasaki F, et al. Serum thymidine kinase and soluble interleukin-2 receptor predict recurrence of malignant lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2002. 81:140–6.

11.Goto H., Tsurumi H., Takemura M., Ino-Shimomura Y., Kasahara S., Sawada M, et al. Serum-soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) level determines clinical outcome in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: in combination with the International Prognostic Index. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2005. 131:73–9.

12.Janik JE., Morris JC., Pittaluga S., McDonald K., Raffeld M., Jaffe ES, et al. Elevated serum-soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels in patients with anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood. 2004. 104:3355–7.

13.Yoshida S., Morii K. Serum concentrations of soluble interleukin-2 receptor in patients with malignant brain tumors. J Surg Oncol. 2000. 75:131–5.

14.Kaminska J., Kowalska M., Kotowicz B., Fuksiewicz M., Glogowski M., Wojcik E, et al. Pretreatment serum levels of cytokines and cytokine receptors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer, and correlations with clinicopathological features and prognosis. M-CSF - an independent prognostic factor. Oncology. 2006. 70:115–25.
15.Witkowska AM. On the role of sIL-2R measurements in rheumatoid arthritis and cancers. Mediators Inflamm. 2005. 2005:121–130.

16.Sakata H., Murakami S., Hirayama R. Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) and immunohistochemical staining of IL-2R/Tac antigen in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2002. 7:312–7.

17.Huang A., Quinn H., Glover C., Henderson DC., Allen-Mersh TG. The presence of interleukin-2 receptor alpha in the serum of colorectal cancer patients is unlikely to result only from T cell up-regulation. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2002. 51:53–7.
Go to : 
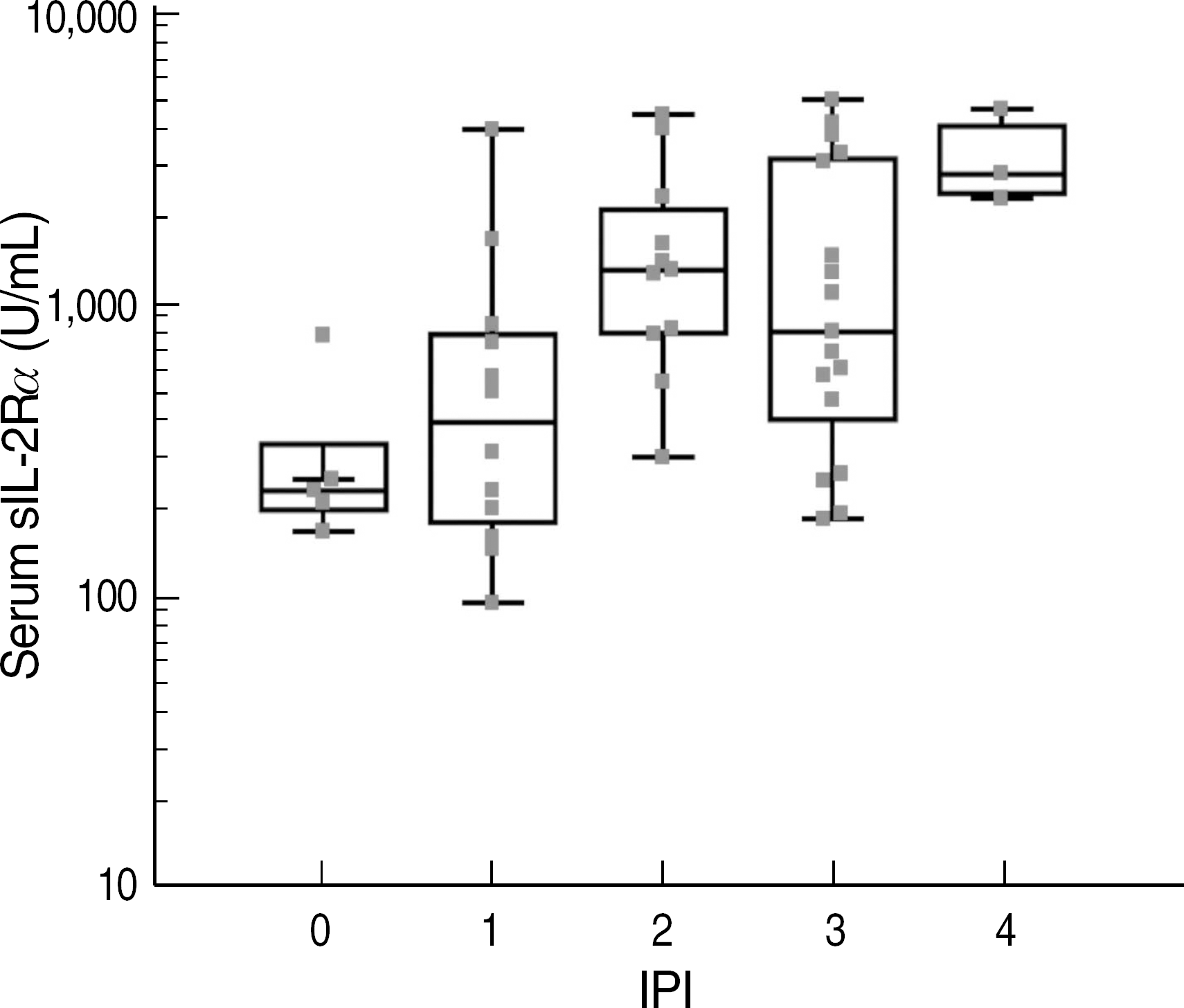 | Fig. 1.Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor alpha (sIL-2Rα) levels according to the International Prognostic Index (IPI) risk group (Kruskall-Wallis test, P=0.005). |
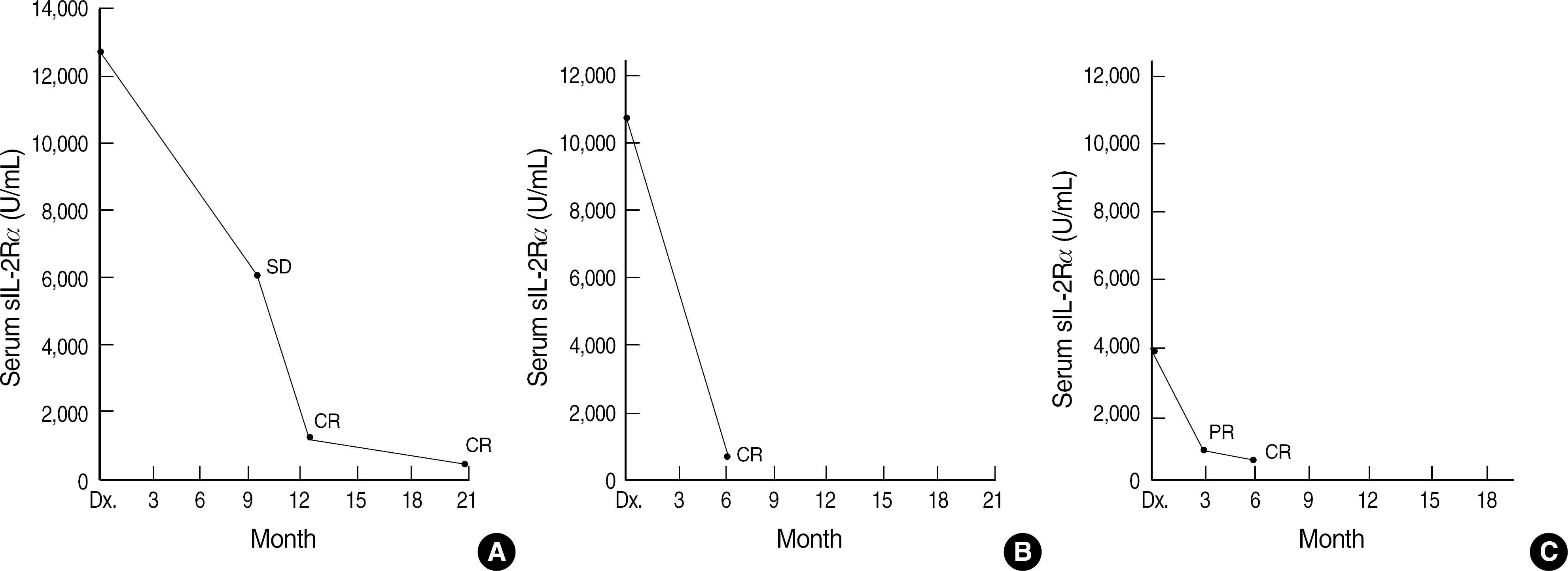 | Fig. 2.Serial analysis of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor alpha (sIL-2Rα) levels in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients showing complete remission (CR), through stable disease (SD) or partial remission (PR); sIL-2Rα levels in relation to the timing of chemotherapy, and with respect to radiographic evaluations. (A) A 36-yr-old man with anaplastic large cell lymphoma in the inguinal lymph nodes treated with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP). (B) A 40-yr-old man with diffuse large B cell lymphoma in the small bowel lymph nodes treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). (C) A 60-yr-old man with B cell malignant lymphoma in the oral cavity treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP). |
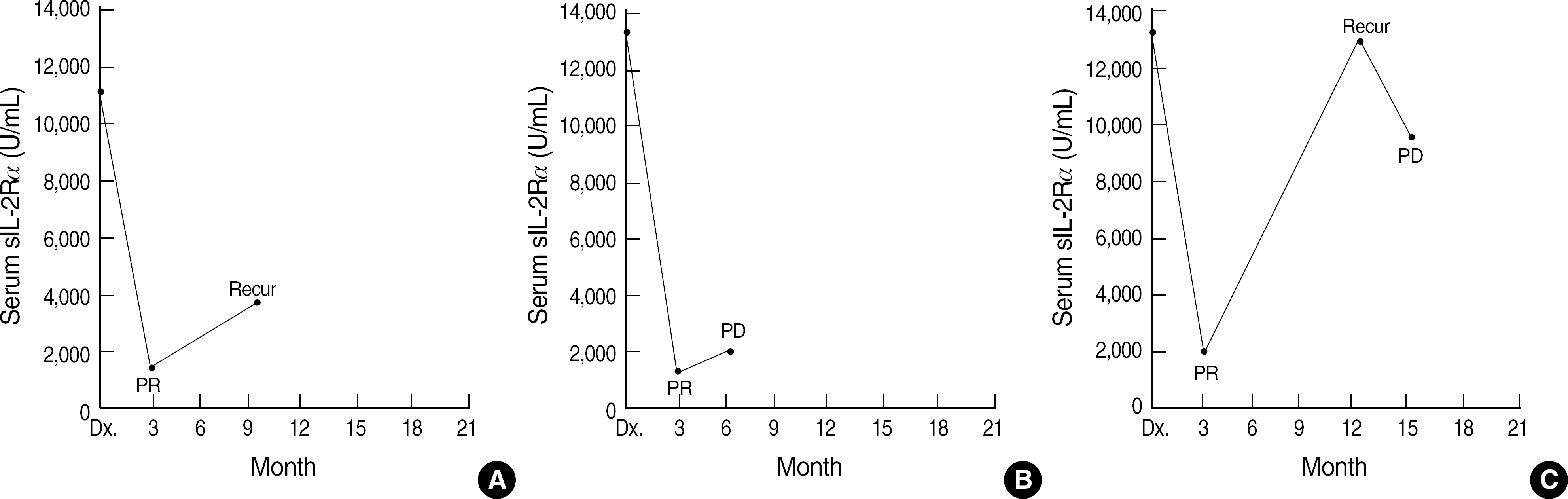 | Fig. 3.Serial analysis of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor alpha (sIL-2Rα) levels in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients showing recurrence or progressive disease (PD) after partial remission (PR); sIL-2Rα levels in relation to the timing of chemotherapy, and with respect to radiographic evaluations. (A) A 48-yr-old woman with follicular lymphoma in the axillary lymph nodes treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP). (B) A 64-yr-old man with angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma in the neck treated with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP). (C) A 53-year-old man with angioimmunoblastic lymphoma in the cervical lymph nodes treated with CHOP. |
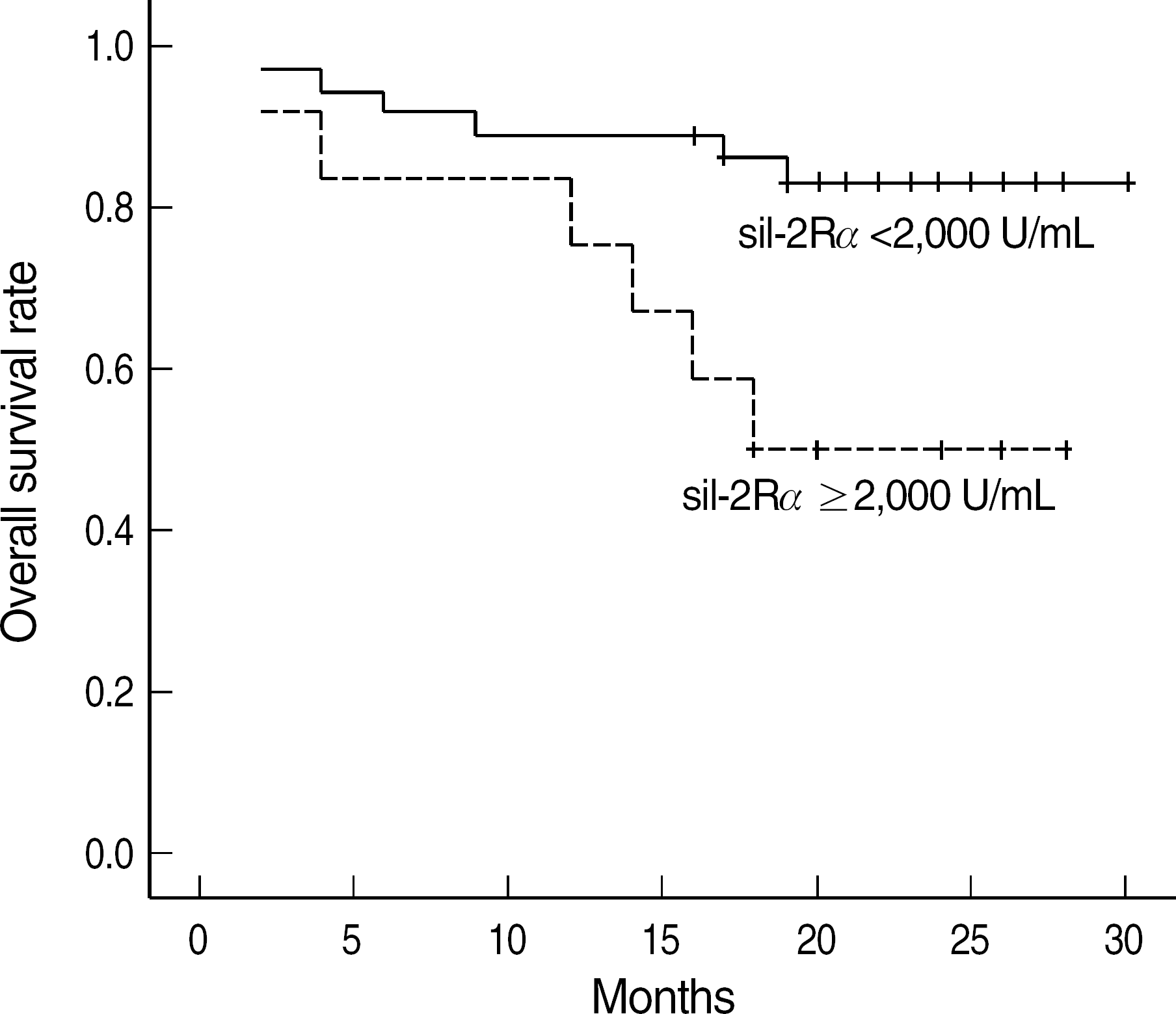 | Fig. 4.Overall survival curves for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients in relation to soluble interleukin-2 receptor alpha (sIL-2Rα) level; overall survival curves according to low (<2,000 U/mL) versus high (≥2,000 U/mL) level of sIL-2Rα (Log-rank test, P=0.041). |
Table 1.
Serum sIL-2Rα levels according to the characteristics of NHL patients
| Clinical factors | N of cases | sIL-2Rα (U/mL) | P value∗ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Range | |||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 29 | 1,940 | 283-15,033 | NS |
| Female | 19 | 2,433 | 495-11,334 | |
| Age | ||||
| <60 | 30 | 1,611 | 283-13,367 | NS |
| ≥60 | 18 | 3,840 | 594-15,033 | |
| Stage | ||||
| I+II | 25 | 1,197 | 283-11,849 | 0.001 |
| III+IV | 23 | 4,559 | 546-16,033 | |
| LD (U/L) | ||||
| <472 | 19 | 1,197 | 476-8,369 | 0.004 |
| ≥472 | 29 | 3,826 | 283-15,033 | |
| Extranodal involvement | ||||
| Absent | 15 | 1,394 | 283-15,033 | NS |
| Present | 32 | 2,358 | 476-13,367 | |
| B symptom | ||||
| Absent | 26 | 1,646 | 283-8,369 | 0.001 |
| Present | 17 | 4,099 | 546-15,033 | |
| Bone marrow involvement | ||||
| Absent | 34 | 1,735 | 283-11,849 | 0.004 |
| Present | 14 | 5,833 | 569-15,033 | |
| Treatment response (CR) | ||||
| Yes | 21 | 688 | 283-4,812 | 0.001 |
| No | 25 | 4,386 | 739-15,033 | |
Table 2.
Univariate analysis on overall survival in NHL patients
| Clinical factors | N of cases | Overall survival, months (rate, %) | P value∗ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Male | 29 | 24.1 (72) | NS |
| Female | 19 | 28.7 (89) | |
| Age | |||
| <60 | 30 | 24.0 (73) | NS |
| ≥60 | 18 | 27.4 (88) | |
| Stage | |||
| I+II | 25 | 27.5 (88) | NS |
| III+IV | 23 | 23.7 (69) | |
| LD (U/L) | |||
| <472 | 19 | 28.2 (89) | NS |
| ≥472 | 29 | 24.3 (72) | |
| Extranodal involvement | |||
| Absent | 15 | 29.0 (93) | NS |
| Present | 32 | 24.0 (71) | |
| B symptom | |||
| Absent | 26 | 28.7 (92) | 0.01 |
| Present | 17 | 21.8 (58) | |
| Bone marrow involvement | |||
| Absent | 34 | 21.8 (85) | NS |
| Present | 14 | 21.0 (64) | |
| sIL-2Rα (U/mL) | |||
| <2,000 | 22 | 27.9 (90) | 0.041 |
| ≥2,000 | 26 | 23.0 (69) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download