Abstract
Background:
Methods:
Results:
Conclusions:
REFERENCES
Table 1.
| Chief complaints | N | Test items | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBC with diff | BUN/Cr | Na/K | LFT∗ | UA/Sedi | Glucose | CRP | ESR | PT/aPTT | Ca/P | Uric acid | GGT | D-bil | ||
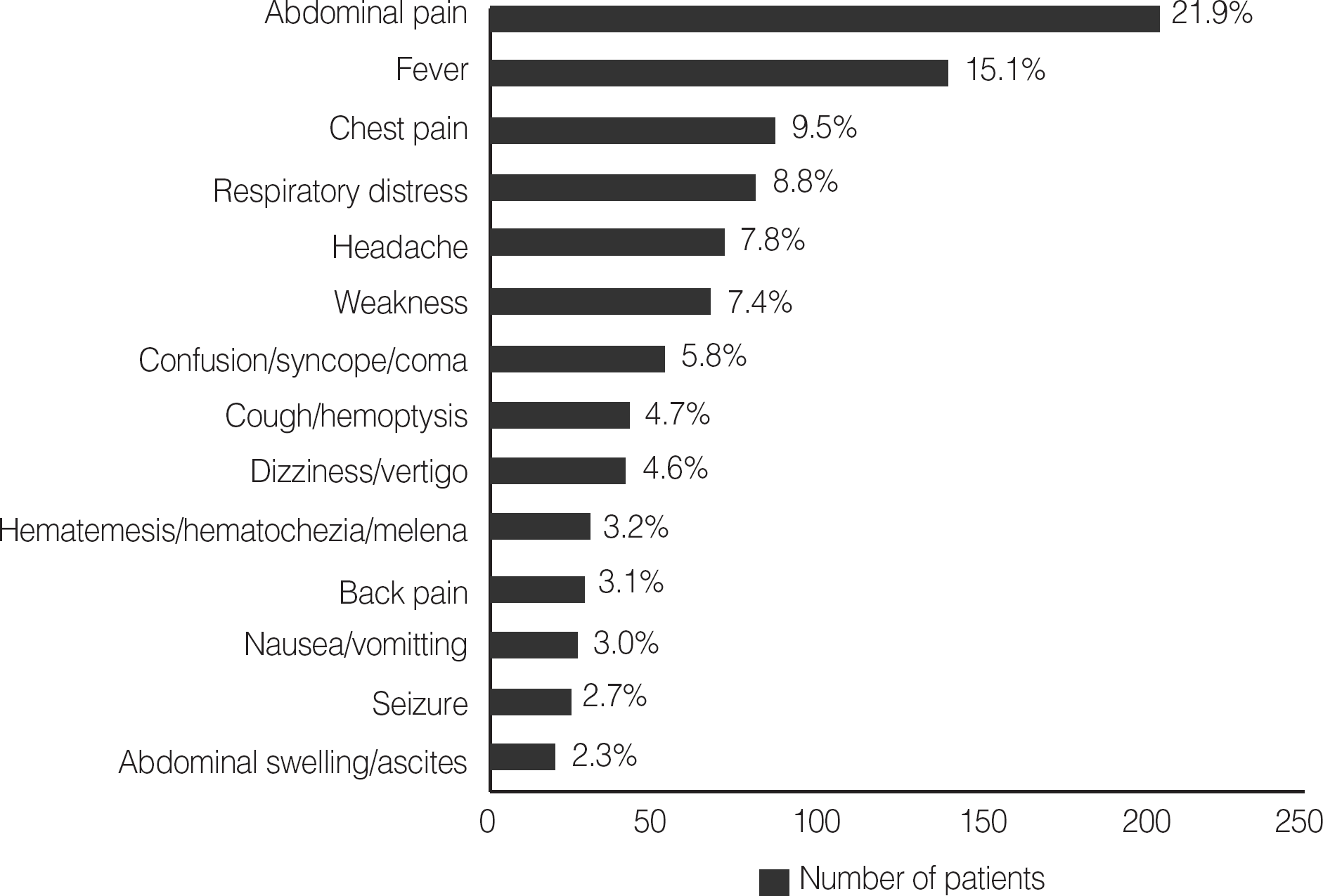
| Abdominal pain | 204 | 96.6 | 96.1 | 96.1 | 95.6 | 95.6 | 88.2 | 87.7 | 80.4 | 94.6 | 77.5 | 73.0 | 80.4 | 85.8 |
| Fever | 141 | 94.3 | 94.3 | 92.9 | 93.6 | 90.8 | 75.9 | 91.5 | 83.0 | 58.2 | 86.5 | 53.2 | 44.0 | 44.0 |
| Chest pain | 89 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 92.1 | 100.0 | 32.6 | 100.0 | 86.5 | 85.4 | 75.3 | 75.3 |
| Respiratory distress | 82 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 97.6 | 91.5 | 85.4 | 97.6 | 93.9 | 91.5 | 80.5 | 79.3 |
| Headache | 73 | 95.9 | 94.5 | 95.9 | 94.5 | 89.0 | 90.4 | 74.0 | 75.3 | 90.4 | 32.9 | 30.1 | 30.1 | 30.1 |
| Weakness | 69 | 97.1 | 98.6 | 97.1 | 98.6 | 97.1 | 97.1 | 92.8 | 85.5 | 95.7 | 58.0 | 58.0 | 68.1 | 66.7 |
| Confusion/syncope/coma | 54 | 98.1 | 98.1 | 98.1 | 98.1 | 98.1 | 98.1 | 79.6 | 75.9 | 98.1 | 68.5 | 68.5 | 29.6 | 31.5 |
| Cough/hemoptysis | 44 | 93.2 | 93.2 | 93.2 | 93.2 | 90.9 | 81.8 | 90.9 | 90.9 | 79.5 | 93.2 | 79.5 | 70.5 | 70.5 |
| Dizziness/vertigo | 43 | 100.0 | 95.3 | 95.3 | 95.3 | 95.3 | 95.3 | 86.0 | 79.1 | 97.7 | 60.5 | 58.1 | 46.5 | 46.5 |
| Hematemesis/hematochezia/melena | 30 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 96.7 | 90.0 | 56.7 | 100.0 | 93.3 | 83.3 | 83.3 | 83.3 |
| Back pain | 29 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 79.3 | 79.3 | 100.0 | 31.0 | 31.0 | 24.1 | 24.1 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 28 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 100.0 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 89.3 | 82.1 | 75.0 | 92.9 | 89.3 | 85.7 | 75.0 | 71.4 |
| Seizure | 25 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 | 32.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 |
| Abdominal swelling/ascites | 21 | 100.0 | 90.5 | 95.2 | 95.2 | 81.0 | 81.0 | 85.7 | 66.7 | 81.0 | 71.4 | 71.4 | 76.2 | 76.2 |
Abbreviations: N, number of patients; CBC with diff, complete blood cell count with differential count; BUN/Cr, blood urea nitrogen/creatinine; LFT, liver function test; UA/Sedi, urinalysis/sediment; CRP, C-reactive protein; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; PT/aPTT, prothrombin time/activated partial thromboplastin time; GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase; D-bil, direct bilirubin.
Table 2.
| Chief complaints | Tests ordered, other than those in table 1, at visit | Additional tests | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test items | (%) | Test items | (%) | |
| Abdominal pain | Amylase/lipase | 73.0 | Blood culture | 30.4 |
| Fever | Blood culture | 100.0 | ||
| Chest pain | CK-MB/Troponin I | 87.6 | ||
| NT pro-BNP | 64.0 | |||
| Blood culture | 73.2 | |||
| ABGA | 73.2 | |||
| Respiratory distress | NT pro-BNP | 58.5 | ||
| CK-MB/Troponin I | 54.9 | |||
| LDH | 50.0 | |||
| Headache | CK-MB | 64.4 | ||
| Weakness | CK-MB/Troponin I | 71.0 | Blood culture | 21.7 |
| Ca/P/Uric acid | 21.7 | |||
| Confusion/syncope/coma | CK-MB/Troponin I | 85.2 | ||
| ABGA | 81.5 | |||
| Amylase/lipase | 57.4 | |||
| NH3 | 53.7 | |||
| Cough/hemoptysis | ABGA | 75.0 | ||
| Blood culture | 70.5 | |||
| D-dimer | 65.9 | |||
| LDH | 61.4 | |||
| PB smear | 61.4 | |||
| Respiratory specimen study∗ | 61.4 | |||
| NT pro-BNP | 59.1 | |||
| Procalcitonin | 59.1 | |||
| Dizziness/vertigo | CK-MB/Troponin I | 58.1 | Ca/P/Uric acid | 20.9 |
| Lipid study† | 18.6 | |||
| Hematemesis/hematochezia/melena | NH3 | 73.3 | Cross Matching | 26.7 |
| Back pain | CK-MB/Troponin I | 72.4 | ||
| ABGA | 65.5 | |||
| Seizure | NH3 | 100.0 | ||
| ABGA | 92.0 | |||
| Ionized calcium | 80.0 | |||
| Abdominal swelling/ascites | Amylase/lipase | 61.9 | Ascitic fluid study‡ | 38.1 |
∗ Respiratory specimen study: wet smear, Gram stain, acid-fast bacilli (AFB) stain, AFB culture, potassium hydroxide mount, and culture for fungal growth;
Table 3.
| CBC with diff |
| LFT (TP/alb/T-bil/AST/ALT/ALP) |
| UA/sedi |
| Coagulation test (PT/aPTT) |
| Na/K |
| BUN/Cr |
| CRP |
| Glucose (blood/serum) |
| Ca/P |
Abbreviations: CBC with diff, complete blood cell count with differential count; LFT, liver function test; TP, total protein; alb, albumin; T-bil, total bilirubin; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; UA/sedi, urinalysis/sediment; PT/aPTT, prothrombin time/activated partial thromboplastin time; BUN/Cr, blood urea nitrogen/creatinine; CRP, C-reactive protein.
Table 4.
| Chief complaints | Essential test panel | Extended test panel |
|---|---|---|
| Abdominal pain | Basic tests∗ | β-HCG (women of child-bearing age) |
| Direct bilirubin | ||
| Amylase/lipase | ||
| Fever | Basic tests | HIV antibody |
| Blood smear | Body fluid study (stain, culture, and chemistry) | |
| Blood/urine culture | ||
| Chest pain | Basic tests | Lipid study† |
| CK-MB/Troponin I (or Troponin T) | ||
| Myoglobin | ||
| NT pro-BNP (or BNP) | ||
| D-dimer | ||
| Respiratory distress | Basic tests | Thyroid function test |
| ABGA | ||
| D-dimer | ||
| Headache | Basic tests | Lipid study |
| CSF study‡ | ||
| Weakness | Basic tests | Lipid study |
| Uric acid | CK-MB/Troponin I (or Troponin T) | |
| Confusion/syncope/coma | Basic tests | Direct bilirubin |
| ABGA | GGT | |
| CSF study | ||
| NH3 | ||
| Osmolality | ||
| Cough/hemoptysis | Basic tests | |
| Sputum culture/stain/cytology | ||
| D-dimer | ||
| Dizziness/vertigo | Basic tests | CK-MB/Troponin I (or Troponin T) Aldosterone |
| Hematemesis/hematochezia/melena | Basic tests | |
| Fecal occult blood | ||
| Fecal leukocyte count | ||
| Back pain | Basic tests | |
| Nausea/vomiting | Basic tests | |
| ABGA | ||
| Amylase/lipase | ||
| Direct bilirubin | ||
| NH3 | ||
| Uric acid | ||
| Seizure | Basic tests | |
| Toxicology (alcohol, drug screen) CSF study | ||
| Abdominal swelling/ascites | Basic tests | |
| Ascitic fluid study§ | ||
| Direct bilirubin | ||
| GGT | ||
| Amylase/lipase | ||
| Uric acid |
‡ CSF study: culture, Gram stain, and cell count; § Ascitic fluid study: Refer to Table 2. Abbreviations: β-HCG, β-human chorionic gonadotropin; CK-MB, creatine kinase-MB; NT pro-BNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; ABGA, arterial blood gas analysis; GGT, γ-glutamyl transferase.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download