Abstract
Background:
We utilized results from the ARTEMIS DISK Global Antifungal Surveillance Program to evaluate the species distribution and fluconazole and voriconazole susceptibilities of yeast isolates from clinical specimens in South Korea from 2001 to 2007.
Methods:
Data were collected on 5,665 yeast isolates from all body sites at three locations. All investigators tested clinical yeast isolates using the CLSI M44-A disk diffusion method. Test plates were automatically read and results were recorded using the BIOMIC image analysis plate reader system (Giles Scientific, USA). Species, drug, zone diameter, susceptibility category, and quality control results were collected quarterly via e-mail for analysis.
Results:
Candida albicans was the most common isolate, but a progressive increase in non-C. albicans Candida and noncandidal yeast species has been observed in recent years. The overall percentages of isolates in each category (susceptible, susceptible dose dependent, and resistant) were 98.8%, 0.5%, and 0.7% and 99.2%, 0.2%, and 0.6% for fluconazole and voriconazole, respectively. Candida of 3 species exhibited decreased susceptibility to fluconazole (<90% S) in the order of that seen with the resistant (R) species: C. krusei, C. guilliermondii, and C. glabrata. Emerging resistance to fluconazole or voriconazole was documented among isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans, Trichosporon spp., and Rhodotorula spp.
Conclusions:
The species distribution and antifungal susceptibilities of yeasts may differ according to specimen type, testing method, hospital, and geographic region. Therefore, further large-scaled, long-term surveillance studies are needed to isolate yeasts and to confirm the species distribution and antifungal susceptibilities of yeast isolates from clinical specimens in Korea.
REFERENCES
1.Chae MJ., Shin JH., Cho D., Kee SJ., Kim SH., Shin MG, et al. Antifungal susceptibilities and distribution of Candida species recovered from blood cultures over an 8-yr period. Korean J Lab Med. 2003. 23:329–35. (채명종, 신종희, 조덕, 기승정, 김수현, 신명근 등. 최근 8
년간 혈액에서 분리된 Candida 균종과 항진균제 감수성. 대한진단
검사의학회지 2003;23:329-35.).
2.Shin JH., Kim HR., Lee JN. Distribution and antifungal susceptibility of Candida species isolated from clinical specimens during the past six years. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 7:164–70. (신정환, 김혜란, 이정녀. 최근 6년간 임상검체에서 분리된 칸디다의 균종 분포와항진균제 감수성. 대한임상미생물학회지 2004;7:164-70.).
3.Lee MK., Kim HR., Kang JO., Kim MN., Kim EC., Kim JS, et al. Susceptibility and trailing growth of Candida albicans to fluconazole: results of a Korean multicentre study. Mycoses. 2007. 50:148–9.
4.Lee JS., Shin JH., Lee K., Kim MN., Shin BM., Uh Y, et al. Species distribution and susceptibility to azole antifungals of Candida bloodstream isolates from eight university hospitals in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2007. 48:779–86.
5.Kim SH., Shin JH., Kim EC., Lee K., Kim MN., Lee WG, et al. The relationship between antifungal usage and antifungal susceptibility in clinical isolates of Candida: a multicenter Korean study. Med Mycol. 2009. 47:296–304.
6.Yoo JI., Choi CW., Lee KM., Kim YK., Kim TU., Kim EC, et al. National surveillance of antifungal susceptibility of Candida species in South Korean hospitals. Med Mycol. 2009. 47:554–8.
7.Pfaller MA., Diekema DJ., Rinaldi MG., Barnes R., Hu B., Veselov AV, et al. Results from the ARTEMIS DISK Global Antifungal Surveillance Study: a 6.5-yr analysis of susceptibilities of Candida and other yeast species to fluconazole and voriconazole by standardized disk diffusion testing. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:5848–59.
8.Pfaller MA., Diekema DJ., Gibbs DL., Newell VA., Meis JF., Gould IM, et al. Results from the ARTEMIS DISK Global Antifungal Surveillance Study, 1997 to 2005: an 8.5-yr analysis of susceptibilities of Candida species and other yeast species to fluconazole and voriconazole determined by CLSI standardized disk diffusion testing. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 45:1735–45.
9.Pfaller MA., Diekema DJ., Gibbs DL., Newell VA., Bijie H., Dzierzanowska D, et al. Results from the ARTEMIS DISK Global Antifungal Surveillance Study, 1997 to 2007: 10.5-yr analysis of susceptibilities of noncandidal yeast species to fluconazole and voriconazole determined by CLSI standardized disk diffusion testing. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. 47:117–23.
10.Isenberg HD. Clinical microbiology procedures handbook. 2nd ed.Washington, DC: ASM Press;2003. :3.11.2.
11.Sheehan DJ; National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Method for antifungal disk diffusion susceptibility testing of yeasts: approved guideline. M44-A. Wayne, PA: NCCLS;2004.
12.Hazen KC., Baron EJ., Colombo AL., Girmenia C., Sanchez-Sousa A., del Palacio A, et al. Comparison of the susceptibilities of Candida spp. to fluconazole and voriconazole in a 4-yr global evaluation using disk diffusion. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:5623–32.
13.Kang BK., Lee HJ., Suh JT. The Trends of the species and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria and fungi isolated from blood cultures (1986-1996). Korean J Clin Pathol. 1998. 18:57–64. (강병기, 이희주, 서진태. 혈액에서 배양된 세균과 진균의 균종 및 항균제 감수성의 추이 (1986-1996). 대한임상병리학회지 1998;18:57-64.).
14.Uh Y., Jang IH., Yoon KJ., Kim HY. Isolation trend and antifungal susceptibility of Candida species isolated from blood cultures. Korean J Infect Dis. 2001. 33:186–93. (어영, 장인호, 윤갑준, 김효열. 최근혈액에서 분리되는 칸디다 균종의 분리추이와 항진균제 감수성. 감염 2001;33:186-93.).
15.Kim YA., Cho DH., Lee K., Chong Y., Kwon HK. Yeasts isolated from oral cavity of the healthy adults. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2000. 20:30–5. (김영아, 조동희, 이경원, 정윤섭, 권호근. 건강 성인의 구강에서 분리되는 효모형 진균. 대한임상병리학회지 2000;20:30-5.).
16.Lee SH., Kim SW., Bang YJ. A study on the distribution of oral candidal isolates in diabetics. Korean J Med Mycol. 2002. 7:139–48. (이시헌, 김상원, 방용준. 당뇨환자에서 구강내 칸디다균의 분포에 대한조사. 대한의진균학회지 2002;7:139-48.).
17.Choi JH., Suh MK., Ha GY. Isolation and identification of Candida species in superficial cutaneous candidiasis. Korean J Dermatol. 2002. 40:1188–94. (최진혁, 서무규, 하경임. 표재성 피부칸디다증에서칸디다 균종의 분리 및 동정. 대한피부과학회지 2002;40:1188-94.).
18.Pfaller MA., Hazen KC., Messer SA., Boyken L., Tendolkar S., Hollis RJ, et al. Comparison of results of fluconazole disk diffusion testing for Candida species with results from a central reference laboratory in the ARTEMIS global antifungal surveillance program. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:3607–12.
19.Pfaller MA., Boyken L., Hollis RJ., Kroeger J., Messer SA., Tendolkar S, et al. Comparison of results of fluconazole and voriconazole disk diffusion testing for Candida spp. with results from a central reference laboratory in the ARTEMIS DISK Global Antifungal Surveillance Program. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009. 65:27–34.
Fig. 1.
Fluconazole (A) and voriconazole (B) zone diameter (mm) distribution of all yeast isolates. Abbreviations: S, susceptible; SDD, susceptible dose dependent; R, resistant.
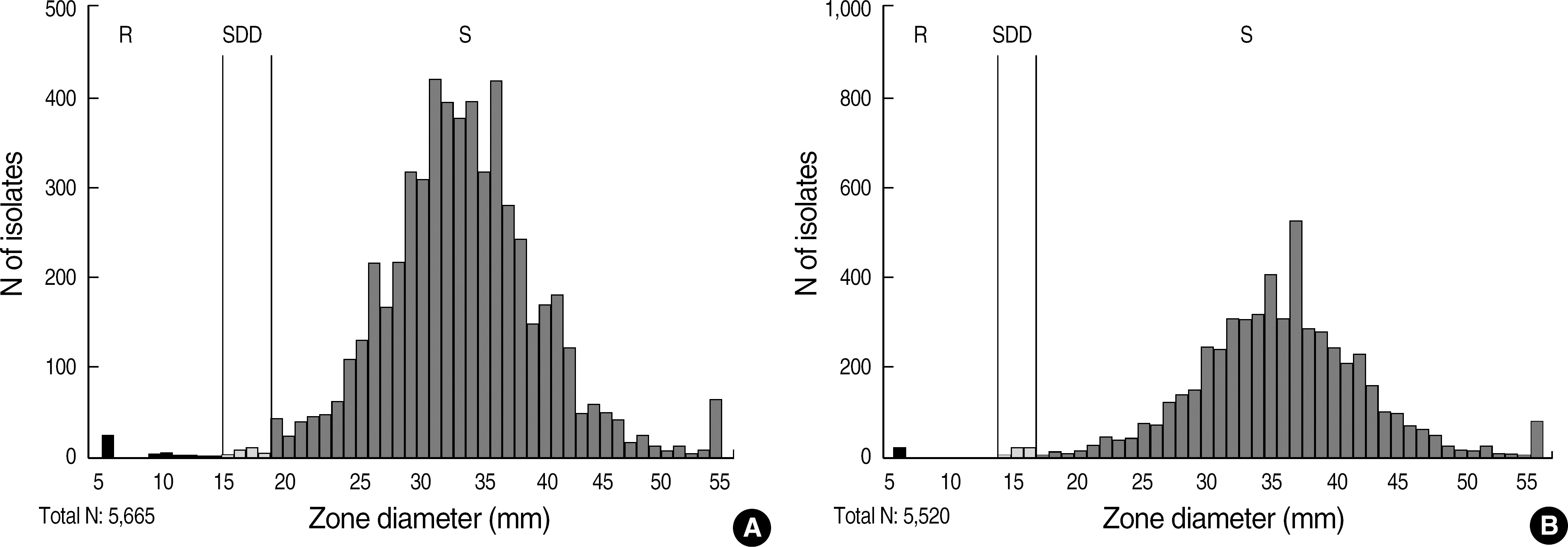
Table 1.
Species distribution of Candida and other yeast isolates by year in South Korea
Table 2.
In vitro susceptibilities of yeast isolates to fluconazole and voriconazole, 2001 to 2007
Table 3.
Trends in resistance to fluconazole among yeast isolates as determined by the CLSI disk diffusion method over a 7-yr period
Table 4.
Trends in resistance to voriconazole among yeast isolates as determined by the CLSI disk diffusion method over a 7-yr period
Table 5.
Susceptibilities of yeast isolates to fluconazole and voriconazole by specimen type




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download