Abstract
We report the case of a 3-yr-old boy with Down-Turner mosaicism and review the previous reports of Down-Turner syndrome with documented karyotyping and clinical features. The patient showed clinical features of Down syndrome without significant stigma of Turner syndrome. Cytogenetic analysis of peripheral blood preparations by using G-banding revealed mosaicism with 2 cell lines (45,X[29]/47,XY,+21[4]). FISH analysis revealed that 87.5% of the cells had monosomy X karyotype and 12.5% of the cells had XY karyotype; trisomy 21 was only detected in the Y-positive cells. We suggest that additional cells should be analyzed and molecular genetic studies should be conducted to rule out double aneuploidy when karyotypes with sex chromosome aneuploidies and mosaicism are encountered, as in our case of Down syndrome mosaic with sex chromosome aneuploidy.
REFERENCES
1.Kovaleva NV., Mutton DE. Epidemiology of double aneuploidies involving chromosome 21 and the sex chromosomes. Am J Med Genet A. 2005. 134A:24–32.

2.Lorda-Sanchez I., Petersen MB., Binkert F., Maechler M., Schmid W., Adelsberger PA, et al. A 48,XXY,+21 Down syndrome patient with additional paternal X and maternal 21. Hum Genet. 1991. 87:54–6.

3.Karaman A., Kabalar E. Double aneuploidy in a Turkish child: Down-Klinefelter syndrome. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2008. 48:45–7.

4.Ford CE., Jones KW., Miller OJ., Mittwoch U., Penrose LS., Ridler M, et al. The chromosomes in a patient showing both mongolism and the Klinefelter syndrome. Lancet. 1959. 1:709–10.

5.Hou JW., Wang TR. Double aneuploidy with Down's-Klinefelter's syndrome. J Formos Med Assoc. 1996. 95:350–2.
6.Akbas E., Soylemez F., Savasoglu K., Halliogluand O., Balci S. A male case with double aneuploidy (48,XXY,+21). Genet Couns. 2008. 19:59–63.
7.Jaruratanasirikul S., Jinorose U. An infant with Down-Turner double aneuploidy: a case report and literature review. J Med Assoc Thai. 1995. 78:108–12.
8.Van Buggenhout GJ., Hamel BC., Trommelen JC., Mieloo H., Smeets DF. Down-Turner syndrome: case report and review. J Med Genet. 1994. 31:807–10.

9.Zaki MS., Kamel AA., El-Ruby M. Double aneuploidy in three Egyptian patients: Down-Turner and Down-Klinefelter syndromes. Genet Couns. 2005. 16:393–402.
10.Jeanty C., Turner C. Prenatal diagnosis of double aneuploidy, 48,XXY,+21, and review of the literature. J Ultrasound Med. 2009. 28:673–81.

11.Sparagana M., Wong PW., Dorsch TR., Casten C., Rauer M., Szego K. 45,X/46,XY/47,XY,+21 mosaicism in a hypogonadal phenotypic male. J Med Genet. 1980. 17:319–21.
12.Jeong HJ., Lee ES., Choi KH., Park YH. A case of Down-Turner syndrome. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol. 2005. 10:120–4. (정희정, 이은실, 최광해, 박용훈. 다운-터너 증후군 1례. 대한소아내분비학회지 2005;10:120-4.).
13.Musarella MA., Verma RS. An infant with Turner-Down aneuploidy and massive capillary hemangioma of the orbit: a case report with review. Ann Genet. 2001. 44:67–70.

14.Ruangdaraganon N., Kotchabhakdi N., Mekanandha V. Double aneuploidy: 46,X,+21 a combination of Down syndrome and Turner syndrome. J Med Assoc Thai. 1993. 76(S2):215–7.
15.Osborne RA., Hennigar GR., Barnett CD. Mosaic double aneuploidy of X and G chromosomes. Am J Ment Defic. 1975. 79:644–7.
16.Harada N., Abe K., Nishimura T., Sasaki K., Ishikawa M., Fujimoto M, et al. Origin and mechanism of formation of 45,X/47,XX,+21 mosaicism in a fetus. Am J Med Genet. 1998. 75:432–7.

17.Townes PL., White MR., Stiffler SJ., Goh K. Double aneuploidy. Turner-Down syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1975. 129:1062–5.
18.Knudtzon J., Aarskog D. 45,X/46,XY mosaicism. A clinical review and report of ten cases. Eur J Pediatr. 1987. 146:266–71.
19.Costa T., Lambert M., Teshima I., Ray PN., Richer CL., Dallaire L. Monozygotic twins with 45,X/46,XY mosaicism discordant for phenotypic sex. Am J Med Genet. 1998. 75:40–4.

20.Arbuzova S., Cuckle H., Mueller R., Sehmi I. Familial Down syndrome: evidence supporting cytoplasmic inheritance. Clin Genet. 2001. 60:456–62.

21.Mutton D., Alberman E., Hook EB. Cytogenetic and epidemiological findings in Down syndrome, England and Wales 1989 to 1993. National Down Syndrome Cytogenetic Register and the Association of Clinical Cytogeneticists. J Med Genet. 1996. 33:387–94.

22.Alfi OS., Chang R., Azen SP. Evidence for genetic control of nondisjunction in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1980. 32:477–83.
Fig. 1.
The G-banded karyotype of the patient showing mosaic double aneuploidy with a loss of Y chromosome (A) and addition of chromosome 21 (B) (arrows); 45,X[29]/47,XY,+21[4].
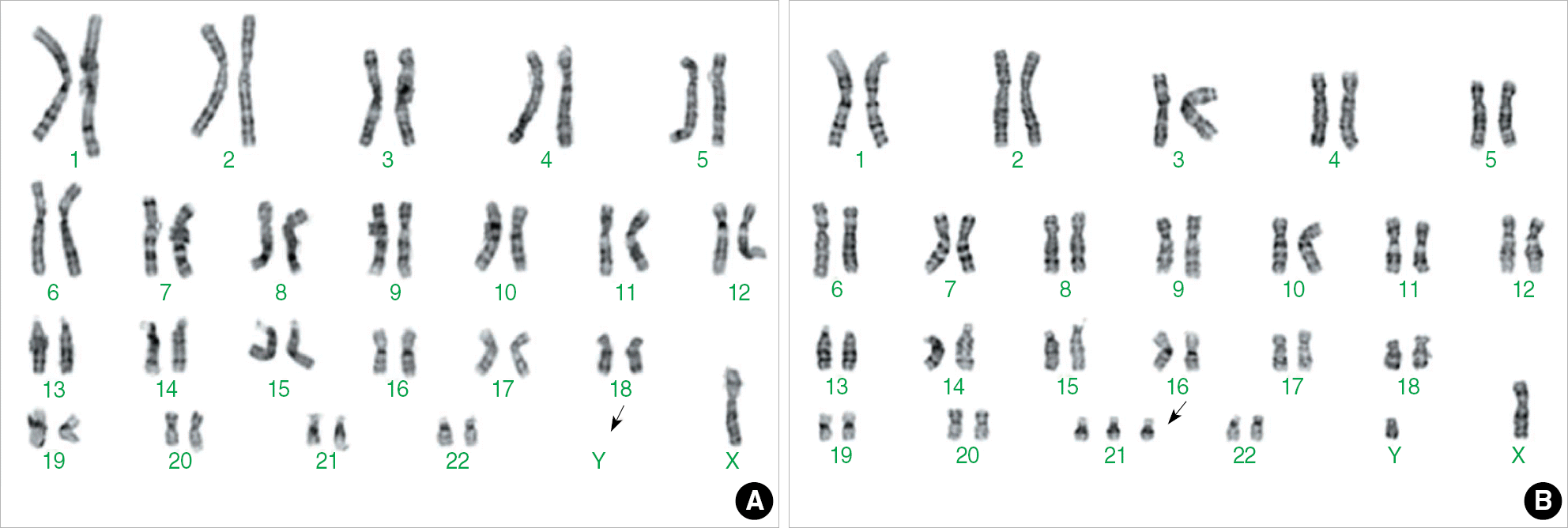
Fig. 2.
FISH analysis with centromeric X (DXZ1; spectrum green) and centromeric Y (DYZ3; spectrum red) probes showing one 46,XY metaphase and five X interphases with one green signal indicating monosomy X.
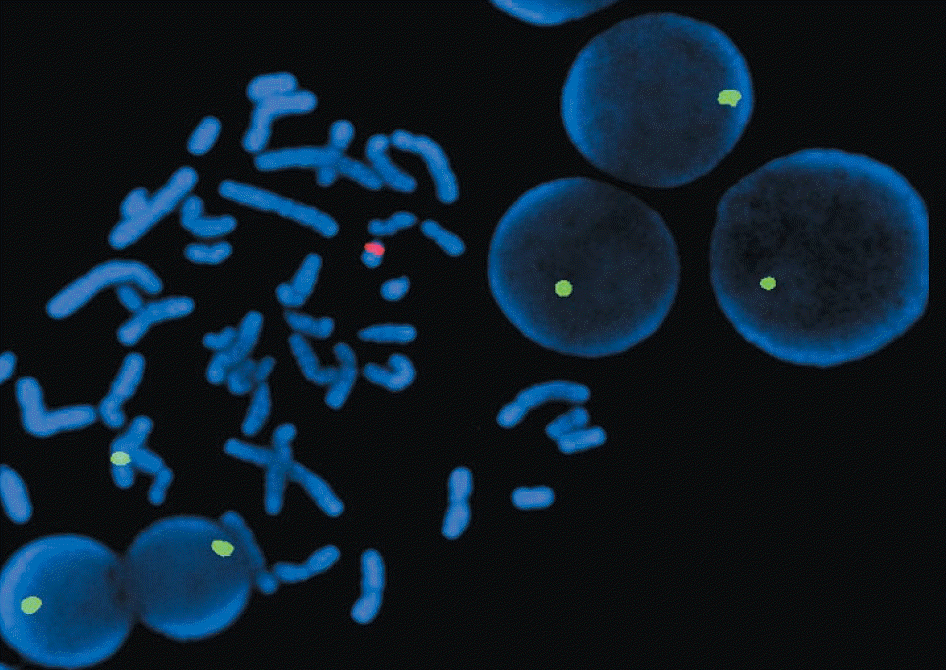
Fig. 3.
FISH analysis with CEP Y probe specific for Y chromosome (DYZ1; spectrum green) and DNA LSI probe specific for chromosome 21 (D21S259, D21S341, and D21S342; spectrum red) revealed that only those cells with a Y chromosome (green signal) show trisomy 21 (triplicate red signals).
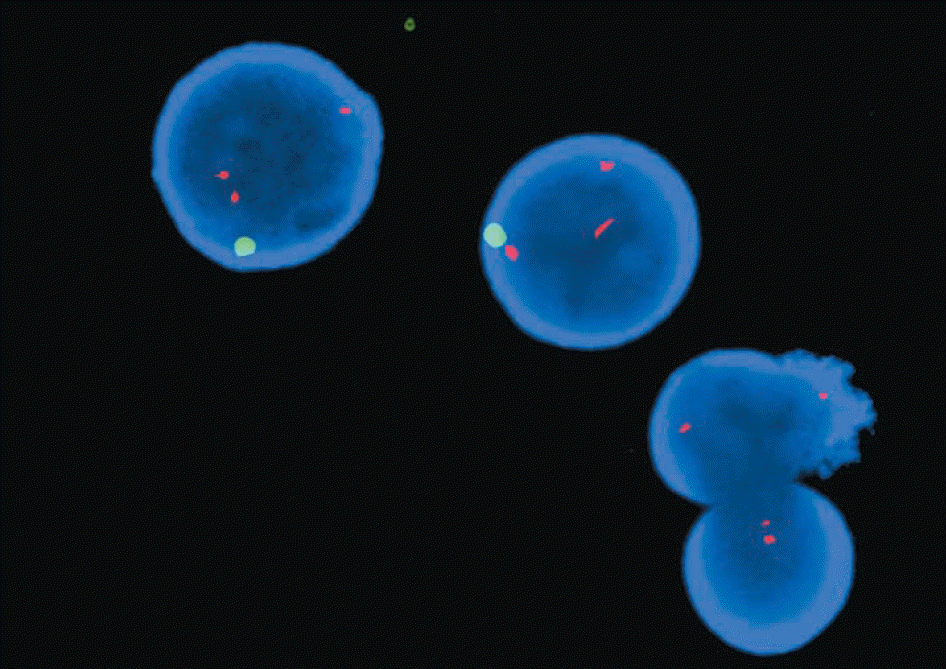
Table 1.
Previously reported cases of Down-Turner syndrome: clinical features and cytogenetic findings, including those of the present case
| Case No. | Year | Author | Karyotype | Genitalia | Phenotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1951 | Villaverde | Not done | Down-Turner | [7] | |
| 2 | 1951 | Villaverde | Not done | Down-Turner | [7] | |
| 3 | 1960 | Hanhardt et al. | Not done | Down | [7] | |
| 4 | 1962 | Medenis et al. | 46,X,+G/47,XX,+G, | F | Down∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 5 | 1964 | Van Wijck et al. | 46,X,+G/47,XX,+G | F | Down | [7, 8, 13] |
| 6 | 1964 | Zergollern et al. | 46,X,+G/47,XX,+G/48,XXX,+G | F | Down | [7, 13] |
| 7 | 1964 | Root et al. | 46,X,+G/47,XX,+G | F | Down∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 8 | 1965 | Candela et al. | 46,XX/46,X,+G | F | Down | [7] |
| 9 | 1966 | Candela et al. | 46,X,+G/47,XX,+G | F | Down∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 10 | 1966 | Feiertag-Koppen et al. | 45,X/46,X,+G/46,XX/47,XX,+G | F | Down | [8] |
| 11 | 1966 | Edgren et al. | 45,X/46,XY/47,XY,+21 | M | Down | [8] |
| 12 | 1967 | van Gelderen et al. | 46,X,+G/46,XX/47,XX,+G | F | Down-Turner | [8] |
| 13 | 1968 | Pfeiffer et al. | 46,X,+21/47,XX,+21 | F | Down | [7, 8] |
| 14 | 1970 | Taylor et al. | 45,X/47,XX,+G | F | Down-Turner | [8] |
| 15 | 1971 | Luthardt et al. | 47,X,Xq-,+21 | F | Down | [8] |
| 16 | 1971 | Grosse et al. | 46,XX/45,X/47,XX,+G | F | Down | [7, 8, 13] |
| 17 | 1972 | Cohen et al. | 45,X/47,XX,+21 | F | Down | [13] |
| 18 | 1971 | Mikel'saar et al. | 47,XX,+21/47,XXp-q-,+21 | F | Down-Turner | [7, 13] |
| 19 | 1972 | Prieur et al. | 45,X/47,XY,+21 | M | Down | [8] |
| 20 | 1973 | barakat et al. | 45,X/47,XX,+G | F | Down | [8] |
| 21 | 1974 | Hustinx et al. | 45,X/47,XX,+21 | F | Down∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 22 | 1974 | Hustinx et al. | 45,X/47,XY,+21 | M | Down-Turner | [8] |
| 23 | 1974 | Santos et al. | 46,X,+21/47,XY,+21 | A | Down-Turner | [8] |
| 24 | 1975 | Osborne et al. | 45,X/46,X,+G/46,XX/47,XX,+G | F | Down-Turner | [15] |
| 25 | 1975 | Villaverde et al. | 45,X/46,X,+G/47,XX,+G | A | Down-Turner∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 26 | 1975 | Townes et al. | 45X/46,X,+21 | F | Down-Turner | [7, 8, 13] |
| 27 | 1975 | Singh et al. | 45,X/46,X,+G/46,XX/47,XX,+G | F | Down∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 28 | 1975 | Singh et al. | 45,X/46,X,+G/46,XX/47,XX,+G | F | Down∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 29 | 1975 | Singh et al. | 46,X,+21/46,XX/47,XX,+21 | F | Down∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 30 | 1976 | Yeung et al. | 46,X,+21/47,XY,+21 | A | Down-Turner | [8] |
| 31 | 1977 | Martsolf et al. | 47,X,del(X)(p11),+21 | F | Down-Turner | [7, 13] |
| 32 | 1978 | Chen et al. | 45,X/48,XXX,t(2;21) | F | Down | [13] |
| 33 | 1980 | Sparagana et al. | 45,X/46,XY/47,XY,+21 | M | Down | [11] |
| 34 | 1981 | Macfual et al. | 46,X,+21/47,X,i(X),+21 | F | Down∗ | [7, 8, 13] |
| 35 | 1981 | Macfual et al. | 46,X,+21/47,XX,+21 | F | Down-Turner | [7, 8, 13] |
| 36 | 1981 | Gatrad et al. | 46,X,+21/47,XX,+21 | F | Down-Turner | [7, 8, 13] |
| 37 | 1989 | Ikonen et al. | 46,X,+21 | F | Down | [13] |
| 38 | 1991 | Jansen et al. | 45,X/47,XX,+21 | F | Down-Turner∗ | [7, 13] |
| 39 | 1994 | Van buggenhout et al. | 45,X/46,X,+21/47,XY,+21 | M | Down-Turner | [8] |
| 40 | 1994 | Digilio et al. | 45,X/46,XX,i(21q) | F | Down-Turner | [13] |
| 41 | 1995 | Jarurantanasirikul et al. | 46,X,+21 | F | Down | [7] |
| 42 | 1993 | Ruangdaraganon et al. | 46,X,+21 | F | Down | [13] |
| 43 | 1998 | Harada et al. | 45,X/47,XX,+21 | F | Down-Turner | [16] |
| 44 | 2001 | Musarella et al. | 45,X/47,XX,+21/46,XX/47,XXX | F | Down | [13] |
| 45 | 2005 | Zaki et al. | 45,X/47,XY,+21 | M | Down-Turner | [9] |
| 46 | 2005 | Zaki et al. | 46,X,+21/47,XX,+21 | F | Down-Turner | [9] |
| 47 | 2009 | Lee et al. | 45,X/47,XY,+21 | M | Down | Present case |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download