Abstract
Background:
To establish effective preventive measures for hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection, a nationwide epidemiologic study on seroprevalence of anti-HAV and the disease prevalence is needed. The aim of this study was to analyze the recent sero-epidemiological changes of hepatitis A markers in Korea.
Methods:
The results of 11,068 anti-HAV total and 32,360 anti-HAV IgM tests by electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) that had been requested in recent four years (2005-2008) to a reference medical laboratory from 1,699 institutions nationwide were retrospectively analyzed according to the distribution of year, sex, and age groups.
Results:
The overall positive rate of anti-HAV total was 62.8%. The overall positive rate of anti-HAV IgM was 11.0%, showing a significantly increasing trend by year: 7.7%, 10.9%, 8.9%, and 14.3% in 2005, 2006, 2007, and 2008, respectively (P<0.0001). The positive rate of anti-HAV IgM was higher in male than in female subjects (11.8% vs 10.0%, P<0.0001), and 81.8% (2,916/3,566) of the anti-HAV IgM positive results were observed in the age groups of 21-40 yr. The annual positive rates of anti-HAV total and anti-HAV IgM showed significantly decreasing and increasing trends, respectively, in the age groups of ≥21 yr.
Conclusion:
In accordance with a decreasing sero-positivity of anti-HAV total, the prevalence of acute hepatitis A virus infection has been considerably increased during the recent four years in the age groups of ≥21 yr. The results of this study could be used effectively as a basic data for establishing effective preventive measures for hepatitis A including vaccination in these susceptible age groups.
REFERENCES
1.Brundage SC., Fitzpatrick AN. Hepatitis A. Am Fam Physician. 2006. 73:2162–8.
2.Hong WS., Kim CY. Seroepidemiology of type A and type B hepatitis in Seoul area. Korean J Med. 1982. 25:19–26. (홍원선및김정룡.서울지역에 있어서의A형 간염 및B형 간염 바이러스 감염에 관한 혈청역학적조사. 대한내과학회지 1982;25:19-26.).
3.Roh HO., Sohn YM., Park MS., Choi B., Bang KN., Ki M, et al. A seroepidemiologic study of hepatitis A virus in the healthy children and adolescent in Kyonggi-do province. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 1997. 4:232–9. (노혜옥, 손영모, 박민수, 최보율, 방금녀, 기모란 등. 경기도 지역의 건강한 소아와청소년에서A형 간염 바이러스의 항체 보유율에 대한역학조사. 소아감염 1997;4:232-9.).

4.Lee D., Cho YA., Park Y., Hwang JH., Kim JW., Kim NY, et al. Hepatitis a in Korea: epidemiological shift and call for vaccine strategy. Intervirology. 2008. 51:70–4.

5.Choi HJ., Lee SY., Ma SH., Kim JH., Hur JK., Kang JH. Age related prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis A virus performed in Korea in 2005. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2005. 12-kjlm-29-563@::186-94. (최혜진, 이수영, 마상혁, 김 현, 허재균, 강진한. 국내에서 2005년에 실시한 연령별 A형 간염 바이러스항체보유율. 소아감염 2005;12:186-94.).

6.Kim TY., Sohn JH., Ahn SB., Son BK., Lee HL., Eun CS, et al. Comparison of recent IgG anti-HAV prevalence between two hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi area. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:363–9. (김태엽,손주현, 안상봉, 손병관, 이항락, 은창수등. 서울과경기지역두병원의최
근A형간염항체양성률에대한비교조사. 대한간학회지 2007;13:363-9.).

7.Kwon YO., Choi IJ., Jung JW., Park JH. An epidemiologic study on the seropositive rate of hepatitis A virus among a selected group of children and adults in Busan. Korean J Pediatr. 2007. 50:262–7. (권영옥, 최임정, 정진화, 박지현. 부산지역 소아 및 성인의A형 간염 바이러스항체양성률에대한역학적조사. 대한소아과학회지 2007;50:262-7.).

8.Choi JO., Lee KY., Lee DJ., Han JW., Hwang SS., Lee KS. Outbreak of hepatitis A in TaeJon in 1996: clinical and epidemiologic study in children. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 1997. 4:90–6. (최진욱, 이경일, 이동준,한지환, 황성수, 이경수. 1996년대전시서북부에서발생한A형급성간염.소아감염 1997;4:90-6.).

9.Kim H., Kim JH., Kim DU., Hur JK., Lee WB., Seo BK, et al. Epidemiological changes and clinical features of hepatitis A in children, living in Kyung-gi Province, since 1988 to 1998. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 1998. 5:230–8. (김현, 김종현, 김동언, 허재균, 이원배, 서병규 등. 최근10년간(1988-1998)경기지역소아에서A형간염의역학적변화및임상에관
한연구. 소아감염 1998;5:230-8.).

10.Kang HM., Jeong SH., Kim JW., Lee D., Choi CK., Park YS, et al. Recent etiology and clinical features of acute viral hepatitis in a single center of Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:495–502. (강형민, 정숙향, 김진욱, 이동훈, 최창규, 박영수등. 단일병원에서경험한최근급성바이러스간염의원인및임상양상. 대한간학회지 2007;13:495-502.).

11.Lim DS., Cho KH., Kim HC. Seroepidemiological study on anti-HAV antibody in Cheon-Buk province in 1989. Korean J Med. 1992. 43:57–65. (임동석, 조규혜, 김학철. 1989년전북서북부지역에서의A형바이러스성간염의역학적조사. 대한내과학회지 1992;43:57-65.).
12.Sohn YM., Rho HO., Park MS., Park JH., Choi BY., Ki M, et al. The changing epidemiology of hepatitis A in children and the consideration of active immunization in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2000. 41:34–9.

13.Song YB., Lee JH., Choi MS., Koh KC., Paik SW., Yoo BC, et al. The age-specific seroprevalence of hepatitis A virus antibody in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:27–33. (송영봉, 이준혁, 최문석, 고광철, 백승운, 유병철 등. 한국인 건강검진자에서연령 특이적A형간염바이러스항체혈청양성률. 대한간학회지 2007;13:27-33.).
14.Kim DY., Ahn SH., Lee HW., Kim SU., Kim JK., Paik YH, et al. Antihepatitis A virus seroprevalence among patients with chronic viral liver disease in Korea. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 19:923–6.

15.Kim JH., Kang JH., Seo K., Kim HM., Choi JY. A survey for seroprevalence of antibody to hepatitis A and development of policy. Seoul: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2006. 1–41.
16.Kim JH. Recent epidemiological status and vaccination of Hepatitis A in Korea. J Korean Med Ass. 2008. 51:110–8. (김종현. A형간염의최근국내역학상황과백신접종. 대한의사협회지 2008;51:110-8.).

17.Kim JH., Kang JH., Lee SY., Choi HA., Kim HM., Seo K, et al. A study for seroprevalence of antibody to hepatitis A in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:S27. .(김종현, 강진한, 이수영, 최현아, 김행미, 서경 등. 국내A형간염항체양성률에대한연구. 대한간학회지 2007;13:S27.).
18.Tong MJ., el-Farra NS., Grew MI. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: recent experience in a community teaching hospital. J Infect Dis. 1995. 171(S1):15–8.

19.Keeffe EB. Is hepatitis A more severe in patients with chronic hepatitis B and other chronic liver diseases? Am J Gastroenterol. 1995. 90:201–5.
20.Vento S., Garofano T., Renzini C., Cainelli F., Casali F., Ghironzi G, et al. Fulminant hepatitis associated with hepatitis A virus superinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 1998. 338:286–90.

21.Heo NY., Lim YS., Kang JM., Oh SI., Park CS., Jung SW, et al. Clinical features of fulminant hepatic failure in a tertiary hospital with a liver transplant center in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2006. 12:82–92. (허내윤,임영석, 강정민, 오세일, 박찬선, 정석원 등. 간이식센터가 있는3차 의료기관에 내원한 전격 간부전 환자의 임상적 특징. 대한간학회지 2006;12:82-92.).
22.Kang JH., Kim HB., Sohn JW., Lee SO., Chung MH., Cheong HJ, et al. Adult immunization schedule recommended by the Korean society of infectious diseases 2007. Infect Chemother. 2008. 40-kjlm-29-563@:1–13. (강진한, 김홍빈, 손장욱, 이상오, 정문현, 정희진등. 2007년대한감염학회권장성인예방접종권장안. 감염과화학요법 2008;40:1-13.).

Fig. 1.
Age related seroprevalence of anti-HAV total from 2005 to 2008.
P for trends were obtained from Cochran-Armitage trend test for positive rates of anti-HAV total by calendar year from 2005 to 2008 in each age groups.
Abbreviation: HAV, hepatitis A virus.
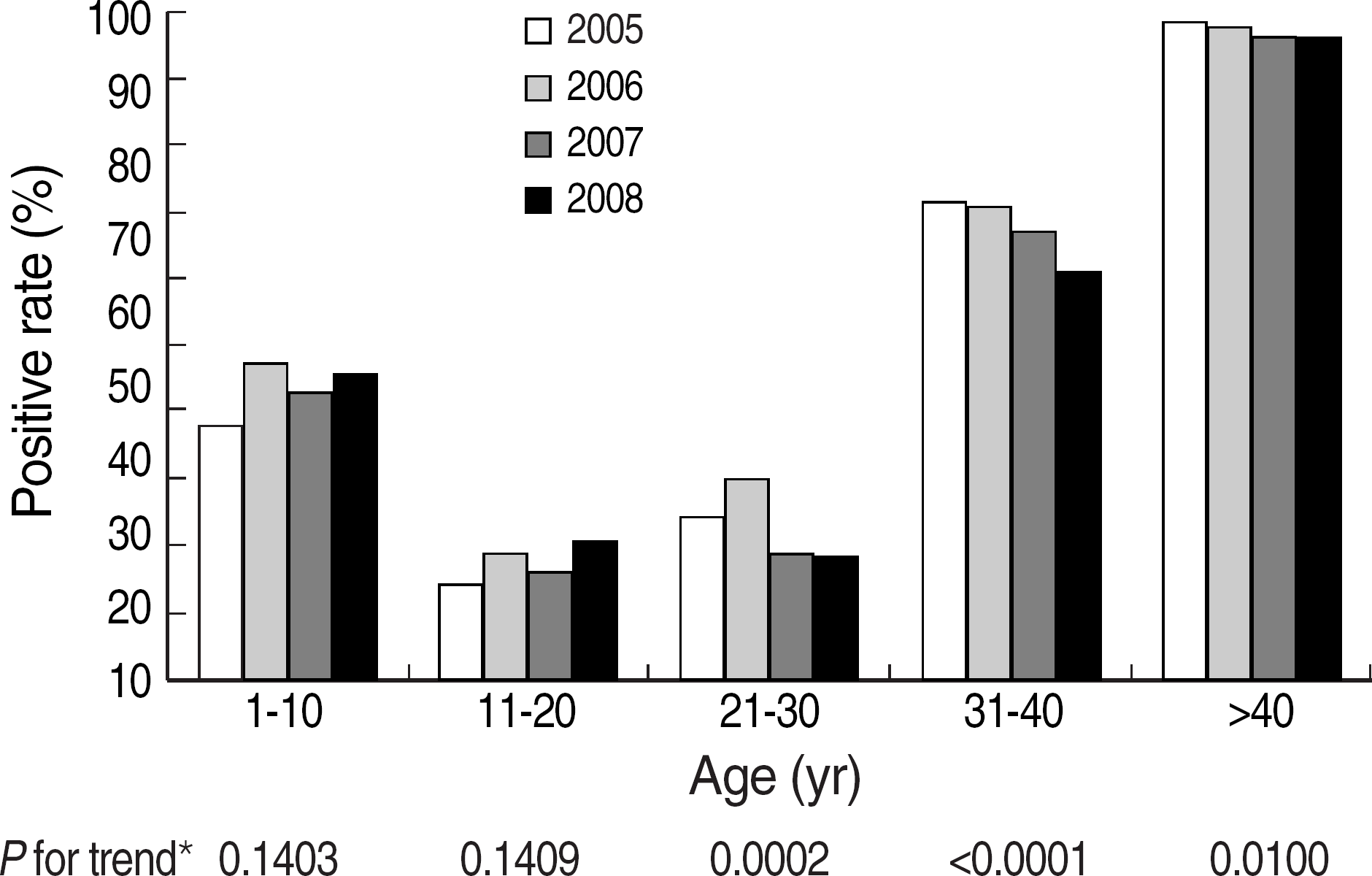
Fig. 2.
Age related seroprevalence of anti-HAV IgM from 2005 to 2008.
P for trends were obtained from Cochran-Armitage trend test for positive rates of anti-HAV IgM by calendar year from 2005 to 2008 in each age groups.
Abbreviation: HAV, hepatitis A virus.
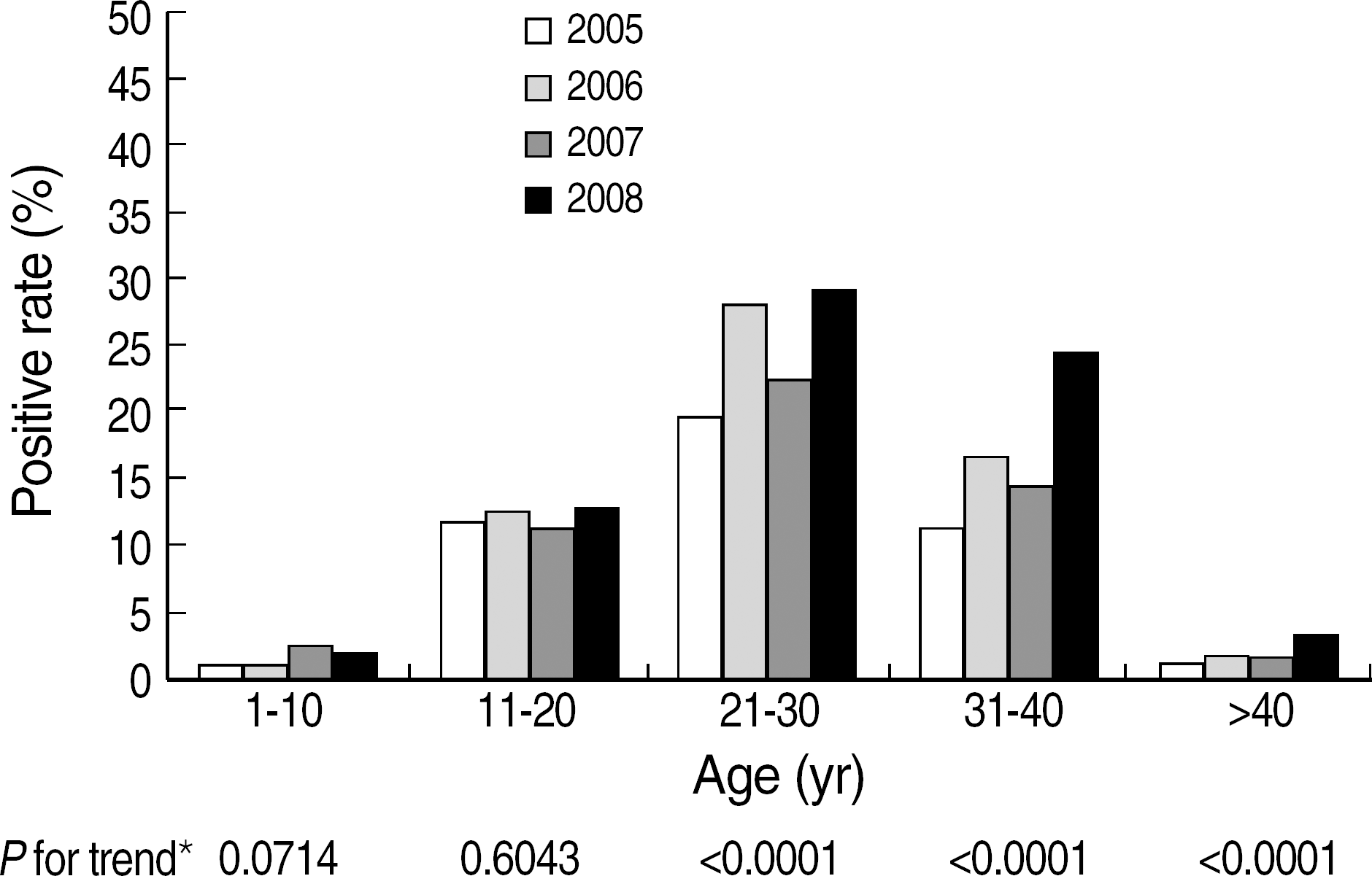
Table 1.
Study population according to year, sex and age groups
Table 2.
Positive rates of anti-HAV total according to sex from 2005 to 2008
| Year | Male | Female | Total | P∗ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 59.4% (382/643) | 58.0% (284/490) | 58.8% (666/1,133) | 0.6233 |
| 2006 | 63.4% (567/895) | 61.9% (454/773) | 62.7% (1,022/1,628) | 0.5570 |
| 2007 | 63.6% (729/1,146) | 59.7% (510/854) | 62.0% (1,239/2,000) | 0.0761 |
| 2008 | 63.9% (2,007/3,141) | 63.4% (2,018/3,166) | 63.8% (4,025/6,307) | 0.8967 |
| 2005-2008 | 63.3% (3,685/5,825) | 62.3% (3,266/5,243) | 62.8% (6,951/11,068) | 0.2922 |
| P for trend† | 0.0761 | 0.0111 | 0.0030 | - |
Table 3.
Positive rates of anti-HAV IgM according to sex from 2005 to 2008
| Year | Male | Female | Total | P∗ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 7.6% (237/3,125) | 7.8% (189/2,428) | 7.7% (426/5,553) | 0.7810 |
| 2006 | 11.1% (465/4,186) | 10.5% (349/3,310) | 10.9% (814/7,496) | 0.4352 |
| 2007 | 9.8% (430/4,410) | 7.9% (283/3,606) | 8.9% (713/8,016) | 0.0029 |
| 2008 | 15.8% (1,011/6,399) | 12.3% (602/4,896) | 14.3% (1,613/11,295) | <0.0001 |
| 2005-2008 | 11.8% (2,143/18,120) | 10.0% (1,423/14,240) | 11.0% (3,566/32,360) | <0.0001 |
| P for trend† | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | - |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download