Abstract
Many AML-associated chromosomal abnormalities, such as t(8;21), t(15;17), inv(16), t(9;11), t(9;22) and t(6;9) are well known. The chromosomal aberration of t(16;21)(p11;q22) in AML is rare and it is known to be associated with poor prognosis, young age (median age, 22 yr), and involvement of various subtypes of the French-American-British classification. We report here 2 AML patients with t(16;21)(p11;q22), proved by conventional cytogenetics and/or reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. Erythrophagocytosis by leukemic blasts was observed in both of the cases. One patient was a 24 yr-old male with acute myelomonocytic leukemia. His karyotype was 46,XY,t(16;21)(p11;q22),del(18)(p11.2) and RT-PCR revealed the TLS/FUS-ERG fusion transcripts. Although he received allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation after the first remission, he died 9 months after the initial diagnosis due to relapse of the disease and graft-versus-host disease. The other patient was a 72 yr-old male with acute myeloid leukemia without maturation. His karyotype was 45,XY,-16,add(21)(q22) and the presence of t(16;21)(p11;q22) was detected by RT-PCR. He was transferred to another hospital with no more follow-up. We suggest that the presence of t(16;21)(p11;q22) and/or TLS/FUS-ERG fusion transcripts has to be considered in cases of AML with erythrophagocytosis.
REFERENCES
1.Ferro MR., Cabello P., Garcia-Sagredo JM., Resino M., San Roman C., Larana JG. t(16;21) in a Ph positive CML. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1992. 60:210–1.

2.Kanazawa T., Ogawa C., Taketani T., Taki T., Hayashi Y., Morikawa A. TLS/FUS-ERG fusion gene in acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(16;21)(p11;q22) and monitoring of minimal residual disease. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005. 46:1833–5.
3.Shimizu K., Ichikawa H., Tojo A., Kaneko Y., Maseki N., Hayashi Y, et al. An ets-related gene, ERG, is rearranged in human myeloid leukemia with t(16;21) chromosomal translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993. 90:10280–4.
4.Ichikawa H., Shimizu K., Hayashi Y., Ohki M. An RNA-binding protein gene, TLS/FUS, is fused to ERG in human myeloid leukemia with t(16;21) chromosomal translocation. Cancer Res. 1994. 54:2865–8.
5.Kong XT., Ida K., Ichikawa H., Shimizu K., Ohki M., Maseki N, et al. Consistent detection of TLS/FUS-ERG chimeric transcripts in acute myeloid leukemia with t(16;21)(p11;q22) and identification of a novel transcript. Blood. 1997. 90:1192–9.
6.Imashuku S., Hibi S., Sako M., Lin YW., Ikuta K., Nakata Y, et al. Hemophagocytosis by leukemic blasts in 7 acute myeloid leukemia cases with t(16;21)(p11;q22): common morphologic characteristics for this type of leukemia. Cancer. 2000. 88:1970–5.
7.Choi HW., Shin MG., Sawyer JR., Cho D., Kee SJ., Baek HJ, et al. Unusual type of TLS/FUS-ERG chimeric transcript in a pediatric acute myelocytic leukemia with 47,XX,+10,t(16;21)(p11;q22). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006. 167:172–6.
8.Perrotti D., Bonatti S., Trotta R., Martinez R., Skorski T., Salomoni P, et al. TLS/FUS, a pro-oncogene involved in multiple chromosomal translocations, is a novel regulator of BCR/ABL-mediated leukemogenesis. EMBO J. 1998. 17:4442–55.
9.Prasad DD., Ouchida M., Lee L., Rao VN., Reddy ES. TLS/FUS fusion domain of TLS/FUS-erg chimeric protein resulting from the t(16;21)chromosomal translocation in human myeloid leukemia functions as a transcriptional activation domain. Oncogene. 1994. 9:3717–29.
10.Imashuku S., Hibi S., Kuriyama K., Todo S. Hemophagocytosis by leukemic blasts in a case of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with t(16;21)(p11;q22). Int J Hematol. 1999. 70:36–9.
11.Shikami M., Miwa H., Nishii K., Tkahashi T., Shiku H., Tsutani H, et al. Myeloid differentiation antigen and cytokine receptor expression on acute myelocytic leukaemia cells with t(16;21)(p11;q22): frequent expression of CD56 and interleukin-2 receptor α chain. Br J Haematol. 1999. 105:711–9.
12.Jekarl DW., Kim YG., Lim JY., Kim MS., Han KJ., Lee AW, et al. CD56 expression and hemophagocytosis of leukemic cells in acute myeloid leukemia with t(16;21)(p11;q22). Korean J Lab Med. 2008. 28(S2):S371.
13.Swerdlow SH, Campo E, editors. WHO classification of tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed.Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2008. p. 137.
14.Perot C., Huret JL. Atlas of genetics and cytogenetics in oncology and haematology. http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t1621.html. (Updated on Jan. 2005.
Fig. 1.
Bone marrow smears of case 1 (A) and case 2 (B) showing blast cells with erythrophagocytic activity and cytoplasmic vacuoles (Wright-Giemsa stain, ×1,000).
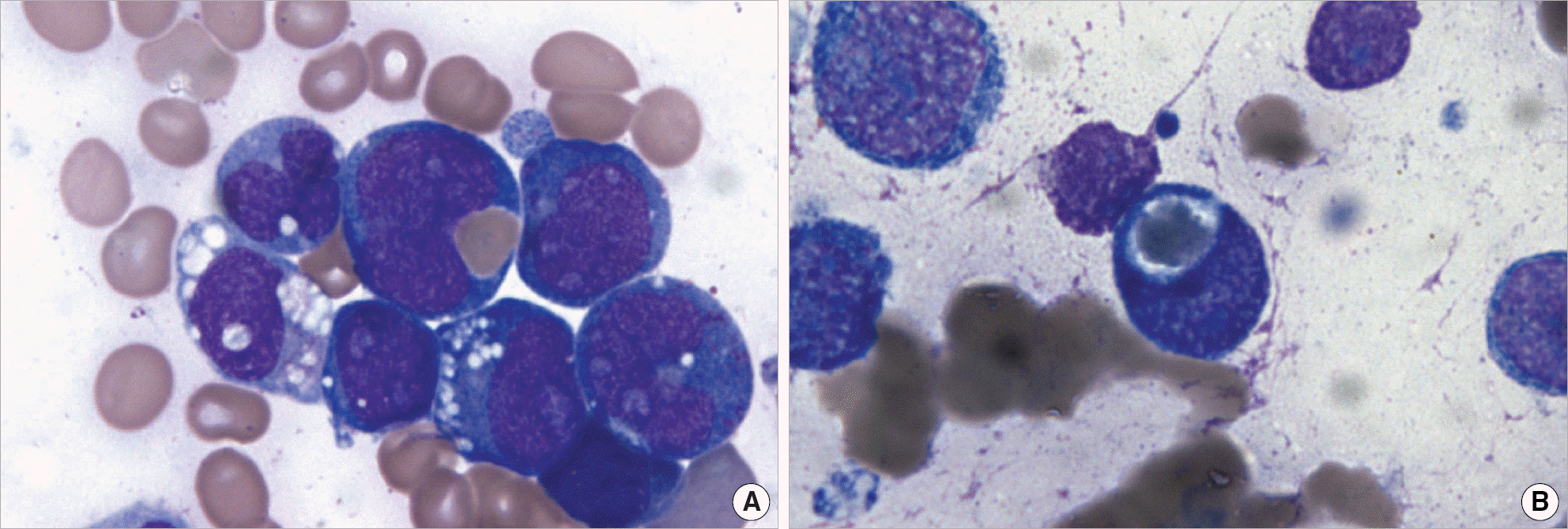
Fig. 2.
Karyograms of the patients presented. (A) Case 1 showing 46,XY,t(16;21)(p11;q22),del(18)(p11.2). (B) Case 2 showing 45,XY, −16,add(21)(q22). Arrows indicate rearranged and abnormal chromosomes.
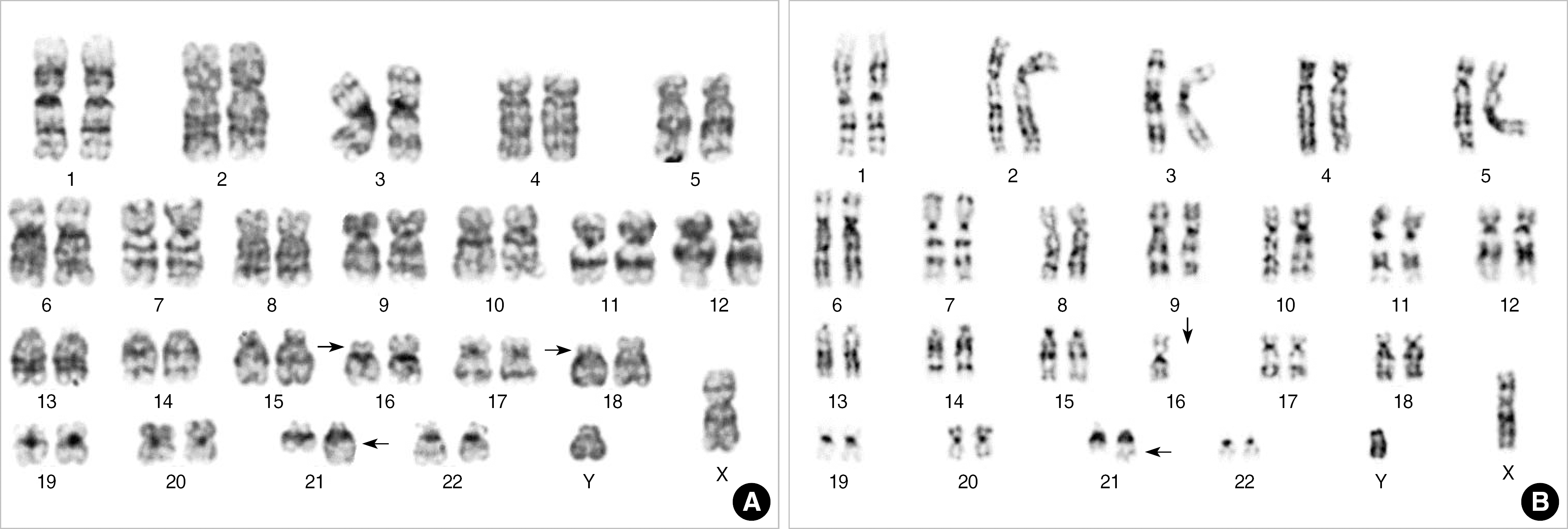
Fig. 3.
(A) Multiplex RT-PCR using HemaVision kit in case 1 (upper) and case 2 (lower). Both show an internal control band (911 bp, arrowhead) in each lane and 2 unknown bands (1 strong, 1 weak) in lane 5. (B) RT-PCR for t(16;21)(p11;q22) using HemaVision split-out PCR kit. Both cases show bands for the internal control (911 bp, arrowhead) and the TLS/FUS-ERG fusion transcripts of type A (313 bp) and type B (269 bp). Lane 1, 100 bp ladder; lane 2, case 1; lane 3, case 2. (C) RT-PCR for t(16;21)(p11;q22) using the primers reported by Kong, et al. Both cases have type A (255 bp), type B (211 bp), and an extra band (∗). Lane 1, 100 bp ladder; lane 2, negative control; lane 3, case 1; lane 4, case 2.
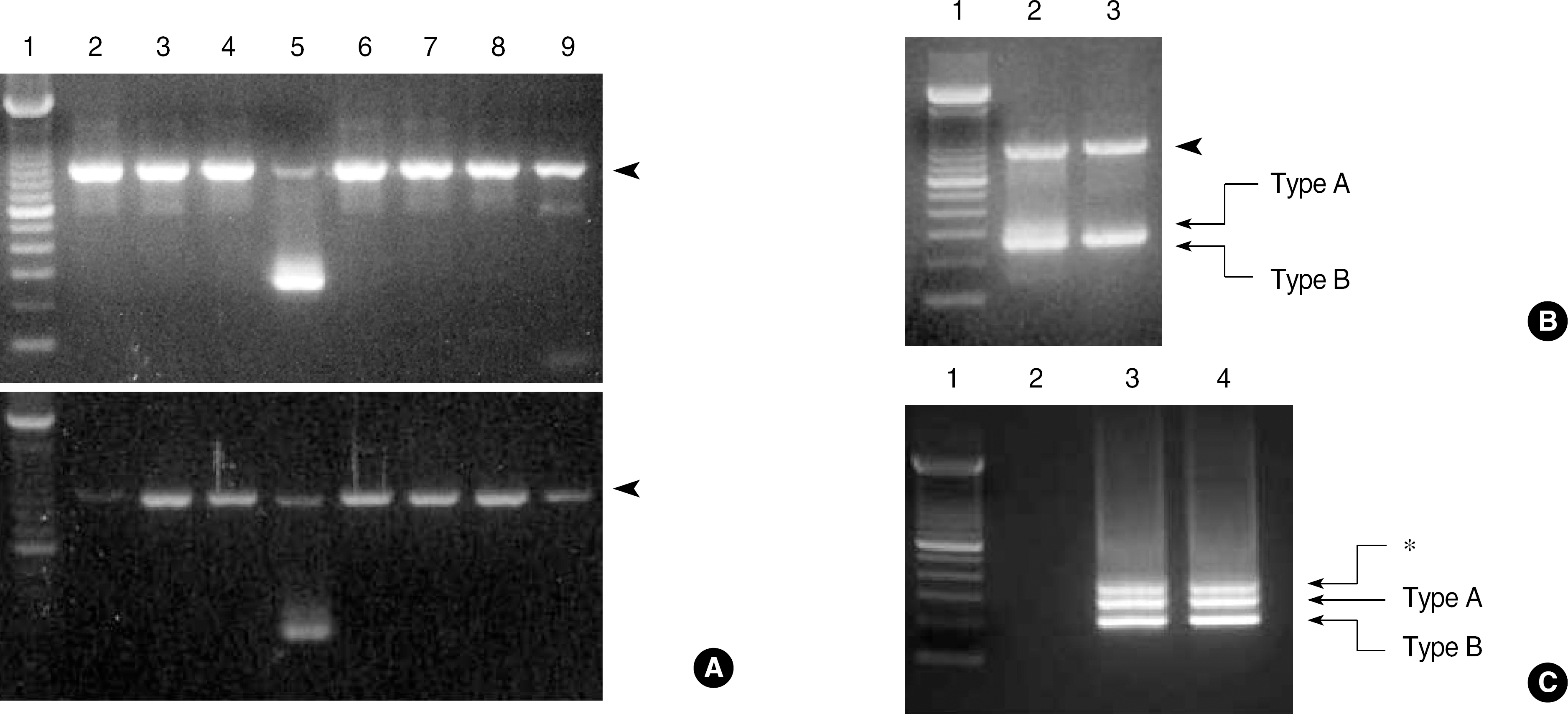
Table 1.
Clinical and hematological characteristics of 2 AML patients with t(16;21)(p11;q22)
| No. Case | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Age/sex | 24/M | 72/M |
| Subtype | Acute myelomonocytic leukemia | AML without maturation |
| Survival (months) | 9 | 1+∗ |
| WBC (/μL) | 7,700 | 2,300 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 4.5 | 8.5 |
| Platelets (/μL) | 10,000 | 124,000 |
| % Blasts | ||
| Peripheral blood | 84 | 29 |
| Bone marrow | 58 | 48 |
| Immunophenotype (% positive cells) | CD13 (46) | CD13 (30) |
| CD14 (23) | CD33 (75) | |
| CD33 (89) | CD34 (76) | |
| CD34 (66) | CD61 (20) | |
| HLA-DR (40) | HLA-DR (21) | |
| Cytochemical stain | ||
| SBB | + | - |
| PAS | - | - |
| ANBE | + | - |
| Immunohistochemical stain (additional) | ||
| CD56 | - | - |
| MPO | ND | + |
| vWF | ND | - |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download