Abstract
Background
HLA-B27 is strongly associated with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and its subtypes differ in their ethnic distribution. Studies worldwide have shown that B∗2701, B∗2702, B∗2704, B∗2705, B∗2707, B∗2708, B∗2714, B∗2715, and B∗2719 are AS-predisposing subtypes, whereas B∗2706 and B∗2709 are reported to be negatively associated with AS. The aim of this study was to investigate HLA-B27 polymorphism and clinical features according to subtypes in Korean patients with AS.
Methods
Two hundred thirty samples from patients with impression of AS were analyzed by polymerase chain reaction using a sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP) method. Pel-Freez SSP Unitray HLA-B∗27 kit (Dynal Biotech, USA) including 16 primers was used to define HLA-B27 subtypes from B∗2701 to B∗2735.
Results
Among 230 samples from patients with impression of AS, 171 were HLA-B27 positive, and among 160 patients diagnosed as AS, 154 (96.3%) were HLA-B27 positive, while 17 patients not diagnosed as AS were HLA-B27 positive. Among 154 HLA-B27 positive patients with AS, 142 (92.2%) were typed as B∗2705 and 9 (5.8%) were typed as B∗2704. Three cases (1.9%) could be interpreted only variously because of their HLA-B27 homogeneous alleles. Between B∗2705 and B∗2704, no specific HLA-B27 subtype appeared to contribute to AS susceptibility (P=0.60). Difference in clinical features between B∗2705 and B∗2704 could not be found in this study (P>0.05).
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Khan MA., Mathieu A., Sorrentino R., Akkoc N. The pathogenetic role of HLA-B27 and its subtypes. Autoimmun Rev. 2007. 6:183–9.

2.Gomez P., Montserrat V., Marcilla M., Paradela A., de Castro JA. B∗ 2707 differs in peptide specificity from B∗2705 and B∗2704 as much as from HLA-B27 subtypes not associated to spondyloarthritis. Eur J Immunol. 2006. 36:1867–81.
3.Garcia F., Marina A., López de Castro JA. Lack of carboxyl-terminal tyrosine distinguishes the B∗2706-bound peptide repertoire from those of B∗2704 and other HLA-B27 subtypes associated to ankylosing spondylitis. Tissue Antigens. 1997. 49:215–21.
4.Fiorillo MT., Meadows L., D'Amato M., Shabanowitz J., Hunt DF., Appella E, et al. Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis correlates with the C-terminal residue of peptides presented by various HLA-B27 subtypes. Eur J Immunol. 1997. 27:368–73.

5.Mear JP., Schreiber KL., Munz C., Zhu X., Stevanovic S., Rammensee HG, et al. Misfolding of HLA-B27 as a result of its B pocket suggests a novel mechanism for its role in susceptibility to spondyloarthropathies. J Immunol. 1999. 163:6665–70.
6.Colbert RA. HLA-B27 misfolding: a solution to the spondyloarthropathy conundrum? Mol Med Today. 2000. 6:224–30.

7.Ramos M., López de Castro JA. HLA-B27 and the pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis. Tissue Antigens. 2002. 60:191–205.

8.Khan MA., Ball EJ. Genetic aspects of ankylosing spondylitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2002. 16:675–90.

9.van der Linden S., Valkenburg HA., Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984. 27:361–8.
10.Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A, et al. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991. 34:1218–27.

11.Sesma L., Montserrat V., Lamas JR., Marina A., Vazquez J., López de Castro JA. The peptide repertoires of HLA-B27 subtypes differentially associated to spondyloarthropathy (B∗2704 and B∗2706) differ by specific changes at three anchor positions. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:16744–9.
12.Ramos M., Paradela A., Vazquez M., Marina A., Vazquez J., López de Castro JA. Differential association of HLA-B∗2705 and B∗2709 to ankylosing spondylitis correlates with limited peptide subsets but not with altered cell surface stability. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:28749–56.
13.Sims AM., Wordsworth BP., Brown MA. Genetic susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Mol Med. 2004. 4:13–20.

14.Nasution AR., Mardjuadi A., Kunmartini S., Suryadhana NG., Setyohadi B., Sudarsono D, et al. HLA-B27 subtypes positively and negatively associated with spondyloarthropathy. J Rheumatol. 1997. 24:1111–4.
15.Lopez-Larrea C., Sujirachato K., Mehra NK., Chiewsilp P., Isarangkura D., Kanga U, et al. HLA-B27 subtypes in Asian patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Evidence for new associations. Tissue Antigens. 1995. 45:169–76.
16.D'Amato M., Fiorillo MT., Carcassi C., Mathieu A., Zuccarelli A., Bitti PP, et al. Relevance of residue 116 of HLA-B27 in determining susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Immunol. 1995. 25:3199–201.
17.Ren EC., Koh WH., Sim D., Boey ML., Wee GB., Chan SH. Possible protective role of HLA-B∗2706 for ankylosing spondylitis. Tissue Antigens. 1997. 49:67–9.
18.Lee KW., Kim JY. HLA-B27 typing using PCR-SSP. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1996. 16:744–50. (이경화 및 김진영. PCR-SSP법을 이용한 HLA-B27 검사. 대한임상병리학회지 1996;16: 744-50.).
19.Bae JS., Kim YR., Choi HI., Cho JY. Comparison of HLA-B27 typing methods-PCR-SSP, microlymphocytotoxicity, and flow cytometry. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2000. 20:198–203. (배준수, 김영리, 최현일, 조윤정. HLA-B27 검사법의 비교-PCR-SSP법, 미량 독성 림프구법, 유세포 분석법 비교. 대한임상병리학회지 2000;20: 198-203.).
20.Kim HS., Hwang YS., Park MH. The distribution of HLA antigens and haplotypes in Koreans. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1997. 17:1109–23. (김현수, 황유성, 박명희. 한국인의 HLA 항원과 일배체형의 분포.대한임상병리학회지 1997;17: 1109-23.).
21.Choi SJ., Park MH. HLA-B27 frequency in Korean patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Seoul J Med. 1987. 28:247–50. (최성재 및 박명희. 한국인 강직성 척추염 환자에서 HLA-B27 빈도에 관한 연구. Seoul J Med 1987;28: 247-50.).
22.Benjamin R., Parham P. Guilt by association: HLA-B27 and ankylosing spondylitis. Immunol Today. 1990. 11:137–42.

23.Feltkamp TE., Mardjuadi A., Huang F., Chou CT. Spondyloarthropathies in eastern Asia. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001. 13:285–90.

24.Garcia-Fernandez S., Gonzalez S., Mina Blanco A., Martinez-Borra J., Blanco-Gelaz M., Lopez-Vazquez A, et al. New insights regarding HLA-B27 diversity in the Asian population. Tissue Antigens. 2001. 58:259–62.

25.Birinci A., Bilgici A., Kuru O., Durupinar B. HLA-B27 polymorphism in Turkish patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 2006. 26:285–7.

27.Yang KL., Chen IH., Hsiao CK., Cherng JM., Yang KZ., Chang CC, et al. Polymorphism of HLA-B27 in Taiwanese Chinese. Tissue Antigens. 2004. 63:476–9.

28.Ma HJ., Hu FP. Diversity of human leukocyte antigen-B27 alleles in Han population of Hunan province, southern China. Tissue Antigens. 2006. 68:163–6.

29.Hwang MW., Cho YJ. HLA-B27 subtypes in Korean patients with ankylosing spondylitis-by polymerase chain reaction-sequence specific primers (PCR-SSP) method. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1999. 19:92–7. (황미원 및 조윤정. 한국인 강직성 척추염 환자에서 HLA-B27 아형에 관한 연구. 대한임상병리학회지 1999;19: 92-7.).
30.Oh WI. HLA-B27 subtypes in Korean patients with spondyloarthropathies and healthy controls. Seoul national university. 1998. The degree of doctor of philosophy in medicine. (오원일. 한국인 척추관절병증 환자와 건강대조군의 HLA-B27 아형에 관한 연구. 서울대학교 1999년 의학박사 학위논문.).
31.Goto K., Ota M., Ando H., Mizuki N., Nakamura S., Inoue K, et al. MICA gene polymorphisms and HLA-B27 subtypes in Japanese patients with HLA-B27-associated acute anterior uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. 39:634–7.
32.Konno Y., Numaga J., Tsuchiya N., Ogawa A., Islam SM., Mochizuki M, et al. HLA-B27 subtypes and HLA class II alleles in Japanese patients with anterior uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999. 40:1838–44.
Go to : 
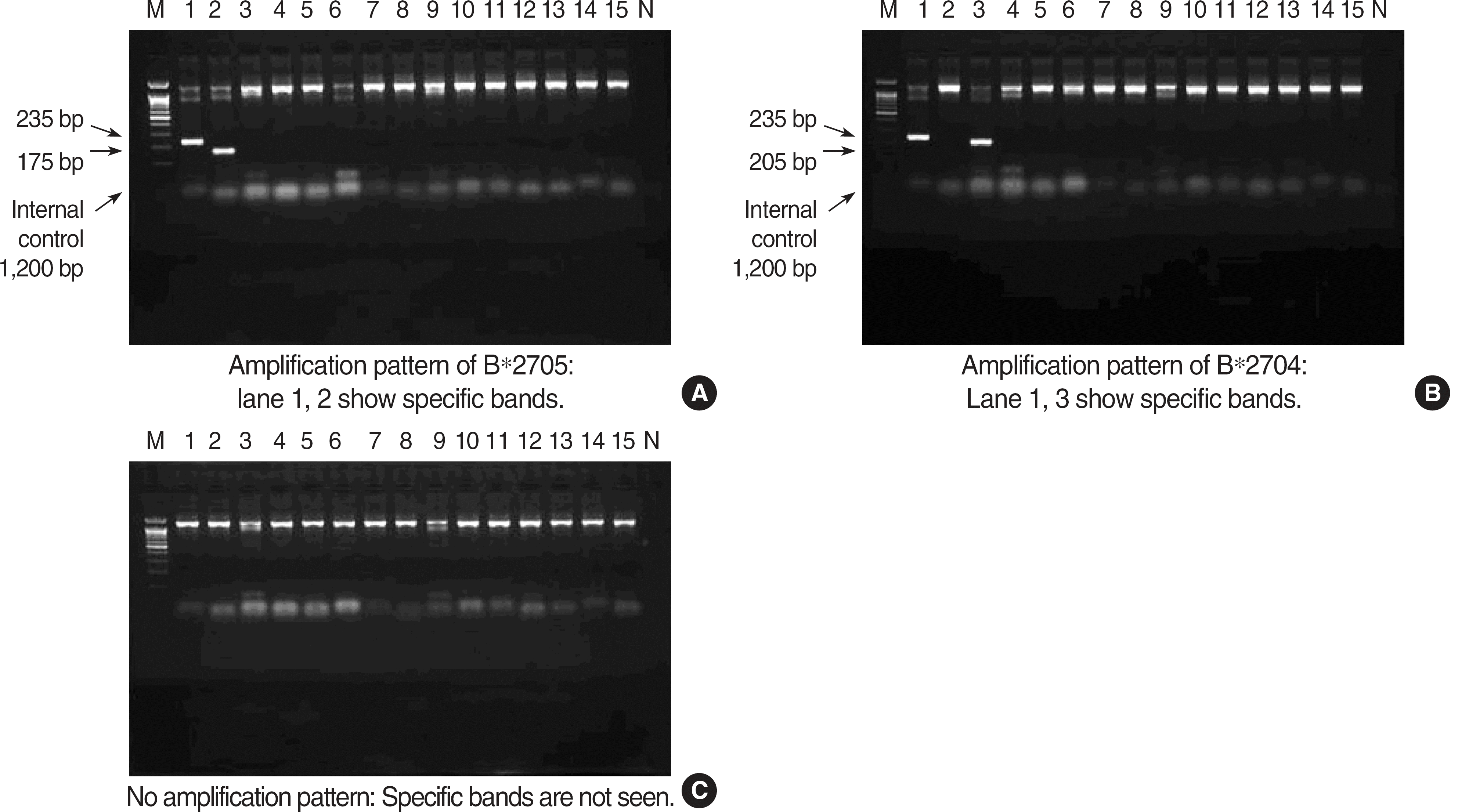 | Fig. 1.Amplification patterns of HLA-B27 positive and negative samples. ∗Each well has internal control (1,200 bp). M, size marker; N, HLA-B27 negative control. |
Table 1.
Number and frequency of HLA-B27 in the patients with and without ankylosing spondylitis
| AS | non AS | Total | P value∗ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-B27 (+) | 154 (96.3%) | 17 (24.3%) | 171 | <0.0001 |
| HLA-B27 (–) | 6 (3.7%) | 53 (75.7%) | 59 | |
| Total | 160 | 70 | 230 |
Table 2.
Number and frequency of HLA-B27 alleles detected in HLA-B27 positive patients
| Allele | HLA-B27 positive patients (n=171) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS (n=154) | non AS (n=17) | Total (n=171) | P value† | |
| B∗2704 | 9 (5.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 9 (5.3%) | 0.60 |
| B∗2705 | 142 (92.2%) | 16 (94.1%) | 158 (92.4%) | |
| B∗2720 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (5.9%) | 1 (0.6%) | |
| Others | 3 (1.9%)∗ | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (1.8%) | |
∗ Others includes 2 cases that were B∗2704 & B∗2705/B∗2704 & B∗2728/B∗2705 & B∗2715/B∗2710 & B∗2704/ B∗2710 & B∗2704/B∗2710 & B∗ 2705/B∗2710 & B∗2715/B∗2710 & B∗2728 and 1 case that was B∗2704 & B∗2715/B∗2704 & B∗2731/B∗2715 & B∗2731. These 3 cases had HLA-B27 homogeneous alleles, which were identified by HLA-B low resolution typing.
Table 3.
Clinical features of patients with ankylosing spondylitis according to the HLA-B27 subtypes
| Clinical features | AS (n=154) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B∗2705 (n=142) | B∗2704 (n=9) | Others∗ (n=3) | Total (n=154) | P value∗ | |
| Sex (M/F) | 114/28 | 6/3 | 3/0 | 123/31 | |
| Age (mean yr) | 30.1 | 32.1 | 28 | 30.0 | |
| Spondyloarthritis | 142 | 9 | 3 | 154 | |
| (100%) | (100%) | (100%) | (100%) | ||
| Peripheral arthritis | 41 | 1 | 3 | 45 | 0.45 |
| (28.9%) | (11.1%) | (100%) | (29.2%) | ||
| Uveitis | 20 | 1 | 2 | 23 | 1.00 |
| (14.1%) | (11.1%) | (66.7%) | (14.9%) | ||
| Enthesitis | 10 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 0.50 |
| (7.0%) | (10.0%) | (0.0%) | (7.1%) | ||
| Family history | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1.00 |
| (4.2%) | (0.0%) | (0.0%) | (3.9%) | ||
Table 4.
Clinical features of patients with ankylosing spondylitis according to HLA-B27 positivity
| Clinical features | AS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-B27 (+) (n=154) | HLA-B27 (–) (n=6) | P value∗ | |
| Sex, M/F | 114/28 | 5/1 | |
| Age (mean yr) | 30.0 | 28 | |
| Spondyloarthritis | 154 (100%) | 6 (100%) | |
| Peripheral arthritis | 45 (29.2%) | 1 (16.7%) | 0.67 |
| Uveitis | 23 (14.9%) | 1 (16.7%) | 1.00 |
| Enthesitis | 11 (7.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 |
| Family history | 6 (3.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download