Abstract
Background
Commercial kits of PCR method are widely used in HLA-B27 typing; however, their cost is relatively high. In this study, we evaluated the utility of an in-house PCR method by comparing it with that of a commercial kit.
Methods
HLA-B27 typing was done in 188 patients by using two PCR methods, Absolute™ HLA-B27 PCR kit (Biosewoom, Korea) and an in-house PCR method. The primers used in the in-house method were prepared by Bioneer (Korea). Both PCR tests were done by Gene Amp PCR System 9600 (Perkin-Elmer Centus Corp., USA).
REFERENCES
1.Seipp MT., Erali M., Wies RL., Wittwer C. HLA-B27 typing: evaluation of an allele-specific PCR melting assay and two flow cytometric antigen assay. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2005. 63:10–5.
2.Downing J., Coates E., Street J., Hammond L., Rees TJ., Pepperall J, et al. A high-resolution polymerase chain reaction-sequence-specific primer HLA-B∗27 typing set and its application in routine HLA-B27 testing. Genet Test. 2006. 10:98–103.
3.Nathalang O., Tantimavanich S., Nillakupt K., Arnutti P., Jaruchaimontree C. HLA-B27 testing in Thai patients using the PCR-SSP technique. Tissue Antigens. 2006. 67:233–6.

4.Bunce M., O'Neill CM., Barnardo MC., Krausa P., Browning MJ., Morris PJ, et al. Phototyping: comprehensive DNA typing for HLA-A, B, C, DRB1, DRB3, DRB4, DRB5 & DQB1 by PCR with 144 primer mixes utilizing sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP). Tissue Antigens. 1995. 46:355–67.
5.Zino E., Di Terlizzi S., Carugo C., Baggi L., Galli A., Bonini C, et al. Rapid detection of all HLA-B∗27 alleles (B∗2701-B∗2725) by group-specific polymerase chain reaction. Tissue Antigens. 2004. 63:88–92.
6.Lucotte G., Burckel A. DNA typing of HLA-B27 by polymerase chain reaction. Mol Cell Probes. 1997. 11:313–5.

7.Bonnaud G., Aupetit C., Preux PM., Cogne M., Drouet M. Optimisation of HLA-B27 testing by association of flow cytometry and DNA typing. Clin Rheumatol. 1999. 18:23–7.

8.Lee KW., Kim JY. HLA-B27 typing using PCR-SSP. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1996. 16:744–50. (이경화 및 김진영. PCR-SSP법을 이용한 HLAB27검사. 대한임상병리학회지 1996;16: 744-50.).
9.Lee JH., Jun JB., Jung S., Bae SC., Yoo DH., Kim TW, et al. Higher prevalence of peripheral arthritis among ankylosing spondylitis patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:669–73.

10.Bae JS., Kim YR., Choi HI., Cho YJ. Comparison of HLA-B27 typing methods- PCR-SSP, microlymphocytotoxicity, and flow cytometry-. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2000. 20:198–203. (배준수, 김영리, 최현일, 조윤정. HLA-B27 검사법의 비교- PCR-SSP법, 미량 독성 림프구법, 유세포분석법비교. 대한임상병리학회지 2000;20: 198-203.).
11.Inaoui R., Bertin P., Preux PM., Treves R. Outcome of patients with undifferentiated chronic monoarthritis: retrospective study of 46 cases. Joint Bone Spine. 2004. 71:209–13.
Fig. 1.
Results of HLA-B27 typing. (A) Absolute™ HLA-B27 PCR kit (Biosewoom), (B) In-house PCR with B27 280 primer.
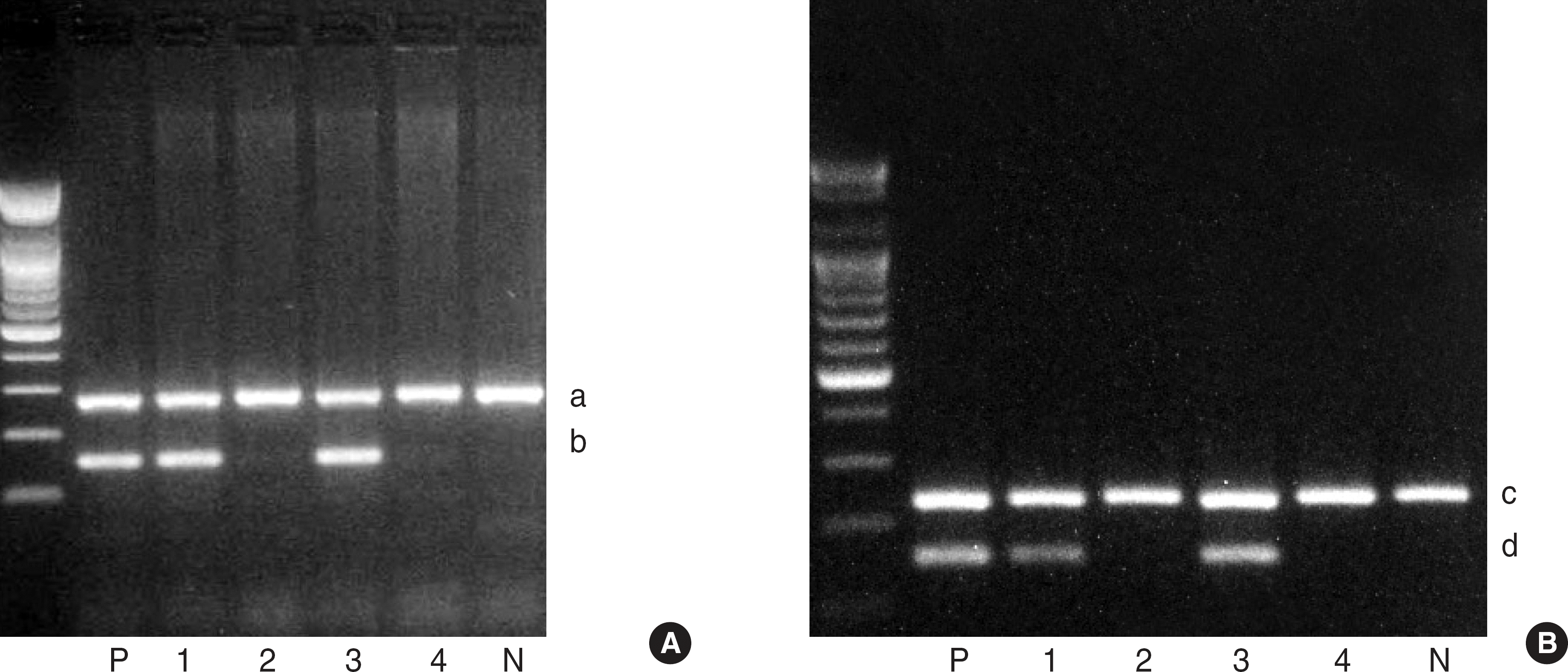
Lanes 1-4, patient 1-4; P, positive control; N, negative control; a, internal control (beta-globin); c, internal control (P53 exon 8); b and d, HLA B27 band.
Table 1.
Patient characteristics and HLA-B27 typing results
| Diseases | N. of patients | HLA- B27 positive cases N (%) | Mean age yr | Sex ratio M/F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankylosing spondylitis | 62 | 50 (80.7) | 35.9 | 48/14 |
| Iridocyclitis | 28 | 6 (21.4) | 38.9 | 17/11 |
| Rheumatism | 16 | 5 (31.3) | 32.1 | 11/5 |
| Arthrosis | 16 | 1 (6.3) | 32.9 | 12/4 |
| Spinal stenosis | 11 | 2 (18.2) | 36.2 | 6/5 |
| Joint pain/myalgia | 11 | 2 (18.2) | 27.6 | 11/0 |
| Optic neuritis | 7 | 0 (0) | 55.9 | 0/7 |
| Other articular diseases∗ | 8 | 4 (50.0) | 34.8 | 5/3 |
| Other diseases† | 29 | 2 (6.7) | 42.3 | 17/12 |
| Total | 188 | 72 (38.3) | 37.0 | 127/61 |
Table 2.
Characteristics of primers used in the in-house PCR




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download