Abstract
Background
Some differences exist among various Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA quantification assays due to lack of standardization and besides clinical usefulness has not been firmly elucidated in Korean HBV patients.
Methods
We compared Bayer VERSANT HBV DNA 3.0 Assay (VERSANT 3.0) with Digene Hybrid Capture II HBV DNA Test (HC-II) according to HBeAg status and ALT levels in 232 HBV-infected Korean patients. One hundred and seventeen sera with undetectable DNA levels by HC-II were further analyzed by Real-Q HBV quantification assay (BioSewoom).
Results
Although VERSANT 3.0 and HC-II showed an excellent correlation (r=0.9739), the results (copies/mL) by VERSANT 3.0 were 0.45 log10 higher than those by HC-II. HBV DNA levels were higher in HBeAg-positive group than in HBeAg-negative group (P=0.002), and in abnormal ALT group than in normal ALT group (P<0.0001). The detection rate of HBV DNA by VERSANT 3.0 was lower in HBeAg-negative and normal ALT group (n=68) than in HBeAg-positive or abnormal ALT group (n=164) (35.3% vs 89.6%, P<0.0001). Fifty two sera out of 61 sera with undetectable DNA by VERSANT 3.0 were measurable by Real-Q with mean value of 3.26 log10 copies/mL.
Conclusions
VERSANT 3.0 and HC-II showed an excellent correlation, but a little difference (0.45 log10) existed. VERSANT 3.0 effectively measured clinically relevant HBV DNA levels in most HBV-infected patients in Korea. However, more sensitive assays are needed for patients with negative HBeAg and normal ALT to see the low copies of HBV DNA levels.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Jardi R., Buti M., Rodriguez-Frias F., Cortina M., Esteban R., Guardia J, et al. The value of quantitative detection of HBV-DNA amplified by PCR in the study of hepatitis B infection. J Hepatol. 1996. 24:680–5.
2.Ho SK., Chan TM. An overview of assays for serum HBV DNA. Clin Lab. 2000. 46:609–14.
3.Zeuzem S. Overview of commercial HBV assays systems. Methods Mol Med. 2004. 95:3–13.
4.Ho SK., Chan TM., Cheng IK., Lai KN. Comparison of the second-generation digene hybrid capture assay with the branched-DNA assay for measurement of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:2461–5.

5.Yao JD., Beld MG., Oon LL., Sherlock CH., Germer J., Menting S, et al. Multicenter evaluation of the VERSANT hepatitis B virus DNA 3.0 assay. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:800–6.

6.Lai CL., Chien RN., Leung NW., Chang TT., Guan R., Tai DI, et al. A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339:61–8.
7.Puchhammer-Stockl E., Mandl CW., Kletzmayr J., Holzmann H., Hofmann A., Aberle SW, et al. Monitoring the virus load can predict the emergence of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus strains in renal transplantation patients during lamivudine therapy. J Infect Dis. 2000. 181:2063–6.

8.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. User verification of performance for precision and trueness; approved guideline-second edition, CLSI document EP15-A2. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2005.
9.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; approved guideline-second edition, CLSI document EP5-A2. 2004. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2004.
10.Bland JM., Altman DG. Comparing methods of measurement: why plotting difference against standard method is misleading. Lancet. 1995. 346:1085–7.

11.Pawlotsky JM., Bastie A., Hezode C., Lonjon I., Darthuy F., Remire J, et al. Routine detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA in clinical laboratories: performance of three commercial assays. J Virol Methods. 2000. 85:11–21.

12.Chan HL., Leung NW., Lau TC., Wong ML., Sung JJ. Comparison of three different sensitive assays for hepatitis B virus DNA in monitoring of responses to antiviral therapy. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:3205–8.

13.Gilbert N., Corden S., Ijaz S., Grant PR., Tedder RS., Boxall EH. Comparison of commercial assays for the quantification of HBV DNA load in health care workers: calibration differences. J Virol Methods. 2002. 100:37–47.

14.Dai CY., Yu ML., Chen SC., Lin ZY., Hsieh MY., Wang LY, et al. Clinical evaluation of the COBAS Amplicor HBV monitor test for measuring serum HBV DNA and comparison with the Quantiplex branched DNA signal amplification assay in Taiwan. J Clin Pathol. 2004. 57:141–5.

15.Ronsin C., Pillet A., Bali C., Denoyel GA. Evaluation of the COBAS AmpliPrep-total nucleic acid isolation-COBAS TaqMan hepatitis B virus (HBV) quantitative test and comparison to the VERSANT HBV DNA 3.0 assay. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 44:1390–9.

16.Heo J., Cho M., Cho BM., Lee SM., Kim TO., Kim GH, et al. Predictors of lamivudine resistance in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:157–65. (허정, 조몽, 조병만, 이선미, 김태오, 김광하등. 만성 B형간질환환자의라미부딘내성예측인자. 대한간학회지 2007;13: 157-65.).
17.Byun KS., Lee KS., Cho M., Suh KS., Kweon Y., Koh KC, et al. Guideline for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Korean J Hepatol. 2004. 10(S):S89–100. (변관수, 이관식, 조몽, 서경석, 권오건, 고광철등. 2004년대한간학회 B형만성간염치료가이드라인. 대한간학회지 2004;. 10:S89-100.).
Go to : 
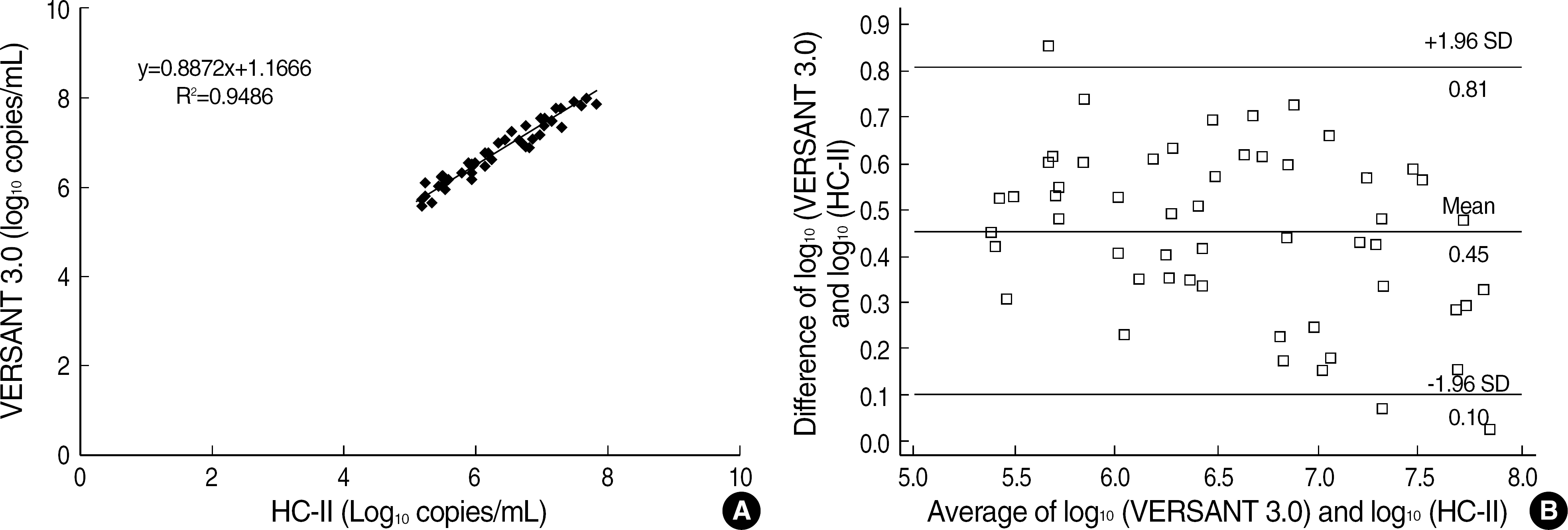 | Fig. 1.(A) Correlation of log10 quantitative HBV DNA levels between VERSANT 3.0 and HC-II. (B) Differences in log 10 quantitative HBV DNA levels between VERSANT 3.0 and HC-II in relation to average log10 quantification (n=54). |
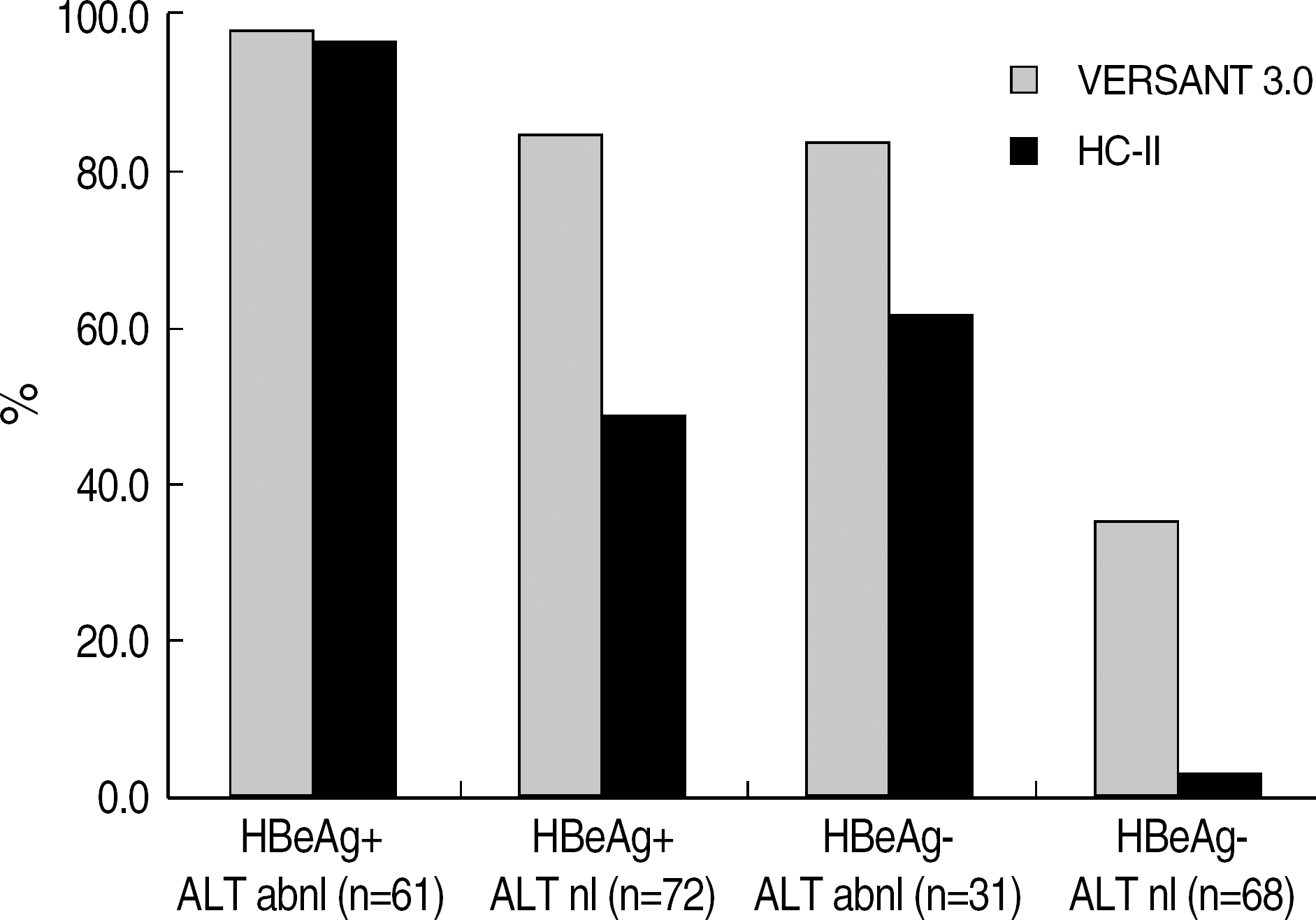 | Fig. 2.Detection rates of HBV DNA by VERSANT 3.0 and HC-II in relation to clinical status of HBV. Abbreviations: HBeAg, hepatitis B virus e antigen; abnl, abnormal; nl, normal. |
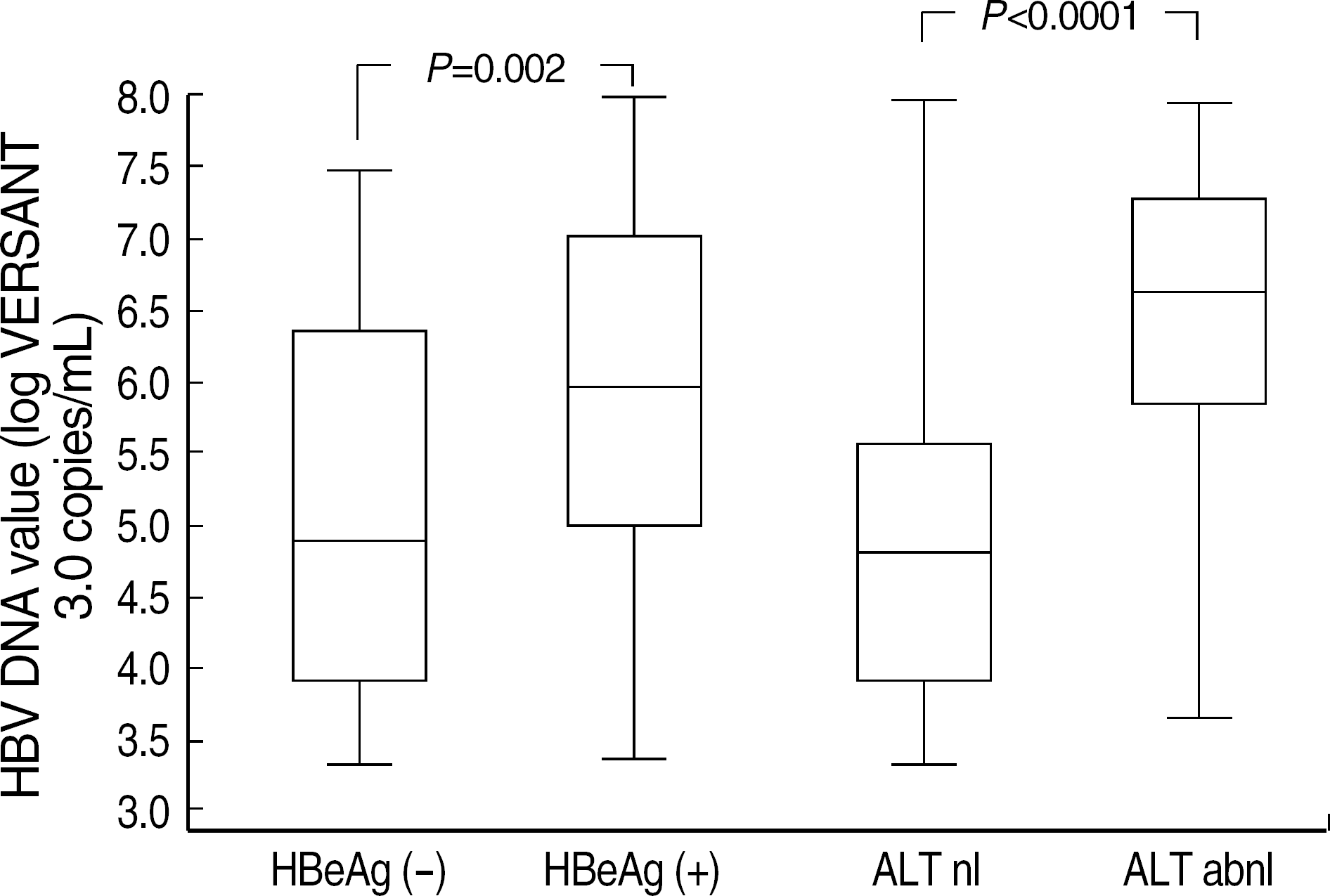 | Fig. 3.HBV DNA levels by VERSANT 3.0 in relation to clinical status of HBV. The plots display the median values (lines inside boxes), 25th and 75th percentiles (lower and upper limits of boxes), and the minimum and 99th percentiles. Abbreviations: nl, normal; abnl, abnormal. |
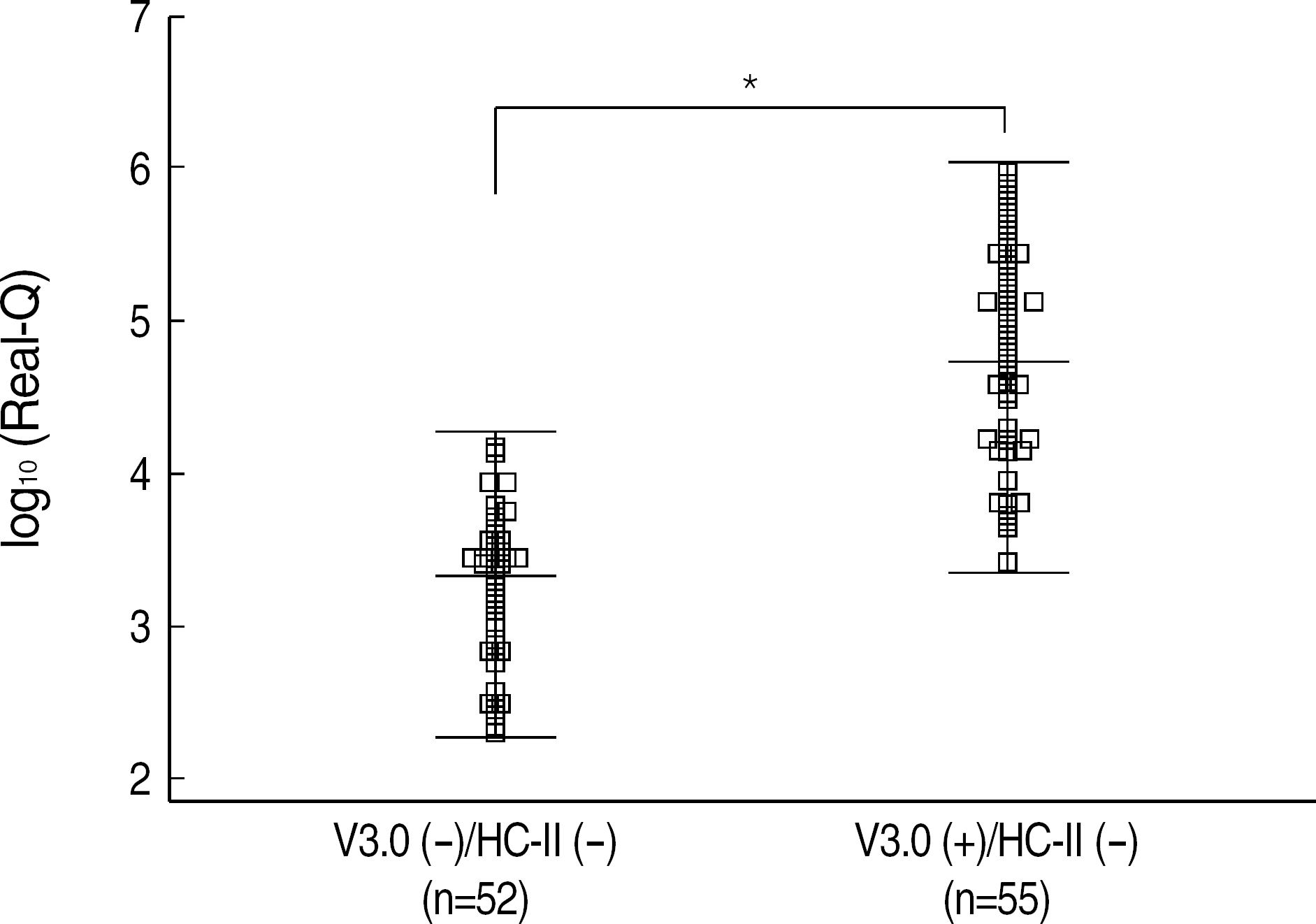 | Fig. 4.Scatter plot shows HBV DNA levels measured by Real-Q (log10 copies/mL) in sera with undetectable DNA by both of VERSANT 3.0 (V3.0) and HC-II (n=52) (left) and in sera with detectable DNA by VERSANT 3.0 (V3.0) but undetectable by HC-II (n=55) (right). Horizontal bars represent the means and±2SD. The difference between two groups was tested by Student's t test. ∗P<0.0001. Abbreviations: nl, normal; abnl, abnormal. |
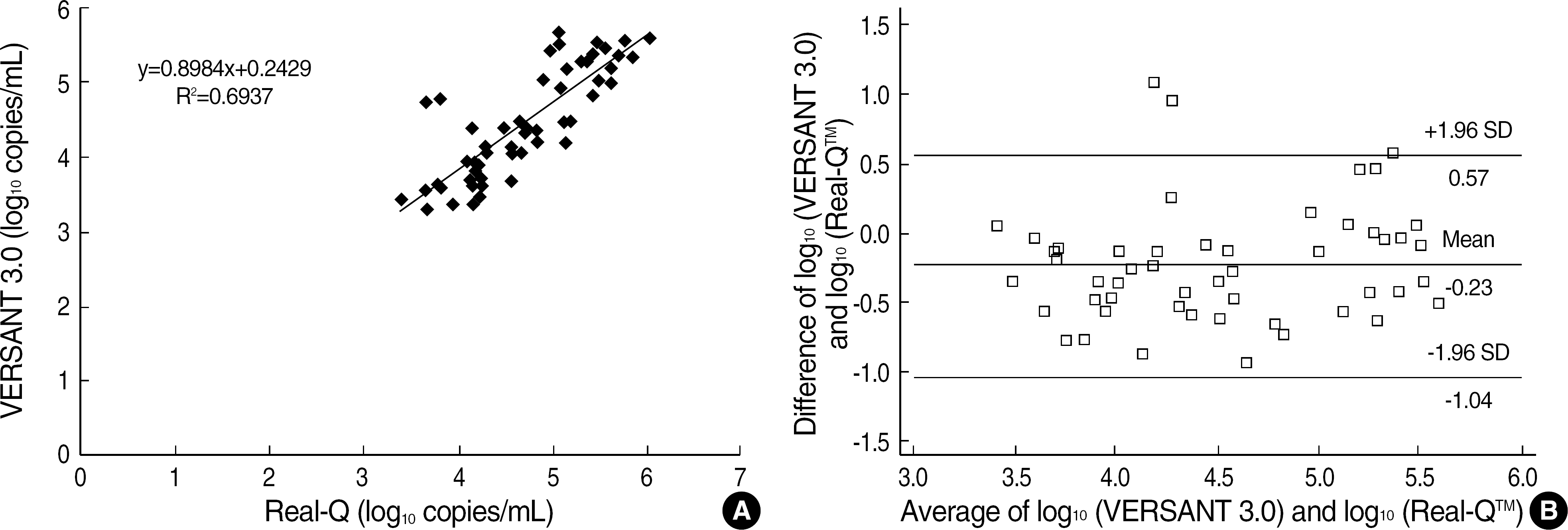 | Fig. 5.(A) Correlation of log10 quantitative HBV DNA levels between VERSANT 3.0 and Real-Q (n=55). (B) Differences in log10 quantitative HBV DNA levels between VERSANT 3.0 and Real-Q in relation to average log10 quantification (n=55). Abbreviations: nl, normal; abnl, abnormal. |
Table 1.
Distribution of HBV DNA levels measured by VERSANT 3.0 and HC-II




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download