Abstract
Background
A questionnaire survey was performed to perceive the problem of the current medical insurance reimbursement system for laboratory tests referred to independent medical laboratories; then, we intended to find a way to improve the reimbursement system.
Methods
Questionnaires were distributed to 220 independent medical laboratories and 700 laboratory physicians from July through October 2005. Frequency analysis was used to analyse the replies from 109 respondents to 25 questionnaire items regarding the current medical insurance reimbursement system for referral tests, problems with the system, and suggestions for the improvement of the system.
Results
Among the 109 respondents to this survey, 49 (45.8%) considered the current reimbursement system to be unsatisfactory, while only 16 (15.0%) answered satisfactory. The problem was that the referral clinics-not the laboratories that performed the tests–would first receive their reimbursement for the laboratory tests from Health Insurance Review Agency (HIRA) and then give a portion of the laboratory test fees to the independent medical laboratories after the deduction of administrative fees. They (62.5% of the respondents) would prefer a separated reimbursement system by which the referral clinic-as well as the independent medical laboratory-would receive their reimbursement directly from HIRA through an Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) system. In this new system, 34% of the respondents expected the quality of the laboratory tests to be improved; however, 41.6% answered that the income of the referral clinic is expected to decrease.
Conclusions
For the improvement of the medical insurance reimbursement system, the administrative fee for the referral clinic and the test fee for the independent medical laboratory should be reimbursed directly to the respective organizations. These changes could be made possible with the proper analysis of medical costs and the development of an effective EDI reimbursement system.
Go to : 
References
1. Henry JB, Kurec AS. The clinical laboratory: organization, purposes, and practice. Henry JB, editor. Clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. 20th ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2001. p. 3–7.
2. Travers ED, McClatchey KD. Basic laboratory management. MaClatchey KD, editor. Clinical laboratory medicine. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2002. p. 3–4.
3. Suh IB, Ma KR, Lee SM, Kwon JA, Bae SY, Yoon SY, et al. Management of clinical laboratory staffs in Korea (II). J Clin Pathol Qual Control. 2002; 24:237–42.
4. Mori M. Activity of clinical laboratory physicians in national health insurance. Rinsho Byori. 2005; 53:1030–5.
5. Korean Hospital Association. Standard for reference of laboratory test. 2005 Health insurance reimbursement. Jan ed. 2005; 439–44.
6. Cha YJ. Analysis of medical insurance costs. Korean J Lab Med. 2005; 25:106–12.
7. Medical Service Act: Section 12. Protection for medical technology. 2006.
Go to : 
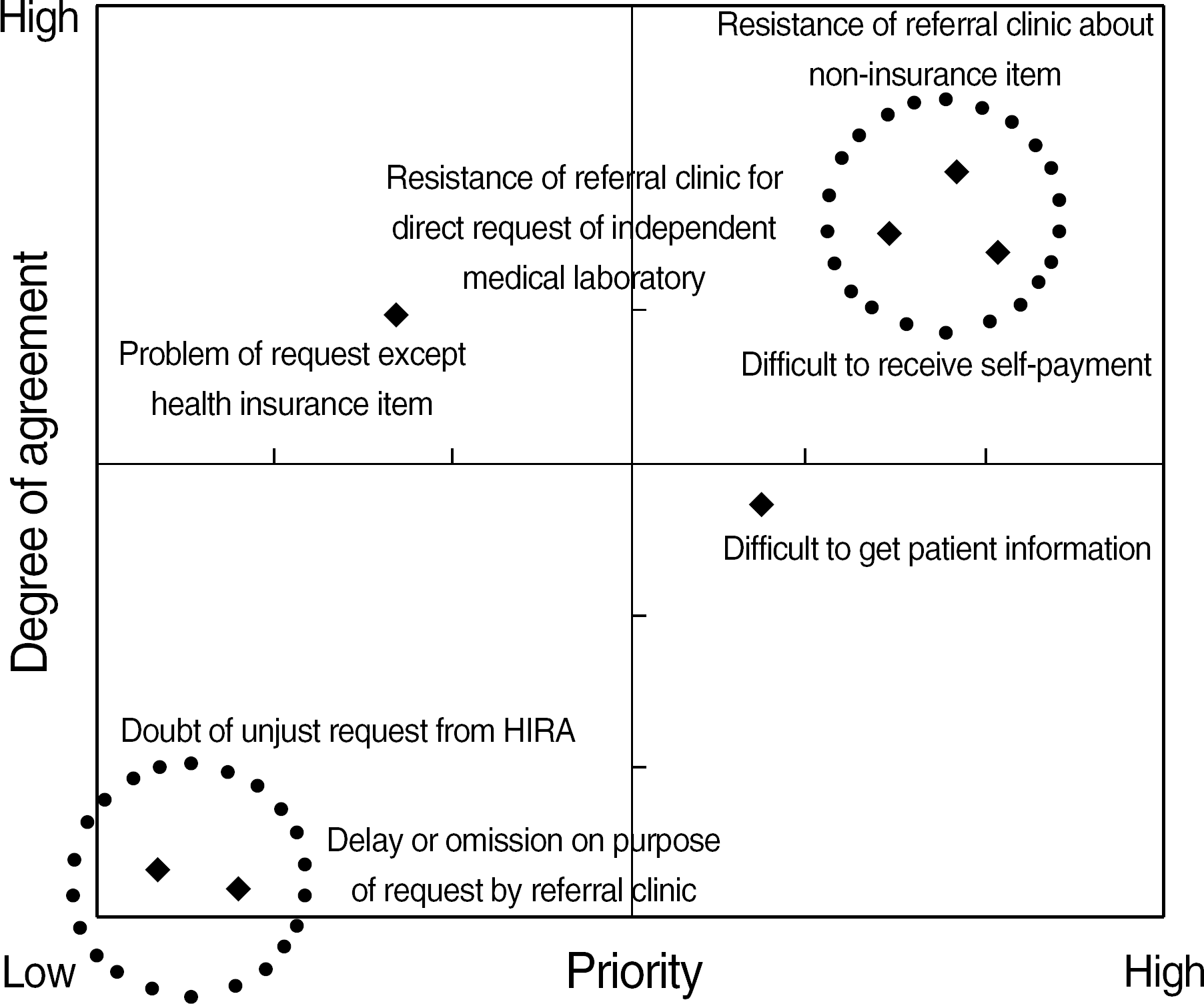 | Fig. 1.Degree of priority and agreement according to the problem of reimbursement process of referral test. |
Table 1.
Characteristics of laboratory physicians* who responded
| Number of results† (%) | |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 27 (43.5) |
| Female | 35 (56.5) |
| Total | 62 (100) |
| Years of board certification | |
| Over 20 yr | 10 (21.7) |
| 10–19 yr | 15 (32.6) |
| Less than 10 yr | 21 (45.7) |
| Total | 46 (100) |
| Hospitals and institutes | |
| Clinics | 1 (1.6) |
| Small hospitals (<200 beds) | 1 (1.6) |
| Large hospitals (>200 beds) | 20 (32.3) |
| University hospitals | 36 (58.1) |
| Independent medical laboratories | 3 (4.8) |
| Blood service centers | 1 (1.6) |
| Total | 62 (100) |
Table 2.
Levels of satisfaction at the current insurance reimbursement system
| Responders to questionnaires | Number of cases (N) |
Satisfaction levels (%) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very dissatisfied | Dissatisfied | Mean | Satisfied | Very satisfied | ||
| Independent medical laboratory* | 44 | 12 (27.3) | 6 (13.6) | 14 (31.8) | 10 (22.7) | 2 (4.5) |
| Laboratory physician† | 63 | 5 (7.9) | 26 (41.4) | 28 (44.4) | 4 (6.3) | 0 (0.0) |
| Total | 107 | 17 (15.9) | 32 (29.9) | 42 (39.3) | 14 (13.1) | 2 (1.9) |
Table 3.
Reasons for dissatisfaction at the current payment system
| Reason |
Number of responders (%) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Independent medical laboratory* | Laboratory physician† | Total | |
| Laboratory test fee not received directly from HIRA | 5 (26.3) | 21 (50.0) | 26 (42.6) |
| Referral clinics' demand for test price discount | 8 (42.1) | 14 (33.3) | 22 (36.1) |
| Difficult to receive laboratory test fee | 2 (10.5) | 4 (9.5) | 6 (9.8) |
| Other | 4 (21.1) | 3 (7.1) | 7 (11.5) |
| Total | 19 | 42 | 61 (100) |
Table 4.
Proposed improvement plans for the insurance reimbursement system
Table 5.
Effects of the improvement of reimbursement process
| Questionnaire items | Number of responders (%)* |
|---|---|
| Prohibition of test price adjustment | 42 (46.2) |
| Decrease in competition among IML for test fee | 25 (27.5) |
| Easier to receive laboratory test fee | 23 (25.3) |
| Improvement of laboratory test quality | 22 (24.2) |
| Convenience of operation process | 15 (16.5) |
| Other | 19 (20.9) |
Table 6.
Expected problems with an improved reimbursement system
| Questionnaire items | Number of responders (%)* |
|---|---|
| Difficulty of accounting for a cut in insurance reimbursement | 48 (53.9) |
| Resistance of referral clinic for direct request of an independent medical laboratory | 35 (39.3) |
| Difficulty of dealing with self-payments by patients | 21 (23.6) |
| Difficulty with billing process | 21 (23.6) |
| Difficulty of getting patient information | 11 (12.4) |
| Other | 12 (13.5) |
Table 7.
Organizational problems expected to occur when the system is changed to allow separate requests for and receipt of insurance reimbursement
| Responders to questionnaires |
Number of responders (%)* |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Referral clinic | Independent medical laboratory | HIRA* | Nowhere | |
| Independent medical laboratory* | 19 (47.5) | 10 (25.0) | 3 (7.5) | 8 (20.0) |
| Laboratory physician† | 43 (69.4) | 7 (11.3) | 3 (4.8) | 9 (14.5) |
| Total | 62 (60.8) | 17 (16.7) | 6 (5.9) | 17 (16.7) |
Table 8.
Plan of investment when the income of the independent medical laboratory increases
| Questionnaire items | Number of responders (%)* |
|---|---|
| Improvement for the quality control and accuracy of laboratory tests | 23 (46) |
| Increase in the employment of laboratory workers | 14 (28) |
| Improvement for the service to client | 9 (18) |
| Investment for facility | 5 (10) |
| Increase in the number of test items | 3 (6) |
| Improvement of turn around time | 3 (6) |
| Fee adjustment of special laboratory tests | 3 (6) |
| Increase in transparency of trade | 2 (4) |
| Setting up a department for quality control | 1 (2) |
| Adjustment of laboratory clerical fee | 1 (2) |
| Development of new technologies | 1 (2) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download