Abstract
Background
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA quantification is important for the management of HBV infection and identification of the development of resistance. The susceptibility to contamination and more variable reproducibility of results with the conventional HBV DNA quantification method have raised the need of a more simple and accurate method for HBV DNA quantification. Real-time quantitative PCR assays recently introduced in the laboratory can meet these needs. In this study, we evaluated the performance of the Real-Q HBV Quantification kit developed in Korea.
Methods
We evaluated the recovery of DNA extraction, the interference of internal control, an analytical sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility, a clinical specificity, and a reportable range of the Real-Q HBV Quantification kit. The quantification result was also compared to that obtained by the Digene Hybrid-Capture II.
Results
The mean percent recovery was 108.6% and there was no interference with the internal control on DNA extraction. None of HIV, hepatitis C virus, or cytomegalovirus showed a cross-reactivity with HBV. This assay detected HBV DNA in a linear range from 102 to 1010 copies/mL, with the detection limit of 56 copies/mL. The assay exhibited a low within-run CV (coefficient of variation) (8.7–11.9%), between-run CV (10.5–14.7%), and between-day CV (13.2–21.4%). No HBV DNA was detected in any of 100 samples without HBV, resulting in a clinical specificity of 100%. The levels of HBV DNA showed a good correlation with those determined with Digene Hybrid-Capture II (R2=0.9827).
References
1. Gerken G, Gomes J, Lampertico P, Colombo M, Rothaar T, Trippler M, et al. Clinical evaluation and applications of the Amplicor HBV Monitor test, a quantitative HBV DNA PCR assay. J Virol Methods. 1998; 74:155–65.

2. Kessler HH, Pierer K, Santner BI, Vellimedu SK, Stelzl E, Lackner H, et al. Quantitative detection of hepatitis B virus DNA with a new PCR assay. Clin Chem Lab Med. 1998; 36:601–4.

3. Urdea MS, Horn T, Fultz TJ, Anderson M, Running JA, Hamren S, et al. Branched DNA amplification multimers for the sensitive, direct detection of human hepatitis viruses. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1991; 24:197–200.
4. Hendricks DA, Stowe BJ, Hoo BS, Kolberg J, Irvine BD, Neuwald PD, et al. Quantitation of HBV DNA in human serum using a branched DNA (bDNA) signal amplification assay. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995; 104:537–46.

5. Pawlotsky JM, Bastie A, Lonjon I, Remire J, Darthuy F, Soussy CJ, et al. What technique should be used for routine detection and quantification of HBV DNA in clinical samples? J Virol Methods. 1997; 65:245–53.

6. Pawlotsky JM, Bastie A, Hezode C, Lonjon I, Darthuy F, Remire J, et al. Routine detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA in clinical laboratories: performance of three commercial assays. J Virol Methods. 2000; 85:11–21.

7. Kohmoto M, Enomoto M, Yano Y, Otani S, Minamitani S, Tamori A, et al. Detection of serum hepatitis B virus DNA by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (TaqMan PCR) during lamivudine treatment: comparison with three other assays. Hepatol Res. 2003; 26:125–33.

8. Brechtbuehl K, Whalley SA, Dusheiko GM, Saunders NA. A rapid real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction for hepatitis B virus. J Virol Methods. 2001; 93:105–13.

9. Paraskevis D, Haida C, Tassopoulos N, Raptopoulou M, Tsantoulas D, Papachristou H, et al. Development and assessment of a novel real-time PCR assay for quantitation of HBV DNA. J Virol Methods. 2002; 103:201–12.

10. Mackay IM. Real-time PCR in the microbiology laboratory. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004; 10:190–212.

11. Clegg RM. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer and nucleic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1992; 211:353–88.
12. Selvin PR. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Methods Enzymol. 1995; 246:300–34.
13. Holland PM, Abramson RD, Watson R, Gelfand DH. Detection of specific polymerase chain reaction product by utilizing the 5′—3′ exonuclease activity of Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991; 88:7276–80.

14. Lee LG, Connell CR, Bloch W. Allelic discrimination by nick-translation PCR with fluorogenic probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993; 21:3761–6.
16. WHO. Hepatitis B. Fact Sheet No. 204. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs204/en/. (Revised on October. 2000.
17. Kim SH, Kim JW, Park S, Cho EH, Kim EJ, Park SS, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in diagnostic genetics in Korea (2004). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2005; 27:141–65.
18. Lee HC, Suh DJ, Ryu SH, Kim H, Shin JW, Lim YS, et al. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for serum hepatitis B virus DNA as a predictive factor for post-treatment relapse after lamivudine induced hepatitis B e antigen loss or seroconversion. Gut. 2003; 52:1779–83.

19. Klein D. Quantification using real-time PCR technology: applications and limitations. Trends Mol Med. 2002; 8:257–60.

20. Bell AS, Ranford-Cartwright LC. Real-time quantitative PCR in parasitology. Trends Parasitol. 2002; 18:337–42.

21. Ginzinger DG. Gene quantification using real-time quantitative PCR: an emerging technology hits the mainstream. Exp Hematol. 2002; 30:503–12.
22. Kuhne BS, Oschmann P. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR using hybridization probes and imported standard curves for cytokine gene expression analysis. Biotechniques. 2002; 33:1078–84.

23. Kubista M, Andrade JM, Bengtsson M, Forootan A, Jonak J, Lind K, et al. The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Mol Aspects Med. 2006; 27:95–125.

24. Ho SK, Yam WC, Leung ET, Wong LP, Leung JK, Lai KN, et al. Rapid quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA by real-time PCR using fluorescent hybridization probes. J Med Microbiol. 2003; 52:397–402.

25. Weiss J, Wu H, Farrenkopf B, Schultz T, Song G, Shah S, et al. Real time TaqMan PCR detection and quantitation of HBV genotypes A-G with the use of an internal quantitation standard. J Clin Virol. 2004; 30:86–93.

26. Zanella I, Rossini A, Domenighini D, Albertini A, Cariani E. Quantitative analysis of hepatitis B virus DNA by real-time amplification. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002; 21:22–6.

27. Hochberger S, Althof D, Gallegos de Schrott R, Nachbaur N, Rock H, Leying H. Fully automated quantitation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA in human plasma by the COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan system. J Clin Virol. 2006; 35:373–80.
Fig. 1.
Quantitative correlation between reference from HBV viral DNA assay validation kit (AcroMetrix corporation) and observed value by Real-Q HBV Quantification kit (BioSewoom Inc.).
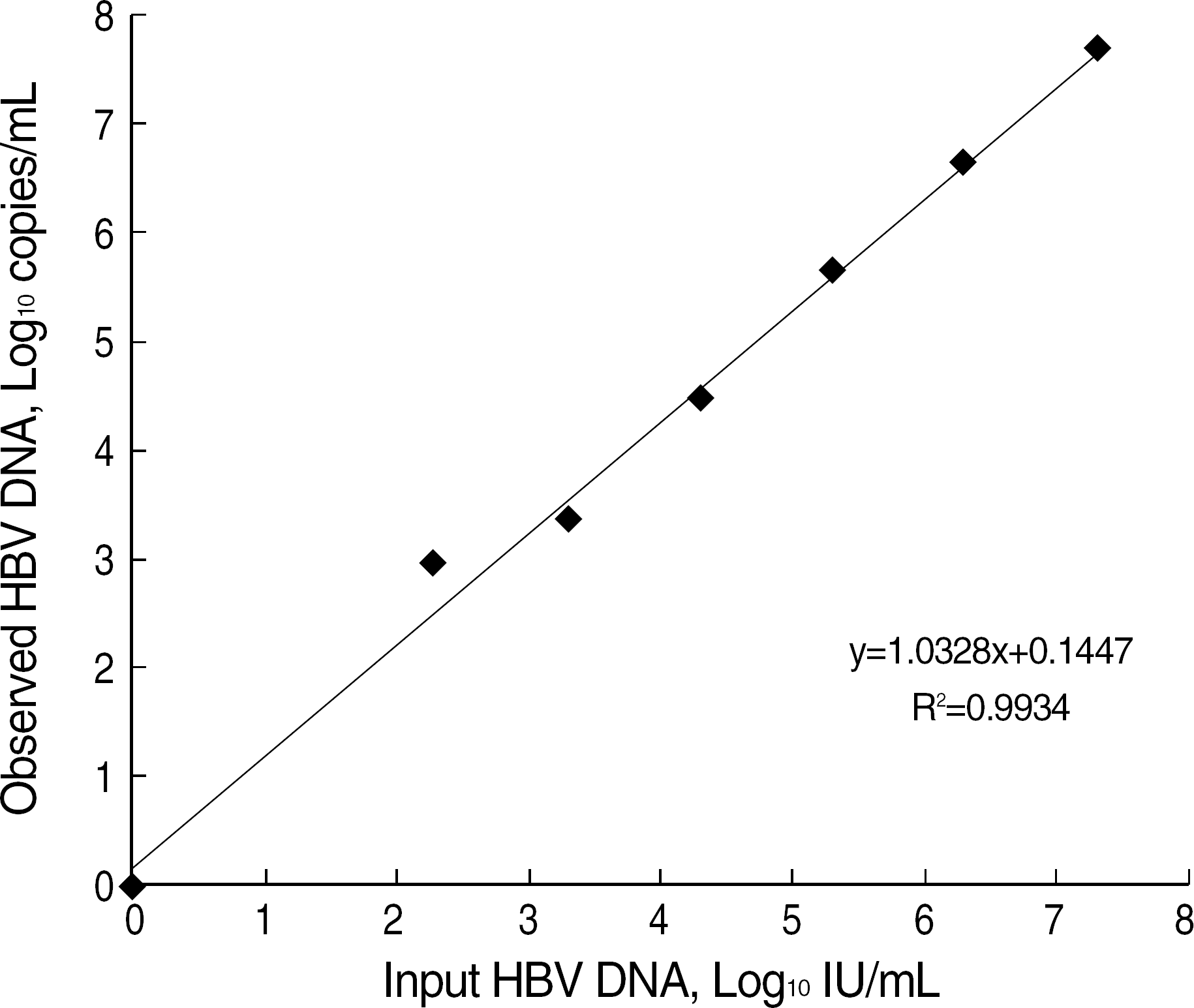
Fig. 2.
Linearity range of Real-Q HBV Quantification kit (BioSewoom Inc.). The straight line was determined by a linear regression of the log 10 estimated concentrations with the log 11 nominal concentrations. Linearity was found from 102 to 1010 copies/mL.
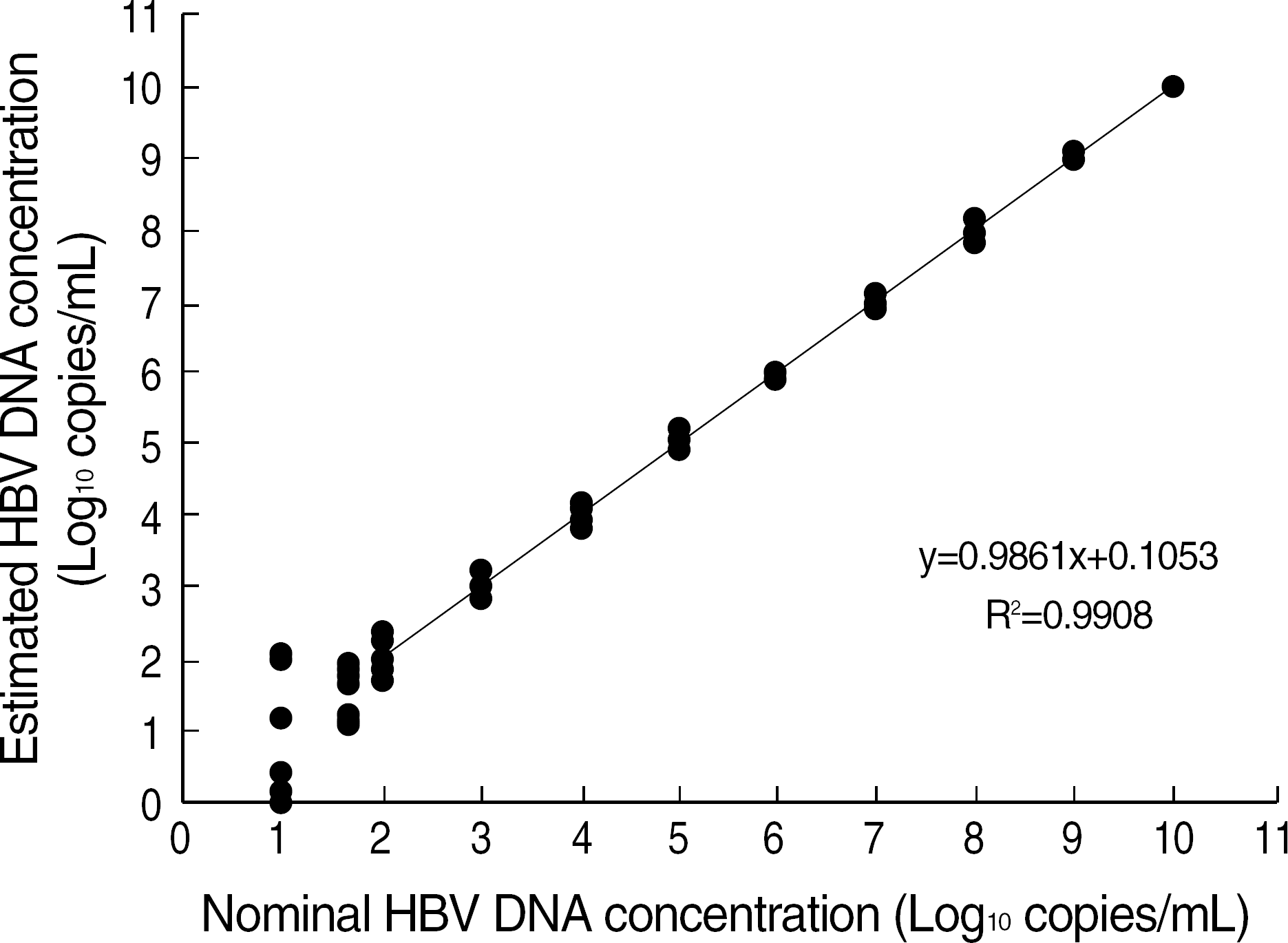
Fig. 3.
Quantitative comparison of Real-Q HBV Quantification kit (BioSewoom Inc.) with Digene Hybrid-Capture II (Murex Diagnostics).
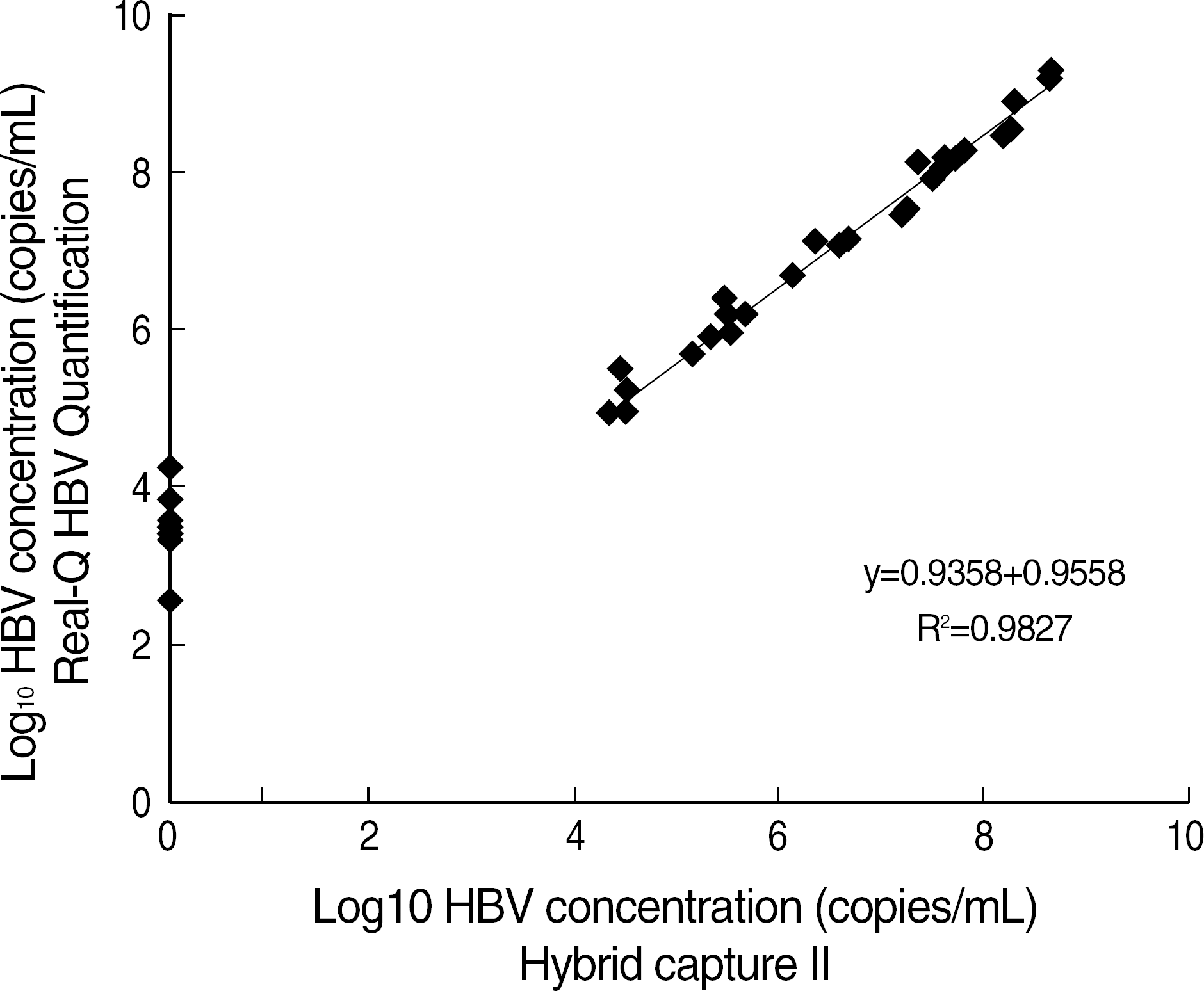
Table 1.
Detection limit of Real-Q HBV Quantification kit
| Input HBV (copies/mL) |
Result |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Replicates | Positive reaction | % | |
| 225 | 50 | 50 | 100 |
| 112.5 | 50 | 50 | 100 |
| 84 | 50 | 49 | 98 |
| 56 | 50 | 48 | 96 |
| 28 | 50 | 39 | 88 |
Table 2.
Analytical specificity of Real-Q HBV Quantification kit




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download