Abstract
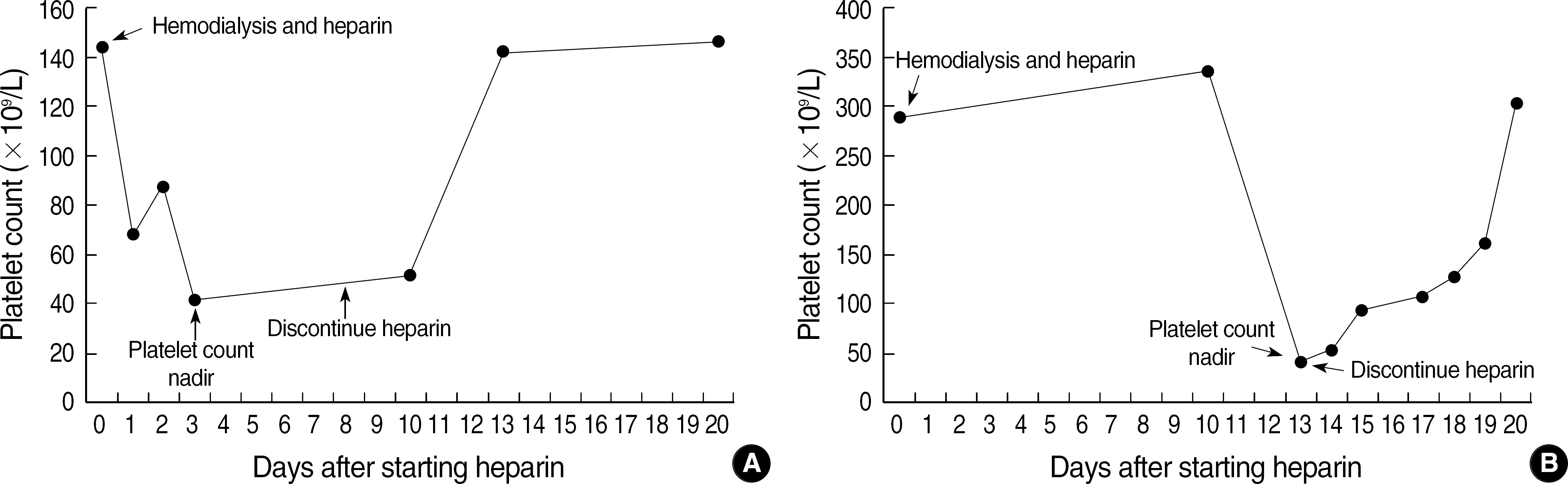
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a serious complication of heparin therapy. It represents initially as thrombocytopenia and is associated with venous or arterial thrombosis. It has been reported that platelet factor 4/heparin complex antibody plays an important role in the pathogenesis of HIT. Patients on hemodialysis have a high risk of developing HIT because heparin is administrated in hemodialysis as anticoagulant. Thrombocytopenia usually occurs 5 to 10 days after the onset of administration, but occasionally, it may occur rapidly in patients who have preformed antibodies from recent heparin use. We report here 2 cases of HIT with platelet factor 4-heparin reactive antibody in hemodialysis patients.
References
1. Rice L, Attisha WK, Drexler A, Francis JL. Delayed-onset heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Ann Intern Med. 2002; 136:210–5.

2. Warkentin TE, Kelton JG. Delayed-onset heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis. Ann Intern Med. 2001; 135:502–6.

3. Warkentin TE. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: pathogenesis and management. Br J Haematol. 2003; 121:535–55.

4. Warkentin TE, Kelton JG. Temporal aspects of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:1286–92.

5. Lubenow N, Kempf R, Eichner A, Eichler P, Carlsson LE, Greinacher A. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: temporal pattern of thrombocytopenia in relation to initial use or reexposure to heparin. Chest. 2002; 122:37–42.
8. Yim SH, Kim HO, Song KS, Choi IS. A case of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1987; 7:259–63.
9. Jeong HJ, Kim JK, Choi JY, Yoon SZ, Jeon YS, Park KU, et al. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia during continuous Veno-Venous hemodiafiltration after total aortic arch replacement-A case report-. Korean J Anesth. 2006; 50:600–3.
10. Warkentin TE, Kelton JG. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1991; 10:1–34.
12. Yamamoto S, Koide M, Matsuo M, Suzuki S, Ohtaka M, Saika S, et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996; 28:82–5.

13. Visentin GP, Ford SE, Scott JP, Aster RH. Antibodies from patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/thrombosis are specific for platelet factor 4 complexed with heparin or bound to endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1994; 93:81–8.

14. Suh JS, Malik MI, Aster RH, Visentin GP. Characterization of the humoral immune response in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am J Hematol. 1997; 54:196–201.

15. Kim KY, Chang YJ, Suh JS, Kim JS. Characterization of Heparin:PF4 isoantibody interaction to platelets in Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/thrombosis. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1997; 17:944–55.
16. Warkentin TE, Levine MN, Hirsh J, Horsewood P, Roberts RS, Gent M, et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients treated with low-molecular weight heparin or unfractionated heparin. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332:1330–5.
17. Warkentin TE, Roberts RS, Hirsh J, Kelton JG. An improved definition of immune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in postoperative orthopedic patients. Arch Intern Med. 2003; 163:2518–24.

18. Lee DH, Warkentin TE. Frequncy of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Warkentin TE, Greinacher A, editors. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. 3rd ed.New York, NY: Marcel Dekker;2004. p. 107–48.
19. Warkentin TE, Kelton JG. A 14-year study of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am J Med. 1996; 101:502–7.

20. Wallis DE, Workman DL, Lewis BE, Steen L, Pifarre R, Moran JF. Failure of early heparin cessation as treatment for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am J Med. 1999; 106:629–35.

21. Sheridan D, Carter C, Kelton JG. A diagnostic test for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood. 1986; 67:27–30.

22. Vinsentin GP, Ford SE, Scott JP, Aster RH. Antibodies from patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/thrombosis are specific for platelet factor 4 complexed with heparin or bound to endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1994; 93:81–8.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download