Abstract
Parathyroid adenoma is a benign neoplasm and accounts for 80∼90% of primary hyperparathyroidism. It is usually accompanied by hypercalcemia, and parathyroid adenomas with normal levels of serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcium have been rarely reported in the literature. We report the case of a 16-year-old female with a large anterior neck mass who had a parathyroid adenoma without hyperparathyroidism. She underwent right thyroid lobectomy due its misinterperetation as a thyroid tumor thenultimately discovered to have been a parathyroid lesion.
References
1. Herrera MF, Gamboa-Dominguez A. Parathyroid embrylogy, anatomy, and pathology. Clark OH, Duh OY, Kebebew E, editors. Textbook of Endocrine Surgery. 2nd ed.Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;2006. p. 365–71.
2. Absher KJ, Truong LD, Khurana KK, Ramzy I. Parathyroid cytology: avoiding diagnostic ptifalls. Head Neck. 2002; 24:157–64.
3. Shim WS, Kim IK, Yoo SD, Kim DH. Non-functional parathyroid adenoma presenting as a massive cervical hematoma: A case report. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2008; 1:46–8.

4. Hotouras A, Sinha P. Parathyroid incidentalomas: case report and literature review. Grand Rounds. 2007; 7:45–7.
5. Abboud B, Sleilaty G, Braidy C, Ghorra C, Abadjian G, Tohme C, et al. Enlarged parathyroid glands discovered in normo-calcemic patients during thyroid surgery. Am J Surg. 2008; 195:30–3.

6. Carnaille BM, Pattou FN, Oudar C, Lecomte-Houcke MC, Rocha JE, Proye CA. Parathyroid incidentalomas in normo-calcemic patients during thyroid surgery. World J Surg. 1996; 20:830–4.

7. Kwak JY, Kim EK, Moon HJ, Ahn SS, Son EJ, Sohn YM. Parathyroid incidentalomas detected on routine ultrasound- di-rected fine-needle aspiration biopsy in patients referred for thyroid nodules and the role of parthyroid hormone analysis in the samples. Thyroid. 2009; 19:743–8.
8. Frasoldati A, Pesenti M, Toschi E, Azzarito C, Zini M, Valcavi R. Detection and diagnosis of parathyorid incidentalomas during thyroid sonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 1999; 27:492–8.
Fig. 1.
Cytologic findings of neck mass. Fine needle aspiration cytology was performed for neck mass with suspected thyroid tumor. The aspiration smear shows cellular and monomorphic population of small cells in three dimensional cluster and follicles. The cells has moderate amount of cytoplasm and small and round nuclei with stippled chroma-tin (Papanicolaou stain, ×400).
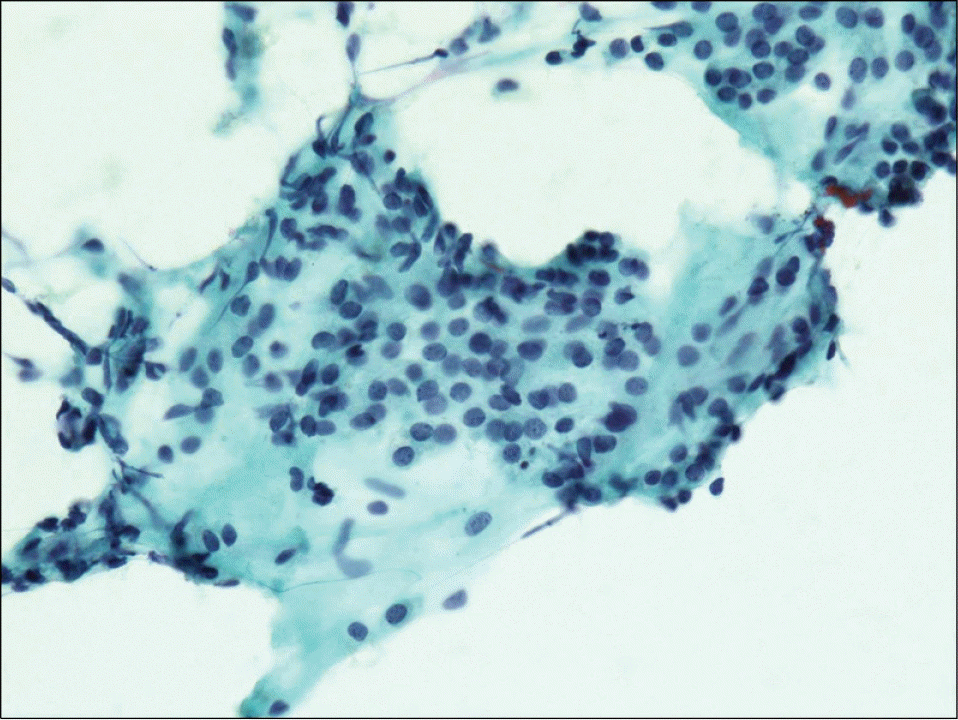
Fig. 2.
Findings of the neck ultrasonography. About 4.5×3.6 cm in size, oval shaped hypoechoic mass (M) is noted in the posterior aspect of the right thyroid gland (T). Although the origin of the tumor is unclear, the boundary with the surroundings is relatively well demarcated and the tumor has proliferated solidly.
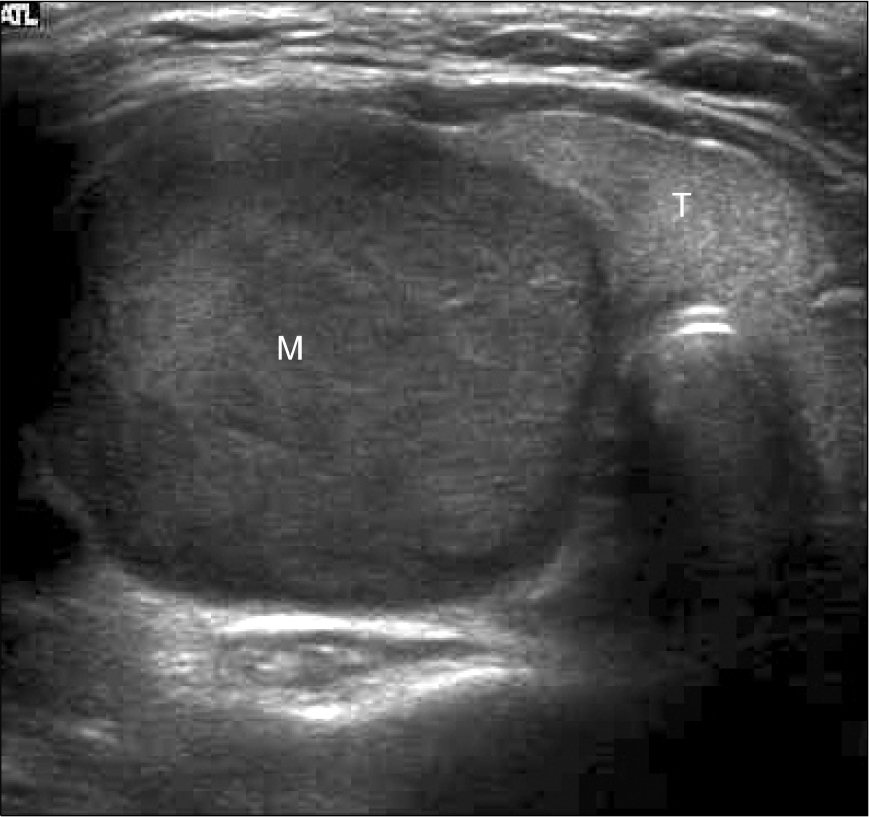
Fig. 3.
CT of the neck. An isodense mass with internal low attenuating area is noted in the posterior aspect of the right thyroid gland. It looks exophytic mass from the thyroid gland and the trachea with the left thyroid gland are displaced to the left side.
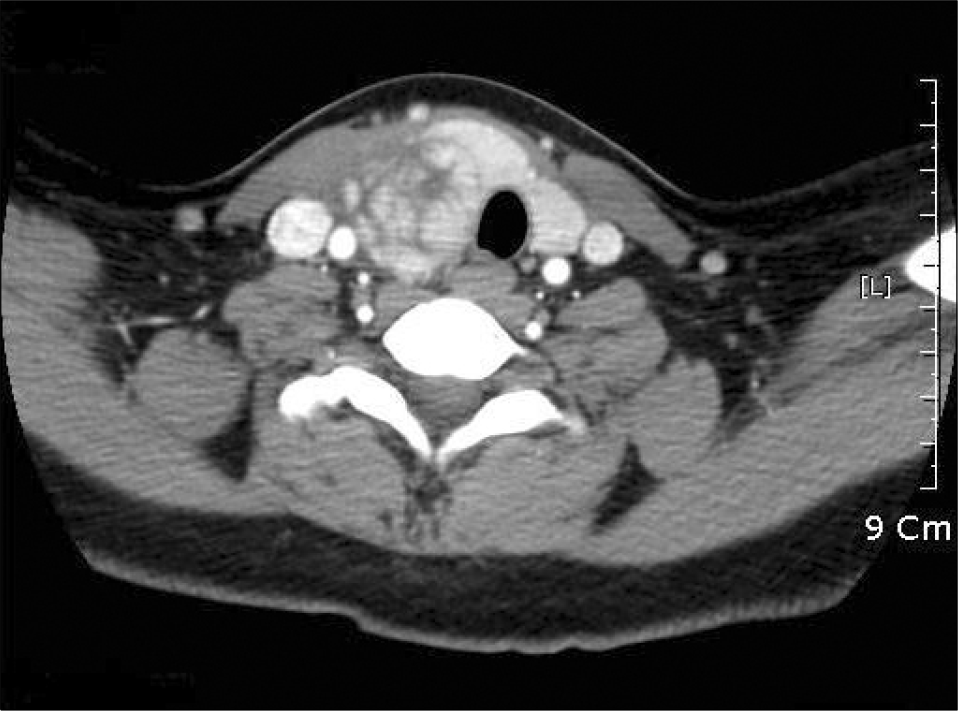




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download