Abstract
Purpose
Recently, there have been several studies on the early results of hepatectomy for various intrahepatic lesions. We report the early experience of our hospital after total laparoscopic left hepatectomy in patients with intrahepatic stones in the left hemi-liver.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of patients who were diagnosed with left intrahepatic stones and underwent hepatectomy between January 2007 and June 2009. The patients were grouped according to operative procedure into open hepatectomy, laparoscopy-assisted hepatectomy, and total laparoscopic hepatectomy.
Results
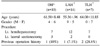
There were 31 patients who underwent Lt hemihepatectomy and Lt lateral sectionectomy during this period. Hepatectomy with open method, laparoscopy-assisted method, and total laparoscopy method were performed in 10, 14, and 7 cases. There were no significant differences between the three methods for operating time and postoperative complications. But the number of fasting times and hospital days was shorter with total laparoscopic hepatectomy than with others.
Conclusion
Total laparoscopic liver resection is a safe and useful method for treating patients with intrahepatic stones and offers the advantage of quick patient recovery. Careful selection of appropriate patients and further development in the laparoscopic surgical technique resulting from accumulated experiences will help enable the laparoscopic hepatectomy to be performed more easily and safely in patients with intrahepatic stones.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Port site. (1) 10 mm camera; (2) 10 mm assist right hand; (3) 5 mm surgeon left hand; (4) 12 mm surgeon right hand; (5) 5 mm assist left hand.
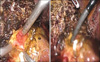
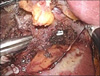
Fig. 3
After liver resection, using the suction device and catheter, remnant bile duct stone removed as many as possible, and then choledocoscopy was inserted to resected bile duct.
References
1. Gagner M, Rogula T, Selzer D. Laparoscopic liver resection: benefits and controversies. Surg Clin North Am. 2004. 84:451–462.
2. Cherqui D, Husson E, Hammoud R, Malassagne B, Stephan F, Bensaid S, et al. Laparoscopic liver resections: a feasibility study in 30 patients. Ann Surg. 2000. 232:753–762.
3. Descottes B, Lachachi F, Sodji M, Valleix D, Durand-Fontanier S, Pech de Laclause B, et al. Early experience with laparoscopic approach for solid liver tumors: initial 16 cases. Ann Surg. 2000. 232:641–645.
4. Gagner M, Rheault M, Dubuc J. Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy for liver tumor [abstract]. Surg Endosc. 1992. 6:99.
5. Fabiani P, Katkhouda N, Iovine L, Mouiel J. Laparoscopic fenestration of biliary cysts. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1991. 1:162–165.
6. Lefor AT, Flowers JL. Laparoscopic wedge biopsy of the liver. J Am Coll Surg. 1994. 178:307–308.
7. Morino M, De Giuli M, Festa V, Garrone C. Laparoscopic management of symptomatic nonparasitic cysts of the liver. Indications and results. Ann Surg. 1994. 219:157–164.
8. John TG, Greig JD, Crosbie JL, Miles WF, Garden OJ. Superior staging of liver tumors with laparoscopy and laparoscopic ultrasound. Ann Surg. 1994. 220:711–719.
9. Ferzli G, David A, Kiel T. Laparoscopic resection of a large hepatic tumor. Surg Endosc. 1995. 9:733–735.
10. Kaneko H, Takagi S, Shiba T. Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy and left lateral segmentectomy: technique and results of a clinical series. Surgery. 1996. 120:468–475.
11. Fong Y, Jarnagin W, Conlon KC, DeMatteo R, Dougherty E, Blumgart LH. Hand-assisted laparoscopic liver resection: lessons from an initial experience. Arch Surg. 2000. 135:854–859.
12. Watanabe Y, Sato M, Ueda S, Abe Y, Iseki S, Horiuchi A, et al. Laparoscopic hepatic resection: a new and safe procedure by abdominal wall lifting method. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997. 44:143–147.
13. Huscher CG, Lirici MM, Chiodini S. Laparoscopic liver resections. Semin Laparosc Surg. 1998. 5:204–210.
14. Kim CG, Yoon YS, Han HS, Shin SH, Chun KS, Jang JY, et al. Experience of total laparoscopic hepatectomy. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007. 73:490–495.
15. Min SK, Han HS, Kim SW, Park YH, Lee HO, Lee JH. Initial experiences with laparoscopy-assisted and total laparoscopy for anatomical liver resection: a preliminary study. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:69–74.
16. Min SK, Han HS, Lee HK, Jie S, Yu K, Yi NJ, et al. Totally laparoscopic anatomic liver resection. J Korean Surg Soc. 2003. 64:390–395.
17. Cai X, Wang Y, Yu H, Liang X, Peng S. Laparoscopic hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis: a feasibility and safety study in 29 patients. Surg Endosc. 2007. 21:1074–1078.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download