Abstract
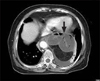
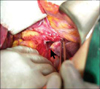
Paraesophageal hernias are usually classified into three distinct types: type I, sliding hernias; type II, paraesophageal hernias; type III, a combination of type I and II. Herniation of other abdominal organs can be classified as type IV, and is a rare situation at the esophageal hiatus. We report herein a 73-year-old female patient who presented with epigastric pain and diagnosed as type IV paraesophageal hernia. Initial evaluation was focused on myocardial ischemia. There was no evidence of myocardial ischemia in the coronary angiography, but follow-up chest X-ray revealed air-fluid levels in the left mediastinum suggested hiatal hernia. On computed tomography, herniation and strangulation of proximal jejunum into the hemithorax via left diaphragmatic defect was found. After reduction of small bowel and resection of strangulated segment, the defect was closed. Fluid collection in the hernia sac was detected at postoperative day nine, but she was discharged without complication.
Figures and Tables
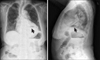
Fig. 1
Chest PA/lateral Jejunal dilatation in upper abdomen with air-fluid level in left mediastinum (arrow).
References
1. Kim HS, Baek HK. Laparoscopic repairing of diaphragmatic hernia. J Korean Surg Soc. 2005. 69:485–487.
2. Kim KC, Park HJ, Yoon DS, Chi HS, Lee WJ, Lee KS, et al. A case of paraesophageal hernia repaired by laparoscopic approach. Yonsei Med J. 1996. 37:151–157.
3. Itano H, Okamoto S, Kodama K, Horita N. Transthoracic Collis-Nissen repair for massive type IV paraesophageal hernia. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008. 56:446–450.
4. Kahrilas PJ, Kim HC, Pandolfino JE. Approaches to the diagnosis and grading of hiatal hernia. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008. 22:601–616.
5. Basaklar AC, Sonmez K, Karabulut R, Turkyilmaz Z, Moralioglu S. An unusual case: a giant paraesophageal hiatalhernia with intrathoracic spleen, preduodenal portal vein, malrotation, and left inferior vena cava. J Pediatr Surg. 2007. 42:e23–e25.
6. Gallimidi Z, Brook OR, Militianu D, Engel A. Liver herniation through gastroesophageal hiatus of diaphragm. Eur J Radiol Extra. 2004. 51:119–120.
7. Grushka JR, Grenon SM, Ferri LE. A type IV paraesophageal hernia containing a volvulized sigmoid colon. Dis Esophagus. 2008. 21:94–96.
8. Sivacolundhu RK, Read RA, Marchevsky AM. Hiatal hernia controversies--a review of pathophysiology and treatment options. Aust Vet J. 2002. 80:48–53.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download