Abstract
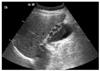
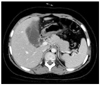
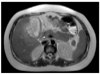
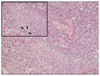
Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis (XGC) is known to be a rare, variant type of chronic cholecystitis and more frequently found in the adults with a prevalence of 0.7 to 13.2% of all cholecystitis, moreover very rare in children. Clinically, this usually presents as chronic or acute cholecystitis associated with gallstones, but biliary colic is unusual. Although it requires surgery for management, it may accompany some difficulties during cholecystectomy and postoperative complications such as biliary fistula. It could also give rise to higher conversion rates than other diseases of the gallbladder during laparoscopic procedures. We experienced a very rare pediatric case of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis not associated with gallstones, successfully managed by laparoscopic cholecystectomy and hereby report it with literature reviews.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Goodman ZD, Ishak KG. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1981. 5:653–659.
2. Kwon AH, Matsui Y, Uemura Y. Surgical procedures and histopathologic findings for patients with xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. J Am Coll Surg. 2004. 199:204–210.
3. Howard TJ, Bennion RS, Thompson JE Jr. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: a chronic inflammatory pseudotumor of the gallbladder. Am Surg. 1991. 57:821–824.
4. Hanada K, Nakata H, Nakayama T, Tsukamoto Y, Terashima H, Kuroda Y, et al. Radiologic findings in xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987. 148:727–730.
5. Kawana T, Suita S, Arima T, Hirayama Y, Ishii K, Minamishima I, et al. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis in an infant with obstructive jaundice. Eur J Pediatr. 1990. 149:765–767.
6. Fligiel S, Lewin KJ. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: case report and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1982. 106:302–304.
7. Guzman-Valdivia G. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: 15 years' experience. World J Surg. 2004. 28:254–257.
8. Dixit VK, Prakash A, Gupta A, Pandey M, Gautam A, Kumar M, et al. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1998. 43:940–942.
9. Parra JA, Acinas O, Bueno J, Guezmes A, Fernandez MA, Farinas MC. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: clinical, sonographic, and CT findings in 26 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:979–983.
10. Chun KA, Ha HK, Yu ES, Shinn KS, Kim KW, Lee DH, et al. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: CT features with emphasis on differentiation from gallbladder carcinoma. Radiology. 1997. 203:93–97.
11. Yang T, Zhang BH, Zhang J, Zhang YJ, Jiang XQ, Wu MC. Surgical treatment of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: experience in 33 cases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007. 6:504–508.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download