Abstract
Purpose
We are to describe the incidence and accordance rate of hernia type in synchronous bilateral and metachronous contralateral inguinal hernia.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 625 adult patients who underwent inguinal hernia repair by a single surgeon at our institute between November 2001 and October 2008. We divided the patients into 3 groups; Synchronous bilateral inguinal hernia group (SH), Metachronous contralateral inguinal hernia group (MH) and Unilateral inguinal hernia group (UH) and analyzed patients' general clinical features and outcomes.
Results
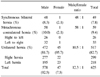
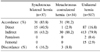
Male patients numbered 578 (92.5%) and female patients numbered 47 (7.5%), so the male to female ratio was 12.3:1. Each number of SH and MH were 49 (7.8%) and 59 (9.4%). In MH, the mean interval of counterlateral hernia development following ipsilateral hernia repair was 8.9 years and 20 (33.9%) were developed in a 3-year period. And the incidence of right hernia development after repair of left hernia predominated over left hernia development after repair of right hernia by a ratio of 1.27:1. Accordance rate of hernia type in both sides was 83.8% in SH and 91.2% in MH.
Conclusion
The incidence of SH and MH were each 7.8% and 9.4% and accordance rate of hernia type is very high in SH and MH. In MH, many patients (33.9%) developed in 3 years after ipsilateral hernia repair. In this study, patients have high accordance rate of hernia type in both sides and indirect type is dominant, especially in MH.
Figures and Tables
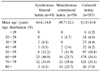
Table 1
Age distribution at the time of symptom onset in synchronous bilateral, metachronous contralateral and unilateral hernia
References
1. Kark AE, Belsham PA, Kurzer MN. Simultaneous repair of bilateral groin hernias using local anaesthesia: a review of 199 cases with a five-year follow-up. Hernia. 2005. 9:131–133.
2. Schmedt CG, Daubler P, Leibl BJ, Kraft K, Bittner R. Simultaneous bilateral laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: an analysis of 1336 consecutive cases at a single center. Surg Endosc. 2002. 16:240–244.
3. Tackett LD, Breuer CK, Luks FI, Caldamone AA, Breuer JG, DeLuca FG, et al. Incidence of contralateral inguinal hernia: a prospective analysis. J Pediatr Surg. 1999. 34:684–688.
4. Jung SW, Heo TG, Lee JM, Choi PW, Park JH, Lee MS, et al. Clinical analysis of 473 cases of inguinal hernia in adult patients. J Korean Surg Soc. 2008. 75:109–115.
5. Dakkuri RA, Ludwig DJ, Traverso LW. Should bilateral inguinal hernias be repaired during one operation? Am J Surg. 2002. 183:554–557.
6. Sayad P, Abdo Z, Cacchione R, Ferzli G. Incidence of incipient contralateral hernia during laparoscopic hernia repair. Surg Endosc. 2000. 14:543–545.
7. Kald A, Domeij E, Landin S, Wiren M, Anderberg B. Laparoscopic hernia repair in patients with bilateral groin hernias. Eur J Surg. 2000. 166:210–212.
8. Manoilo MV. Treatment of bilateral inguinal hernia. Klin Khir. 2006. 8:34–36.
9. Zamakhshardy M, Ein A, Ein SH, Wales PW. Predictors of metachronous inguinal hernias in children. Pediatr Surg Int. 2009. 25:69–71.
10. Gilbert AI. Simultaneous repair of bilateral groin hernias using local anaesthesia. Hernia. 2005. 9:401.
11. Beitler JC, Gomes SM, Coelho AC, Manso JE. Complex inguinal hernia repairs. Hernia. 2009. 13:61–66.
12. Fernandez-Lobato R, Tartas-Ruiz A, Jimenez-Miramon FJ, Marin-Lucas FJ, de Adana-Belbel JC, Esteban ML. Stoppa procedure in bilateral inguinal hernia. Hernia. 2006. 10:179–183.
13. Berndsen F, Petersson U, Montgomery A. Endoscopic repair of bilateral inguinal hernias--short and late outcome. Hernia. 2001. 5:192–195.
14. Gainant A, Geballa R, Bouvier S, Cubertafond P, Mathonnet M. Prosthetic treatment of bilateral inguinal hernias via laparoscopic approach or Stoppa procedure. Ann Chir. 2000. 125:560–565.
15. Bochkarev V, Ringley C, Vitamvas M, Oleynikov D. Bilateral laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair in patients with occult contralateral inguinal defects. Surg Endosc. 2007. 21:734–736.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download