Abstract
Purpose
Triple negative breast cancer (estrogen receptor-negative, progesterone receptor-negative, and HER2/neu negative) is associated with high risk of recurrence and poor prognosis. We investigated the characteristics and prognosis of triple negative early-stage breast cancer.
Methods
We reviewed the records of 821 early-stage breast cancer patients treated at our hospital from 1995 to 2005. We studied the differences between a triple negative group compared with a non-triple negative group.
Results
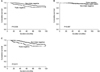
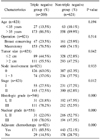
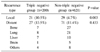
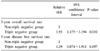
Of 821 early-stage breast cancer patients, 200 (24.4%) were classified as triple negative. Large tumors (>2 cm) in the triple negative group were significantly more than those in the non-triple negative group (P=0.042). Histologic and nuclear grade of the triple negative group were significantly higher than those of the non-triple negative group (P<0.001). The median follow-up time is 50 months (1~135). There have been 50 local recurrences, 98 distant metastases, and 65 deaths. There were high rates of local recurrence in the triple negative group but no difference in 5-year disease free survival rates (P=0.178). The 5-year overall survival rate showed 85% in the triple negative group but 92.8% in the non-triple negative group (P=0.008). The relative risk for overall survival was 1.93 times higher in the triple negative group.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000. 406:747–752.
2. Banerjee S, Reis-Filho JS, Ashley S, Steele D, Ashworth A, Lakhani SR, et al. Basal-like breast carcinomas: clinical outcome and response to chemotherapy. J Clin Pathol. 2006. 59:729–735.
3. Konecny G, Pauletti G, Pegram M, Untch M, Dandekar S, Aguilar Z, et al. Quantitative association between HER-2/neu and steroid hormone receptors in hormone receptor-positive primary breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003. 95:142–153.
4. Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989. 244:707–712.
5. Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, et al. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:5367–5374.
6. Cleator S, Heller W, Coombes RC. Triple-negative breast cancer: therapeutic options. Lancet Oncol. 2007. 8:235–244.
7. Siziopikou KP, Cobleigh M. The basal subtype of breast carcinomas may represent the group of breast tumors that could benefit from EGFR-targeted therapies. Breast. 2007. 16:104–107.
8. Yuli C, Shao N, Rao R, Aysola P, Reddy V, Oprea-llies G, et al. BRCA1a has antitumor activity in TN breast, ovarian and prostate cancers. Oncogene. 2007. 26:6031–6037.
9. Livasy CA, Karaca G, Nanda R, Tretiakova MS, Olopade OI, Moore DT, et al. Phenotypic evaluation of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2006. 19:264–271.
10. van de Rijn M, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Haas P, Kallioniemi O, Kononen J, et al. Expression of cytokeratins 17 and 5 identifies a group of breast carcinomas with poor clinical outcome. Am J Pathol. 2002. 161:1991–1996.
11. Abd El-Rehim DM, Pinder SE, Paish CE, Bell J, Blamey RW, Robertson JF, et al. Expression of luminal and basal cytokeratins in human breast carcinoma. J Pathol. 2004. 203:661–671.
12. Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. 13:4429–4434.
13. Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T, Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, et al. Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:5652–5657.
14. Kim MJ, Ro JY, Ahn SH, Kim HH, Kim SB, Gong G. Clinicopathologic significance of the basal-like subtype of breast cancer: a comparison with hormone receptor and Her2/neu-overexpressing phenotypes. Hum Pathol. 2006. 37:1217–1226.
15. Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006. 295:2492–2502.
16. Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer. 2007. 109:1721–1728.
17. Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2007. 109:25–32.
18. Kang SP, Martel M, Harris LN. Triple negative breast cancer: current understanding of biology and treatment options. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2008. 20:40–46.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download