Abstract
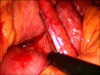
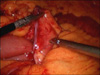
Internal abdominal hernia is an unusual cause of intestinal obstruction. Paraduodenal hernia is relatively rare congenital malformations resulting from incomplete rotation of the midgut with entrapment of the small intestine beneath the developing colon. We report a case of paraduodenal hernia treated by laparoscopic approach. The patient was a 45-year-old man presenting with severe abdominal pain for 5 hours. Left paraduodenal hernia with jejunum hernia containing jejunal loops showed in abdominal CT. At operation, herniation of the small intestine into a retroperitoneal space through a defect on the left mesocolon was noted. After the herniated bowel was fully reduced, the hernia orifice was closed intra-corporeally in the manner of interrupted sutures with absorbable suture materials. The patient was discharged home without any serious complications on postoperative day 9. Conclusively, we think laparoscopic surgery in left paraduodenal hernia is feasible.
Figures and Tables
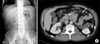
Fig. 1
Radiologic findings of paraduodenal hernia. (A) Abdomen plain radiograph demonstrates a mass-like density and mild dilated small bowel loops in left upper abdomen. (B) Contrast-enhanced axial CT scan of the upper abdomen shows a sac-like mass of aggregated jejunal loops between the pancreatic head and descending colon. The inferior mesenteric vein (arrows) is located at the anterior border of the encapsulated jejunal loops. J: jejunal loops, P: Pancreatic head, D: descending colon.
References
1. Bartlett MK, Wang C, Williams WH. The surgical management of paraduodenal hernia. Ann Surg. 1968. 168:249–254.
2. Khan MA, Lo AY, Vande Maele DM. Paraduodenal hernia. Am Surg. 1998. 64:1218–1222.
3. Moon CH, Chung MH, Lin KM. Diagnostic laparoscopy and laparoscopic repair of a left paraduodenal hernia can shorten hospital stay. JSLS. 2006. 10:90–93.
4. Uematsu T, Kitamura H, Iwase M, Yamashita K, Ogura H, Nakamuka T, et al. Laparoscopic repair of a paraduodenal hernia. Surg Endosc. 1998. 12:50–52.
5. Jeong GA, Cho GS, Kim HC, Shin EJ, Song OP. Laparoscopic repair of paraduodenal hernia: comparison with conventional open repair. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2008. 18:611–615.
6. Kim KH, Yoon YC, Seo HJ, Kim JI, Ahn CH, Chin HM, et al. Clinical analysis of an acute intestinal obstruction with a paraduodenal hernia. J Korean Surg Soc. 2004. 66:484–489.
7. Andrews E. Duodenal hernia: a misnomer. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1923. 37:740–750.
8. Willwerth BM, Zollinger RM Jr, Izant RJ Jr. Congenital mesocolic (paraduodenal) hernia. Embryologic basis of repair. Am J Surg. 1974. 128:358–361.
9. Roh SI, Kim CD, Kim SM, Mok DS. Intestinal obstruction due to paraduodenal hernia. J Korean Surg Soc. 1974. 16:49–51.
10. Woo SU, Yoon DK, Kang HJ, Chon SE, Park SG, Lee JJ. Paraduodenal hernia. J Korean Surg Soc. 2004. 66:347–350.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download