Abstract
Purpose
T2 gastric cancer is tumor invading proper muscle or subserosal layer. The 2002 American Joint Committee on Cancer subdivided the pT2 gastric adenocarcinoma into a type pT2a (invasion of the proper muscle) and a type pT2b (invasion of the subserosa). The aim of this study was to evaluate the differences between pT2a and pT2b gastric cancers of the clinicopathological features and the prognostic factors.
Methods
A series of curative operations were performed on 194 patients with pT2 gastric cancer from January 1999 to February 2006. We reviewed, retrospectively, the clinicopathologic characteristics, the 3-year disease free survival and the 5-year disease specific survival rates.
Results
There were significant clinicopathologic differences between pT2a and pT2b gastric cancer in tumor size and the number of metastatic lymph nodes. Both of the 3-year disease free survival time and the 5-year disease specific survival time were much longer for the pT2a gastric carcinoma patients than those for the pT2b gastric carcinoma patients.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Comparison of overall survival for patients with pT2a and pT2b gastric cancer. The overall survival of pT2a group is 83.3% and that of pT2b is 65.6% (P=0.009).
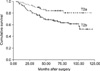
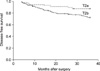
Fig. 2
Comparison of disease free survival for patients with pT2a and pT2b gastric cancer. The 3-year disease free survival of pT2a group is 88.1% and that of pT2b is 73.2% (P=0.022).
References
1. Park DJ, Kong SH, Lee HJ, Kim WH, Yang HK, Lee KU, et al. Subclassification of pT2 gastric adenocarcinoma according to depth of invasion (pT2a vs pT2b) and lymph node status (pN). Surgery. 2007. 141:757–763.
2. Lu Y, Liu C, Zhang R, Li H, Lu P, Jin F, et al. Prognostic significance of subclassification of pT2 gastric cancer: a retrospective study of 847 patients. Surg Oncol. 2008. 17:317–322.
3. Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A, Balch CM, Haller DG, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 2002. 6th ed. New York: Springer.
4. Townsend CM, Evers BM, Beauchamp RD, Mattox KL. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery: The Biological Basis of Modern Surgical Practice. 2008. 18th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders/Elsevier.
5. Fotia G, Marrelli D, De Stefano A, Pinto E, Roviello F. Factors influencing outcome in gastric cancer involving muscularis and subserosal layer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004. 30:930–934.
6. Kinoshita T, Maruyama K, Sasako M, Okajima K. Nishi M, Ichikawa H, Nakajima T, Maruyama K, Tahara E, editors. Treatment result of gastric cancer patients: Japanese experience. Gastric Cancer. 1993. 1st ed. Tokyo: Springer-Verlag;319–330.
7. Yoshikawa K, Maruyama K. Characteristics of gastric cancer invading to the proper muscle layer--with special reference to mortality and cause of death. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1985. 15:499–503.
8. Harrison JC, Dean PJ, Vander Zwaag R, el-Zeky F, Wruble LD. Adenocarcinoma of the stomach with invasion limited to the muscularis propria. Hum Pathol. 1991. 22:111–117.
9. Ichiyoshi Y, Tomoda M, Tomisaki S, Oda S, Ohno S, Maehara Y, et al. Macroscopic appearance and biological character of gastric cancer invading the muscularis propria. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996. 43:553–559.
10. Fletcher CDM. Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors. 2007. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier.
11. Ishigami S, Natsugoe S, Miyazono F, Hata Y, Uenosono Y, Sumikura S, et al. Clinical merit of subdividing gastric cancer according to invasion of the muscularis propria. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004. 51:869–871.
12. Otsuji E, Kuriu Y, Ichikawa D, Okamoto K, Hagiwara A, Yamagishi H. Characteristics of gastric carcinoma invading the muscularis propria. J Surg Oncol. 2005. 92:104–108.
13. Sarela AI, Turnbull AD, Coit DG, Klimstra D, Brennan MF, Karpeh MS. Accurate lymph node staging is of greater prognostic importance than subclassification of the T2 category for gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003. 10:783–791.
14. Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Kurioka H, Kan K, Shioaki Y, Ueshima Y, et al. Prognostic and clinical evaluation of patients with T2 gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005. 52:965–968.
15. Schwartz GK, Winter K, Minsky BD, Crane C, Thomson PJ, Anne P, et al. Randomized phase II trial evaluating two paclitaxel and cisplatin-containing chemoradiation regimens as adjuvant therapy in resected gastric cancer (RTOG-0114). J Clin Oncol. 2009. 27:1956–1962.
16. Abbas SM, Booth MW. Correlation between the current TNM staging and long-term survival after curative D1 lymphadenectomy for stomach cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2005. 390:294–299.
17. Kim SW, Song SK, Kim SW. The clinical relevance of distinguishing pT2 gastric cancer according to the depth of invasion and a difference of prognosis. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2007. 24:S416–S423.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download