Abstract
We report a fibroadenoma with extensive squamous metaplasia in the breast. A 21-year-old woman presented with a mass of the left breast. Breast ultrasonography showed a 1.8×1.7 cm sized, well-circumscribed mass in left subareolar region. The mass was excised. Grossly, the mass was well circumscribed and the cut surfaces were grayish-white in color and elastic in consistency. Microscopically, the breast lesion showed the histological features of fibroadenoma. There were areas of extensive squamous metaplasia seen as isolated clusters or involving duct. But some metaplastic clusters surrounded by fibrous stroma were compressed and distorted and separation of cells into isolated clusters mimicked invasive carcinoma. Co-expression of CK 5/6, high molecular weight CK and p63 in areas of squamous metaplasia and normal myoepithelial cells supported myoepithelial cell origin of metaplastic cells.
Figures and Tables
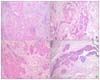 | Fig. 2(A) Extensive squamous metaplasia showing large sheet, isolated nest or involving duct (H&E stain, ×100). (B) Small clusters of epithelial cells surrounded by fibrous tissue and fibrous distortion resembled infiltrative carcinoma (H&E stain, ×400). (C) Mitotic activity is identified up to 4/high power field in some area of squamous metaplasia (H&E stain, ×400). (D) Involving ducts shows transition zone with squamous metaplastic cells apparently arising from basal cells (H&E stain, ×100). |
References
1. Takei H, Iino Y, Horiguchi J, Maemura M, Yokoe T, Koibuchi Y, et al. Natural history of fibroadenomas based on the correlation between size and patient age. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1999. 29:8–10.
2. Devi PM, Singh LR, Gatphoh ED. Fibroadenoma with squamous metaplasia. Singapore Med J. 2007. 48:682–683.
3. Esposito NN, Mohan D, Brufsky A, Lin Y, Kapali M, Dabbs DJ. Phyllodes tumor: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 30 cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006. 130:1516–1521.
4. Cornog JL, Mobini J, Steiger E, Enterline HT. Squamous carcinoma of the breast: report of a case. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971. 55:410–417.
5. Flint A, Oberman HA. Infarction and squamous metaplasia of intraductal papilloma. Hum Pathol. 1984. 15:764–767.
6. Powell BC, Maull KI, Sachatello CR. Recurrent subareolar abscess of the breast and squamous metaplasia of the lactiferous ducts: a clinical syndrome. South Med J. 1977. 70:935–937.
7. Gottfried MR. Extensive squamous metaplasia in gynecomastia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986. 110:971–973.
8. Salm R. Massive epidermoid metaplasia with keratin cyst formation in a giant fibroadenoma of the breast. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959. 77:297–299.
9. Salm R. Epidermoid metaplasia in mammary fibroadenoma with formation of keratin cysts. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1957. 74:221–223.
10. Soderstrom KO, Toikkanen S. Extensive squamous metaplasia simulating squamous cell carcinoma in benign breast papillomatosis. Hum Pathol. 1983. 14:1081–1082.
11. Ng WK, Kong JH. Significance of squamous cells in fine needle aspiration cytology of the breast. A review of cases in a seven-year period. Acta Cytol. 2003. 47:27–35.
12. Ribeiro-Silva A, Luzzatto F, Chang D, Zucoloto S. Limitations of fine-needle aspiration cytology to diagnose metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. Pathol Oncol Res. 2001. 7:298–300.
13. Toikkanen S. Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. Cancer. 1981. 48:1629–1632.
14. Nakayama Y, Iwasaki H, Ixanaga S, Nakamura H, Shiroshita T, Kikuchi M, et al. Spindle cell carcinoma of the breast: a case report and an immunohistochemical study including p53 and Ki-67 expression. Pathol Int. 1997. 47:404–411.
15. Reddick RL, Jennette JC, Askin FB. Squamous metaplasia of the breast; An ultrastructural and immunologic evaluation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985. 84:530–533.
16. Raju GC. The histological and immunohistochemical evidence of squamous metaplasia from myoepithelial cells in the breast. Histopathology. 1990. 17:272–275.
17. Mills AE, Daniel WJ. Primary squmous metaplasia of the breast. Pathol Int. 1997. 47:618–621.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download