Abstract
Purpose
Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis (XGC) is an uncommon, benign destructive and chronic inflammatory disease which is characterized by a marked proliferative fibrosis within the gallbladder wall. XGC occasionally involves adjacent organs and mimicking an advanced gallbladder carcinoma (GBC). The purpose of this study was to review the clinical manifestations, radiologic and pathologic findings of XGC and to investigate an appropriate treatment plan for patients with XGC.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 36 patients with a pathologic diagnosis of XGC operated between January 2003 and June 2008.
Results
The most frequent clinical symptom was biliary colic (88.8%). Radiologic studies revealed cholelithiasis in 30 patients (83.3%), thickening of gallbladder wall in 24 patients (66.6%), suspicious cancer in 11 patients (30.5%) and Mirizzi syndrome in 3 patients (8.3%). Laparoscopic cholecystectomy was planned in 18 patients but converted to open surgery in 9 patients. Open cholecystectomy was planned and performed in 13 patients including 8 cases of T-tube choledocholithotomy and 1 case of excision of a cholecystoduodenal fistula. Extended cholecystectomy was performed on 3 patients. GBC was suspected before operation in 11 patients. Of these, frozen-section biopsy was performed in 6 and found to be malignant in 1 patient. One patient who had no operative suspicion of malignancy turned out to have GBC at final histology.
Figures and Tables
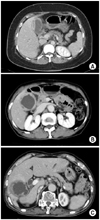 | Fig. 1Several computed tomographic findings in patients with xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. (A) CT scan shows focal gallbladder wall thickening and mass like lesion. This patient was diagnosed with gallbladder carcinoma preoperatively. (B) CT scan shows diffuse gallbladder wall thickening with multiple intramural hypoattenuated nodules. (C) CT scan shows irregular gallbladder wall thickening with hyperemic change of gallbladder bed, and pericholecytic infiltration. |
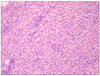 | Fig. 2Microscopic finding of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis Xanthogranulomatous inflammation of the gallbladder wall, characterized by histocytes containing neutral fat and lipofucin pigment (H&E, ×200). |
Table 5
Postoperative complications in patients with xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis underwent cholecystectomy

Table 6
Profiles of patients with radiologically suspected gallbladder carcinoma

*additional operation was not performed due to patient's refusal; †LC = laparoscopic cholecystectomy; ‡EC = extended cholecystectomy; §OC = open cholecystectomy; ∥TTC = T-tube choledocholithotomy; ¶TG = total gastrectomy; **RH = right hepatectomy; ††PD = pancreaticoduodenectomy; ‡‡XGC = xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis; §§GBC = gallbladder carcinoma.
References
1. Christensen AH, Ishak KG. Benign tumors and pseudotumors of the gallbladder. Report of 180 cases. Arch Pathol. 1970. 90:423–432.
2. Takahashi K, Oka K, Hakozaki H, Kojima M. Ceroid-like histiocytic granuloma of gall-bladder --a previously undescribed lesion. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1976. 26:25–46.
3. Mehrotra ML, Bhatnagar BN. Biliary granulomatous cholecystitis. J Indian Med Assoc. 1982. 79:144–145.
4. McCoy JJ Jr, Vila R, Petrossian G, McCall RA, Reddy KS. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Report of two cases. J S C Med Assoc. 1976. 72:78–79.
5. Joo YE, Lee JJ, Chung IJ, Kim HS, Rew JS, Kim HJ, et al. A case of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Korean J Intern Med. 1999. 14:90–93.
6. Maeda T, Shimada M, Matsumata T, Adachi E, Taketomi A, Tashiro Y, et al. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis masquerading as gallbladder carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994. 89:628–630.
7. Guzman-Valdivia G. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: 15 years' experience. World J Surg. 2004. 28:254–257.
8. Dao AH, Wong SW, Adkins RB Jr. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. A clinical and pathologic study of twelve cases. Am Surg. 1989. 55:32–35.
9. Roberts KM, Parsons MA. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: clinicopathological study of 13 cases. J Clin Pathol. 1987. 40:412–417.
10. Benbow EW. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Br J Surg. 1990. 77:255–256.
11. Kwon AH, Matsui Y, Uemura Y. Surgical procedures and histopathologic findings for patients with xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. J Am Coll Surg. 2004. 199:204–210.
12. Solanki RL, Arora HL, Gaur SK, Anand VK, Gupta R. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis (XGC): a clinicopathological study of 21 cases. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 1989. 32:256–260.
13. Tyagi SP, Maheshwari V, Sahoo P, Tyagi N, Ashraf SM. Chronic granulomatous cholecystitis: a clinicopathological study of 17 cases. J Indian Med Assoc. 1991. 89:284–287.
14. Yang T, Zhang BH, Zhang J, Zhang YJ, Jiang XQ, Wu MC. Surgical treatment of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: experience in 33 cases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007. 6:504–508.
15. Kim PN, Lee SH, Gong GY, Kim JG, Ha HK, Lee YJ, et al. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: radiologic findings with histologic correlation that focuses on intramural nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 172:949–953.
16. Chun KA, Ha HK, Yu ES, Shinn KS, Kim KW, Lee DH, et al. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: CT features with emphasis on differentiation from gallbladder carcinoma. Radiology. 1997. 203:93–97.
17. Shuto R, Kiyosue H, Komatsu E, Matsumoto S, Kawano K, Kondo Y, et al. CT and MR imaging findings of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: correlation with pathologic findings. Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:440–446.
18. Kim MJ, Oh YT, Park YN, Chung JB, Kim DJ, Chung JJ, et al. Gallbladder adenomyomatosis: findings on MRI. Abdom Imaging. 1999. 24:410–413.
19. Roh NG, Kim IG, Jung JP, Park JW, Kim HJ, Joo SH, et al. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: clinical review of 14 cases. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006. 10:7–13.
20. Chun HB, Lee SG, Lee YJ, Park KM, Hwang S, Kim PN, et al. Xanthogranulomatous colecystitis. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999. 3:203–209.
21. Guzman-Valdivia G. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis in laparoscopic surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 2005. 9:494–497.
22. Houston JP, Collins MC, Cameron I, Reed MW, Parsons MA, Roberts KM. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Br J Surg. 1994. 81:1030–1032.
23. Yamaguchi K, Enjoji M. Carcinoma of the gallbladder. A clinicopathology of 103 patients and a newly proposed staging. Cancer. 1988. 62:1425–1432.
24. Spinelli A, Schumacher G, Pascher A, Lopez-Hanninen E, Al-Abadi H, Benckert C, et al. Extended surgical resection for xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis mimicking advanced gallbladder carcinoma: a case report and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:2293–2296.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download