Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1The relationship between delta sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score and mortality according to re-operation. In patients not undergoing re-operation (A), the sequential changes of delta SOFA scores between live and dead differed significantly (P=0.021). The former had a gradual reducing trend, while the latter had an abrupt increasing trend. In patients undergoing re-operation (B), however, both those sequential changes did not differ and had downward directions together. |
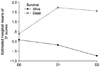 | Fig. 2The interaction between the sequential changes of each delta sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) scores and survival on condition of adjustment by re-operation. Live had a gradual reducing trend of delta SOFA scores while dead had an increasing trend (P=0.035). |
Table 1

*values are with respiratory support; †to convert bilirubin from mg/dl to µmol/L, multiply by 17.1; ‡adrenergic agents administered for at least 1 hour (dose given are in µg/kg per minute); §to convert creatnine from mg/dl to µmol/L, multiply by 88.4; ∥MAP = mean arterial pressure; ¶Dop = dopamine; **Dob = dobutamine; ††Epi = epinephrine; ‡‡Norepi = norepinephrine; §§GCS = Glasgow Coma Score.
Table 3
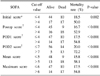
Table 4

The values are mean±standard deviation. *D0 = postop score-initial score; †D1 = POD1 score-initial score; ‡D2 = POD2 score-initial score; §Analyzed by repeated measured ANOVA and the others student's t-test; ∥On condition that it was adjusted by re-operation, difference between sum of each D scores and survival was marginally significant (P=0.070), and also interaction between the sequential changes of each D scores and survival was significant (P=0.035).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download