Abstract
Pancreaticopleural fistula is an uncommon complication of chronic pancreatitis. We report a case of pancreaticopleural fistula that was presented with right-sided hemothorax. A 49-year-old male with a history of chronic alcoholism was presented with a month of dyspnea. A chest radiography showed a right-sided massive pleural effusion with old-blood-colored fluids and amylase levels of 1,020 IU/L. On the chest computerized tomography (CT), there was pleural effusion and a well-defined tract from the posterior mediastinum to the pseudocyst in the tail of the pancreas. Even with conservative treatment with closed thoracostomy, octreotide and gabexate mesilate, he developed hemothorax. Abdominal CT revealed an increase of the hemorrhagic pancreatic pseudocyst. Distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy and external drainage of the pancreaticopleural fistula on the posterior mediasternum were performed. The patient had an uneventful course and was discharged on the 27th postoperative day. Management of pancreaticopleural fistula is multimodal included medication, endoscopic stenting and surgery. Surgery in pancreaticopleural fistula might be beneficial in selective cases.
Figures and Tables
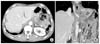
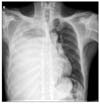 | Fig. 1Chest radiograph on admission showed marked haziness on the right lung field that revealed hemothorax. |
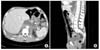
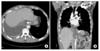 | Fig. 2Chest CT scan showed fistula (arrow) entering the thorax posterior to the diaphragmatic crura, anterior to the aorta. (A) Horizontal view, (B) Coronal view. |
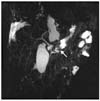 | Fig. 4Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed a stenosis (arrow) of main pancreatic duct just proximal to pancreatic cyst. |
References
1. Rockey DC, Cello JP. Pancreaticopleural fistula. Report of 7 patients and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1990. 69:332–344.
2. Amer K, Mahesh B, Ascione R. Pedicled intercostal muscle flap: a simple technique of closing pancreatico-pleural fistula from a thoracic approach. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002. 22:831–832.
3. Oh YS, Edmundowicz SA, Jonnalagadda SS, Azar RR. Pancreaticopleural fistula: report of two cases and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci. 2006. 51:1–6.
4. Boudaya MS, Alifano M, Baccari S, Regnard JF. Hemothorax as the clinical presentation of a pancreaticopleural fistula: report of a case. Surg Today. 2007. 37:518–520.
5. Iglesias JI, Cobb J, Levey J, Rosiello RA. Recurrent left pleural effusion in a 44-year-old woman with a history of alcohol abuse. Chest. 1996. 110:547–549.
6. Materne R, Vranckx P, Pauls C, Coche EE, Deprez P, Van Beers BE. Pancreaticopleural fistula: diagnosis with magnetic resonance pancreatography. Chest. 2000. 117:912–914.
7. Fulcher AS, Capps GW, Turner MA. Thoracopancreatic fistula: clinical and imaging findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999. 23:181–187.
8. Neher JR, Brady PG, Pinkas H, Ramos M. Pancreaticopleural fistula in chronic pancreatitis: resolution with endoscopic therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000. 52:416–418.
9. Burgess NA, Moore HE, Williams JO, Lewis MH. A review of pancreatico-pleural fistula in pancreatitis and its management. HPB Surg. 1992. 5:79–86.
10. Williams SG, Bhupalan A, Zureikat N, Thuluvath PJ, Santis G, Theodorou N, et al. Pleural effusions associated with pancreaticopleural fistula. Thorax. 1993. 48:867–868.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download