Abstract
Purpose
To report a case of orbital apex syndrome (OAS) combined with central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) and central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) following blunt trauma.
Case summary
A 4-year-old female visited the hospital following a traffic accident. She was admitted because of multiple fractures of the skull and pneumocephalus. On day 5, she was referred to us with decreased visual acuity in her right eye. Her initial visual acuity was hand motions in the right eye and 0.8 in the left eye. The right eye showed a dilated pupil, ptosis, and total ophthalmoplegia, and the left eye showed limited abduction. A fundus examination revealed multiple retinal hemorrhages, tortuous veins, and an edematous white retina with a cherry-red spot in the right eye. Brain magnetic resonance imaging revealed an entrapped right optic nerve because of bony fragments in the orbital apex. The patient was diagnosed with OAS accompanied by CRAO and CRVO in the right eye, and with traumatic abducens nerve palsy in the left eye. After 6 months, the visual acuity was hand motions, and the fundus examination showed absorbed retinal hemorrhages, pale discs, and general retinal thinning of the right eye. Ptosis of the right eye and extraocular muscle movement of both eyes were improved.
REFERENCES
1). Park SJ, Choi NK, Seo KH, et al. Nationwide incidence of clinically diagnosed central retinal artery occlusion in Korea, 2008 to 2011. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:1933–8.

2). Varma DD, Cugati S, Lee AW, Chen CS. A review of central retinal artery occlusion: clinical presentation and management. Eye (Lond). 2013; 27:688–97.

3). Lee WS, Yoon WT, Choi YJ, Park SP. Multiple cerebral infarctions with neurological symptoms and ophthalmic artery occlusion after filler injection. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:285–90.

4). Kim BO, Jin KH, Kwak HW. Retinal vessel obstruction caused by orbital compression after paranasal sinus surgery. J Korean Ophtalmol Soc. 1995; 36:130–4.
5). Lim HW, Ko BW, Song Y, et al. Combined central retinal vein and artery occlusion after retrobulbar anesthesia: A case report. J Korean Ophtalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1013–7.

6). Koh JS, Woo SJ. Central retinal artery occlusion after trauma: Report of two cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016; 57:324–9.

7). Risk factors for central retinal vein occlusion. The Eye Disease Case-Control Study Group. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996; 114:545–54.
8). Richards RD. Simultaneous occlusion of the central retinal artery and vein. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1979; 77:191.
9). Durukan AH, Akar Y, Bayraktar MZ, et al. Combined retinal artery and vein occlusion in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. Can J Ophthalmol. 2005; 40:87–9.

10). Hamann S, Johansen S. Combined central retinal artery and vein occlusion in Churg-Strauss syndrome: case report. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2006; 84:703–6.

11). Schaible ER, Golnik KC. Combined obstruction of the central retinal artery and vein associated with meningeal carcinomatosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111:1467–8.

13). Stowe GC 3rd, Zakov ZN, Albert DM. Central retinal vascular occlusion associated with oral contraceptives. Am J Ophthalmol. 1978; 86:798–801.

14). Singh NKK, Bhattacharya UK, Kamai GL, Fanai VR. Traumatic optic neuropathy with combined central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) and central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) following blunt ocular trauma. J Med Soc. 2014; 28:128.

15). Noble MJ, Alvarez EV. Combined occlusion of the central retinal artery and central retinal vein following blunt ocular trauma: a case report. Br J Ophtalmol. 1987; 71:834–6.

16). Cumurcu T, Doganay S, Demirel S, Cankaya C. Traumatic optic neuropathy and central retinal artery occlusion following blunt ocular trauma. J Clin Med Res. 2011; 3:55–7.

17). Scheerlinck TA, Van den Brande P. Post-traumatic intima dissection and thrombosis of the external iliac artery in sportsman. Eur J Vasc Surg. 1994; 8:645–7.
20). Lenzi GL, Fieschi C. Superior orbital fissure syndrome. Review of 130 cases. Eur Neurol. 1977; 16:23–30.
21). Garland SD, Maloney PL, Doku HC. Carotid-cavernous sinus fistula after trauma to the head. J Oral Surg. 1977; 35:832–5.
Figure 1.
Wide field fundus photography (WFP) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) image on initial presentation. (A) WFP after two weeks of trauma shows pseudo-cherry red spot and multiple retinal hemorrhages near the optic disc in the right eye. (B) The normal WFP image of the left eye. (C) OCT image of the right eye revealed severe inner retinal edema. (D) The normal OCT image of the left eye.
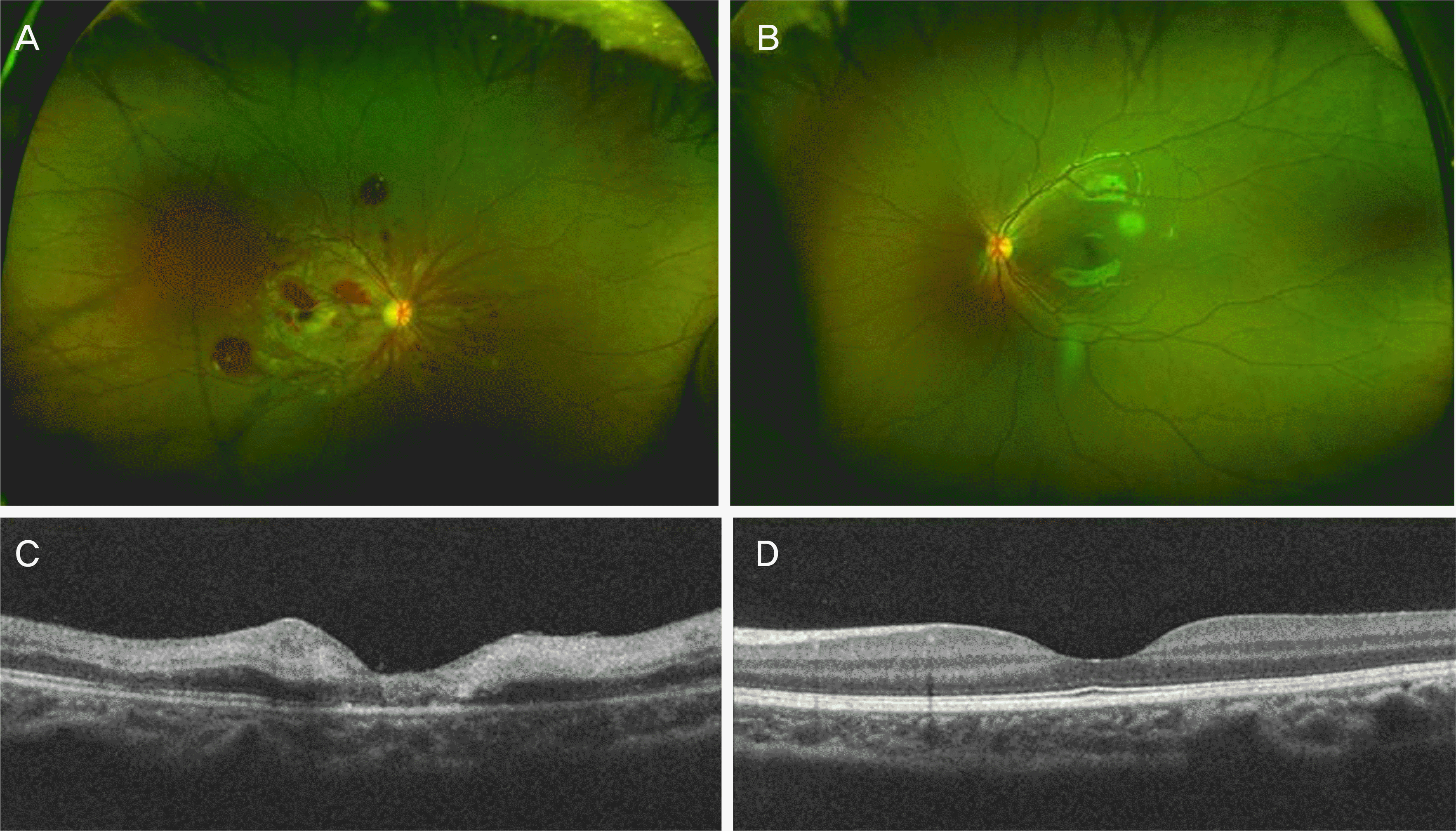
Figure 2.
Fields of gaze of extraocular movement. (A) Initial examination shows limitation of movement in all directions in the right eye. Ptosis of the right upper eyelid and abduction limitation of the left eye are also noted. (B) At 6 months after trauma, ptosis of the right upper eyelid was improved. The extraocular muscle movements of both eyes were also improved. However, abduction of the right eye was still limited.

Figure 3.
Computed tomography (CT) image and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) on initial presentation. (A) Axial CT scan demonstrates multiple fractures including orbital apex of the right eye and skull base. (B) Axial MRI (T2 weighted image) scan on 7 days after trauma shows bony fragments (dotted arrow) and hematoma (solid arrow) along the optic nerve pathway. (C) Sagittal MRI (T1 weighted image) scan reveals entrapped and stretched optic nerve of the right eye (solid arrow) because of bony fragments (dotted arrow).





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download