Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the degree of eyelid deformation and satisfaction after direct closure in patients with 40–70% eyelid defects after resection of an eyelid malignant tumor.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the clinical records of patients diagnosed with eyelid malignant tumors between January 2009 and June 2016, who were treated with resection of 40–70% of the eyelid, followed by reconstructed direct closure only or by direct closure with lateral canthotomy and cantholysis. Age, sex, diagnosis, tumor location, satisfaction, and complications were analyzed, and the ratio of horizontal width ratio and vertical height ratio were compared before and after surgery.
Results
The results of satisfaction were: 12 patients (60%), very good; five patients (25%), good; and three patients (15%), fair. The average preoperative horizontal width ratio and vertical height ratio were 1.03 ± 0.01 and 1.08 ± 0.30, respectively. The average postoperative horizontal width ratio and vertical height ratio were 1.04 ± 0.08 and 1.01 ± 0.17, respectively There was no significant difference in horizontal width ratio or vertical height ratio before and after surgery (p = 0.314 and p = 0.087, respectively).
Go to : 
References
1. Werner MS, Olson JJ, Putterman AM. Composite grafting for abdominal reconstruction. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 116:11–6.
2. Putterman AM. Combined viable composite graft and temporal semicircular skin flap procedure. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984; 98:349–54.

4. Renner G, Kang T. Periorbital reconstruction: brows and eyelids. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2005; 13:253–65. vi.

5. Rafii AA, Enepekides DJ. Upper and lower eyelid reconstruction: the year in review. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 14:227–33.

6. Moss AL, Cooper MA, Lendrum J, Hiles RW. The sanctity of the upper lid in lower eyelid reconstruction questioned. A modification of a lid sharing procedure with a long-term follow-up. Br J Plast Surg. 1987; 40:246–57.

7. Putterman AM. Reconstruction of the eyelids following resection for carcinoma. Clin Plast Surg. 1985; 12:393–410.

8. Mehta MP, Lewis CD, Perry JD. Internal cantholysis for full abdominal eyelid defects. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2011; 25:31–6.
9. Tenzel RR, Stewart WB. Eyelid reconstruction by the semicircle flap technique. Ophthalmology. 1978; 85:1164–9.

10. Hornblass A, Vincent MP. Oculoplastic, orbital and reconstructive surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 86:1033.

11. Tse DT, McCafferty LR. Controlled tissue expansion in periocular reconstructive surgery. Ophthalmology. 1993; 100:260–8.

12. Petro JA, Niazi ZB. Immediate skin expansion: an old concept by a novel and inexpensive technique. Ann Plast Surg. 1996; 36:479–84.
13. Marcus J, Horan DB, Robinson JK. Tissue expansion: past, abdominal, and future. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990; 23(5 Pt 1):813–25.
14. Foster JA, Scheiner AJ, Wulc AE, et al. Intraoperative tissue abdominal in eyelid reconstruction. Ophthalmology. 1998; 105:170–5.
15. Papadopoulos O, Konofaos P, Chrisostomidis C, et al. Orbitopalpebral repair after 835 excisions of malignant tumours. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2005; 39:353–9.

16. Miller EA, Boynton JR. Complications of eyelid reconstruction abdominal a semicircular flap. Ophthalmic Surg. 1987; 18:807–10.
17. Thaller VT, Then KY, Luhishi E. Spontaneous eyelid expansion abdominal full thickness eyelid resection and direct closure. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001; 85:1450–4.
Go to : 
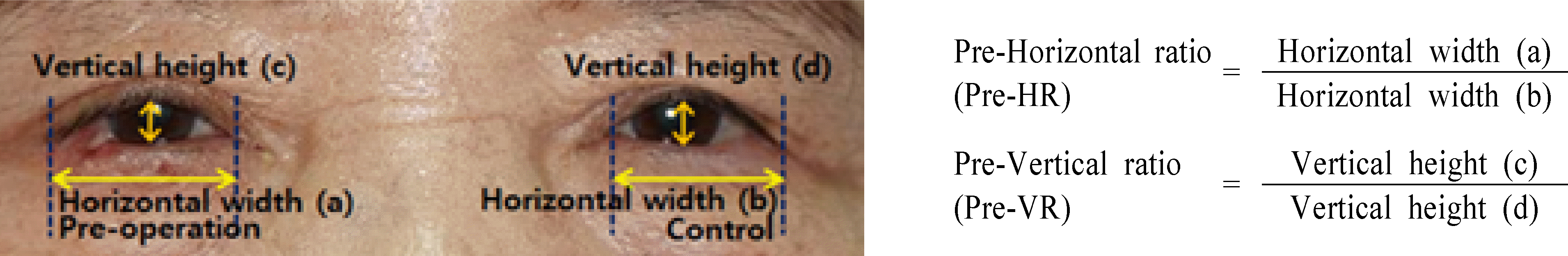 | Figure 1.An example of photograph. It shows how to measure vertical height ratio and horizontal width ratio in pre-operative photograph. The pre-operative horizontal width ratio of eyelid is obtained by dividing the horizontal width of eyelid in the contralateral (b) from the horizontal width of eyelid in the lesion (a). Pre-operative vertical height ratio of eyelid is obtained by dividing the vertical height of eyelid in the contralateral (d) from the vertical height of eyelid in the lesion (c). Pre-HR = pre-operative horizontal width ratio of eyelid; Pre-VR = pre-operative vertical height ratio of eyelid. |
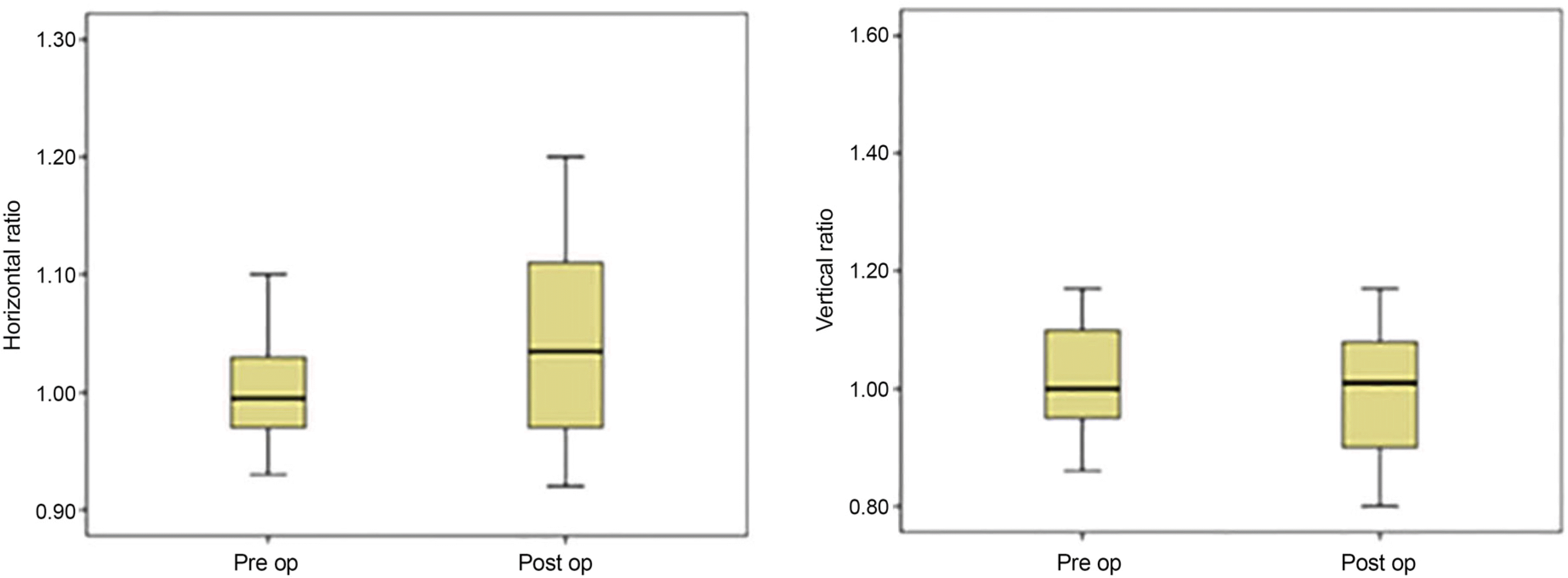 | Figure 2.Statistical results box plots. It shows the distribution of horizontal ratio and vertical ratio of eyelid (y-axis) in preoperative and postoperative photographs (x-axis). The box plots show the median, interquartile range, 95% percentile, outliers, and extreme values. Pre op = in preoperative photographs; Post op = in postoperative photographs. |
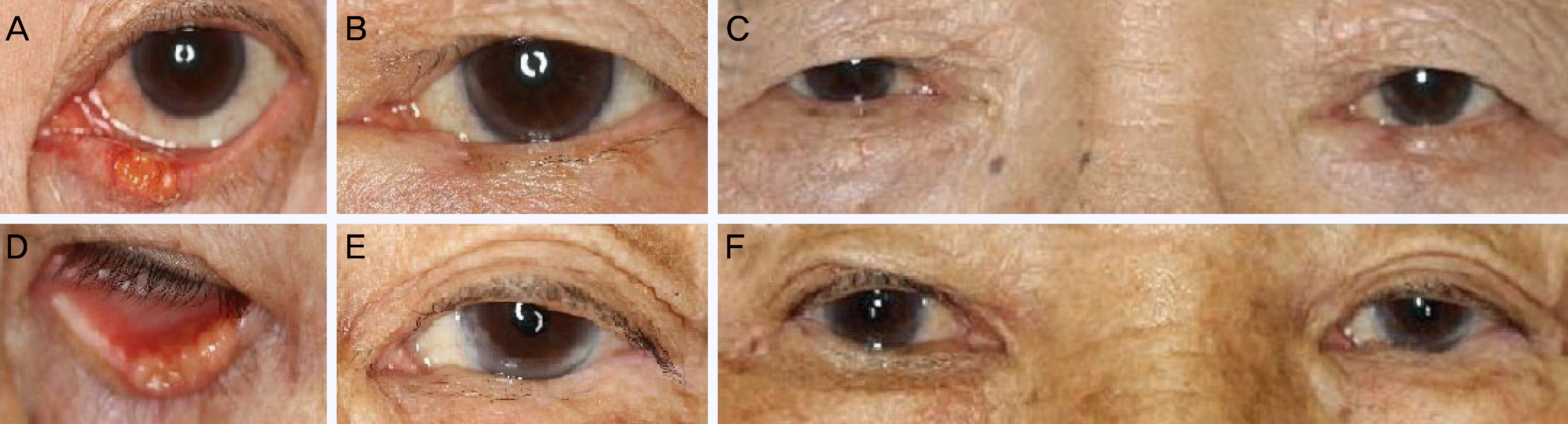 | Figure 3.Patient's photographs included in the series. (A) The preoperative left lower lid squamous cell carcinoma, which measured 0.333 in its horizontal width ratio of eyelid mass. (B) The 3 month postoperative result after about 45% horizontal lid resection and direct closure. (C) Photograph also taken at 3 months and it allows a comparison with the normal unoperated right eye. (D) The pre-operative left lower lid sebaceous carcinoma, which measured 0.318 in its horizontal width ratio of eyelid mass. (E) The 3 month postoperative result after about 41% horizontal lid resection and direct closure. (F) Photograph also taken at 3 months and it allows a comparison with the normal unoperated right eye. |
Table 1.
Raw data of patients
Pre-HR = pre-operative horizontal width ratio of eyelid; Pre-VR = pre-operative vertical height ratio of eyelid; Post-HR = post-operative horizontal width ratio of eyelid; Post-VR = post-operative vertical height ratio of eyelid; M-HR = horizontal width ratio of eyelid mass; M-VR = vertical height ratio of eyelid mass; M = male; F = female; BCC = basal cell carcinoma; SCC = squamous cell carcinoma.
Table 2.
Comparison of eyelid deformations between pre and post operation
| Pre op | Post op | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 1.03 ± 0.01 | 1.04 ± 0.08 | 0.314 |
| VR | 1.08 ± 0.30 | 1.01 ± 0.17 | 0.087 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download